

K-WANG


Bentley 3500/42 Proximitors ®/ Earthquake monitoring module
Bentley 3500/42 Proximitors ®/ Earthquake monitoring module
Product Overview
Core functions
3500/42 Proximitor ®/ The earthquake monitoring module is a four channel monitoring device that can receive input signals from a proximity probe and seismic sensors, and achieve monitoring functions such as radial vibration, thrust position, eccentricity, differential expansion, acceleration, and velocity through configuration. Its core function is to drive alarm output by comparing the current machine vibration value with the preset alarm threshold, and provide machine status data for operation and maintenance personnel.
Key Features
TMR architecture: Supports triple modular redundancy (TMR) configuration, avoids single point of failure through a 2 out of 3 voting mechanism, and ensures system reliability.
Flexible configuration: Customize channel types, alarm thresholds, filtering parameters, etc. through 3500 rack configuration software to adapt to different monitoring scenarios.
Real time diagnosis: Built in self checking function, quickly locate faults through LED indicator lights and event logs.
Safety certification: Compliant with standards such as IEC 61508, suitable for hazardous areas (such as Class I, Division 1/2).
Product Architecture and Working Principle
Hardware Architecture
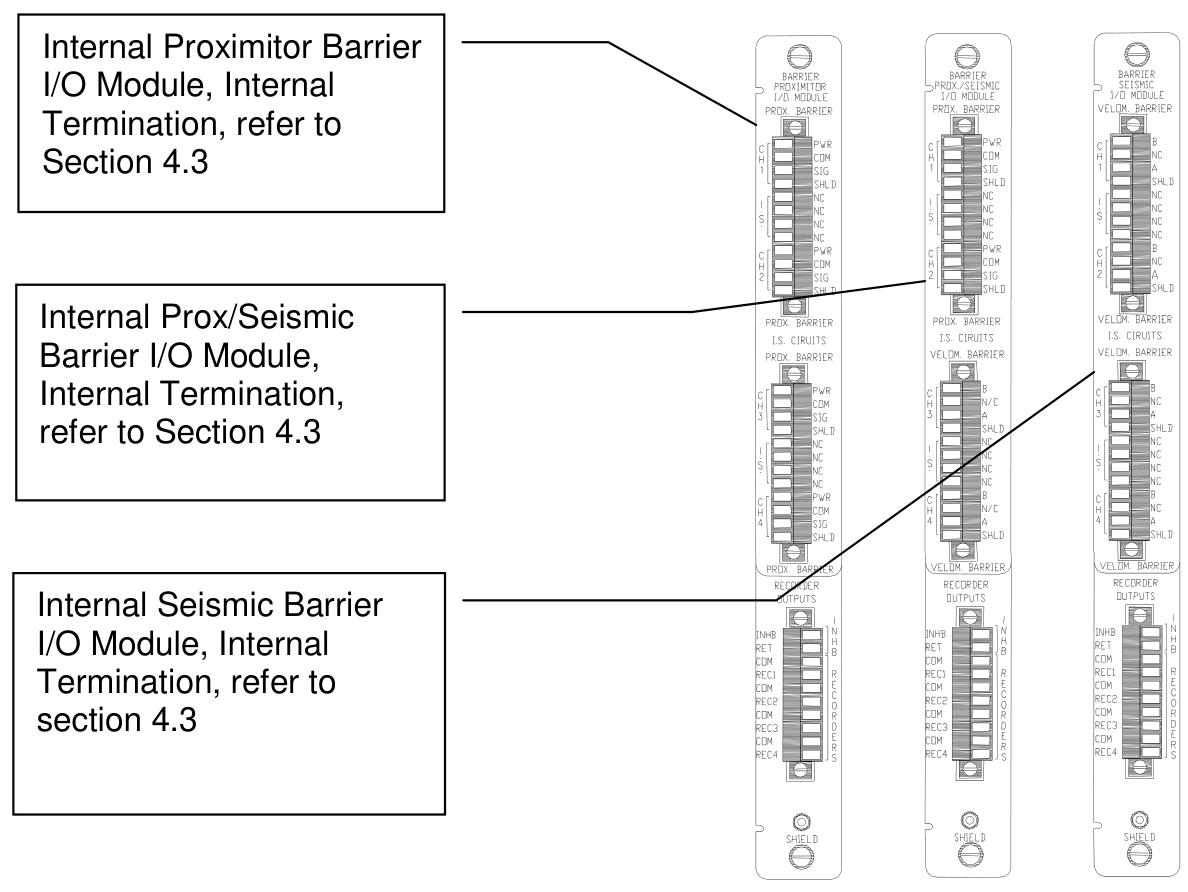
Input module: support multiple I/O modules, including internal terminal, external terminal, TMR terminal and terminal module with barrier, and adapt to different sensor wiring requirements (such as Proximitor, accelerometer, speed sensor).
Signal processing: Each channel integrates filtering, amplification, and digitization circuits, supporting bandpass, high pass, and low-pass filtering, with a configurable frequency response range (such as radial vibration channels supporting 1 Hz to 4000 Hz).
Communication interface: communicates with other modules through the rack backplane, supports serial protocols such as RS-232/485, and can be connected to the upper computer for data monitoring.
TMR redundancy mechanism
Voting logic: In the TMR configuration, three monitoring modules vote 2 out of 3 for the input signal. If the deviation between the output of one module and that of other modules exceeds the set threshold (such as% Comparison), event logging will be triggered.
Input configuration:
Bus configuration: A single non redundant sensor signal is distributed to three modules through the bus.
Discrete configuration: Three redundant sensors are connected to three modules respectively to improve reliability.
Data output and status monitoring
Proportional value output: Output different parameters based on channel type, such as Direct (peak to peak), 1X/2X amplitude, phase lag, etc. for radial vibration; Gap (gap voltage) and Direct (axial displacement) at the thrust position.
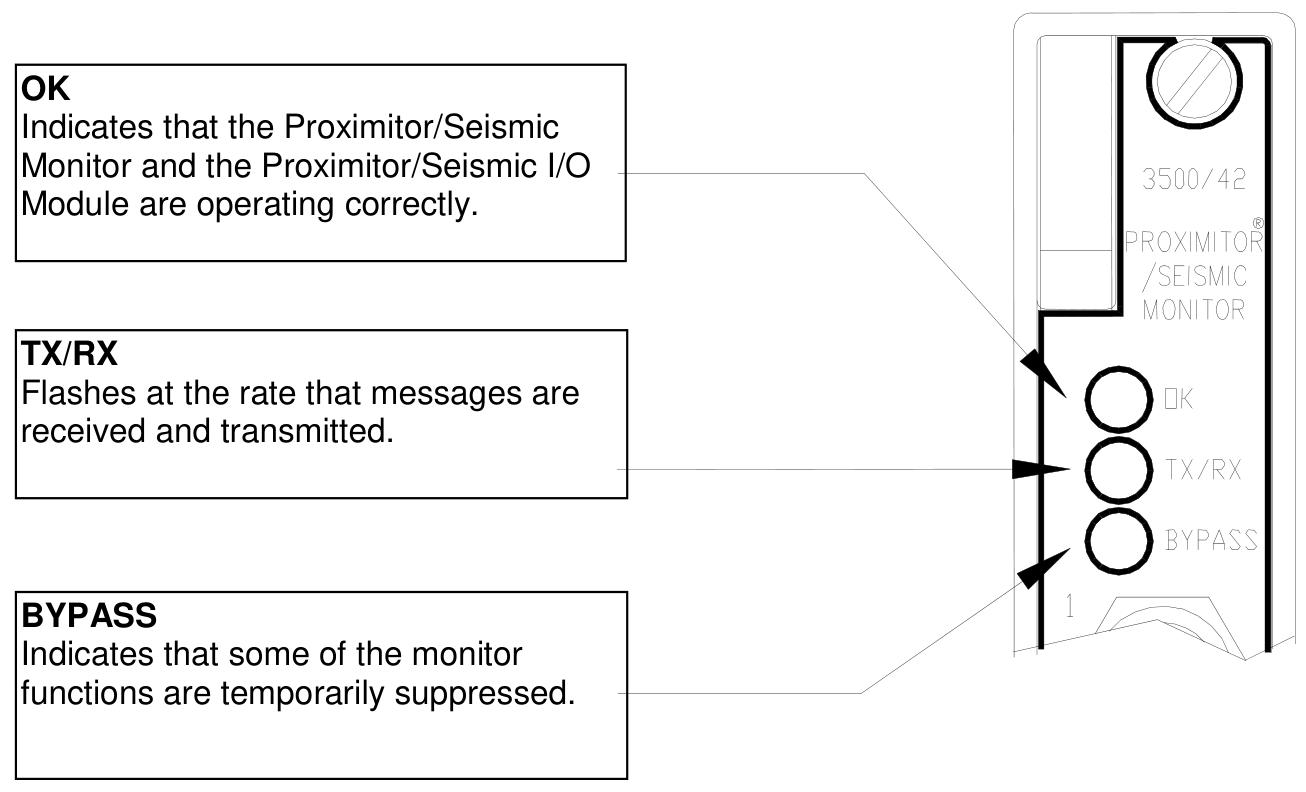
Status identification: Feedback module health status, communication status, and alarm events through LED (OK, TX/RX, BYPASS) and event logs (System Event List, Alarm Event List).
Configuration Guide
Software Configuration Tool
Use 3500 Rack Configuration Software for parameter settings, with core configuration items including:
Channel type: Select radial vibration, thrust position, etc. Different types correspond to different filtering and scaling factors.
Full range: For example, radial vibration Direct can choose 0-10 mil pp (peak to peak), and acceleration can choose 0-20 g pk (peak to peak).
Alarm threshold: Set the Alert/Alarm 1 and Danger/Alarm 2 thresholds for each proportional value, and support lag adjustment (e.g., hysteresis is 1/64 of full scale).
Filter parameters: Set the cut-off frequency of the high/low-pass filter (e.g. acceleration channel supports 3 Hz to 30 kHz).
Example of Key Parameter Configuration
Radial vibration channel:
Select a 3300-8 mm Proximitor sensor and set the Scale Factor to 200 mV/mil.
Set the 1X Amplitude full-scale to 10 mil pp, the Alert threshold to 6 mil pp, the Danger threshold to 8 mil pp, and the delay time to 1 second.
Thrust position channel:
The Zero Position voltage is set to -9.75 Vdc (corresponding to the center value of the gap), the full range is set to 25-0-25 mil, and the direction is set to "Forward Probe" (displacement increases when the rotor moves towards the probe).
Key points of TMR configuration
Three monitoring modules need to be installed adjacent to each other and configured with Comparison Voting (if comparing 1X Amplitude, a deviation of 5% is allowed).
Bussed External Termination Block is used for bus configuration, while three independent sensors and terminal blocks are used for discrete configuration.
I/O modules and wiring
Module type and function
Internal terminal module: directly connected to sensors and recorders, suitable for non hazardous areas, wiring should pay attention to electrostatic protection (such as using anti-static wrist straps).
Internal Barrier Module: Integrated Zener Barrier, suitable for explosion-proof areas (such as Class I, Division 1), to restrict energy flow into hazardous areas.
External terminal module: Connect the sensor with a 25 pin cable and the recorder with a 9-pin cable to simplify the internal wiring of the rack.
Wiring specifications
Proximitor sensor: The power supply (PWR) is connected to -24 Vdc, the signal (SIG) is connected to the channel input, and the shielding layer (SHLD) is grounded.
Seismic sensors (such as Velomitor) require series connection of resistors and capacitors (such as 4 k Ω resistors+10 μ F capacitors) for signal conditioning.
TMR wiring: In discrete configuration, three sensors are connected to independent channels of three modules, and in bus configuration, sensor signals are shared through a Bussed Terminal Block.
Maintenance and testing
Regular verification testing
Testing cycle: It is recommended to conduct it once a year. If the equipment is a critical unit or operates in harsh environments, it can be shortened to once every quarter.
Testing equipment: function generator, multimeter, oscilloscope, Keyphasor Multiplier/Diverder, etc.
Test steps (taking radial vibration channel as an example):
Simulate sensor signals (such as a 100 Hz sine wave with a peak to peak value of 2 V).
Verify the display accuracy of proportional values such as Direct and 1X Amplitude (error ≤ ± 1% of full scale).
Trigger Alert/Arm 1 and Danger/Arm 2 thresholds, confirm that the alarm delay time is consistent with the configuration.
Disconnect the input signal and verify the OK state recovery time (Timed OK Channel Defeat set to 30 seconds).
Scale factor and zero position adjustment
Scale Factor: Used to calibrate the linearity deviation of sensors, such as the default 200 mV/mil for 3300-8 mm Proximitors, which can be adjusted by ± 15%.
Zero Position: For channels such as thrust position and eccentricity, adjust the voltage to make the displayed value zero (such as setting the zero position of thrust position to -9.75 Vdc, corresponding to mechanical zero position).
Recorder output verification
The 4-20 mA output should correspond to the full-scale proportional value. For example, when the full-scale is 10 mil pp, 20 mA corresponds to 10 mil pp, and 4 mA corresponds to 0 mil pp, with an error of ≤± 1%.
Troubleshooting
LED fault diagnosis
OK light off: It may be due to module failure, hardware malfunction, or sensor disconnection. Check the power and wiring, restart the module, or replace spare parts.
BYPASS light on: The channel is bypassed by software or the sensor is faulty. Check the Software Switches configuration and confirm that the sensor is in an OK state.
TX/RX light does not flash: communication failure, check the rack backplane connection and serial port parameters (baud rate, data bits).
Analysis of System Event List
Event 11 (Flash Memory Failure): Flash memory failure, module replacement required immediately.
Event 62 (I/O Module Mismatch): The I/O module type does not match the software configuration. Check the module model and reconfigure it.
Event 493 (Kph Lost): Keyphasor signal loss. Check the Keyphasor sensor and wiring to confirm if the speed is within the valid range (60-60000 cpm).
Common alarm handling
Alert/Arm 1 trigger: If the vibration value exceeds the threshold, check whether the machine is unbalanced, misaligned, or has bearing faults.
Trigger of Danger/Arm 2: Emergency stop condition, immediately stop the machine and troubleshoot equipment faults. If the shaft displacement exceeds the limit, it may cause dynamic and static friction.
Technical specifications and ordering information
key parameter
Input impedance: Proximitor channel 10 k Ω, TMR configuration with bus mode 50 k Ω and discrete mode 150 k Ω.
Frequency response: The radial vibration Direct channel supports 1 Hz-4000 Hz, and the acceleration channel supports 3 Hz-30 kHz.
Environmental conditions: Operating temperature -30 ℃~65 ℃ (non barrier module), storage temperature -40 ℃~85 ℃, humidity ≤ 95% non condensing.
Order Parts
Monitor module: 3500/42-01-00 (discrete internal terminal, no authentication), 3500/42-03-01 (TMR external terminal, CSA authentication).
Spare parts: I/O module (such as 128229-01), terminal block (125808-02 Euro style), cable (129525-0010-01, 10 foot assembly cable).
Safety and Compliance
Explosion proof certification: With barrier module supporting Class I, Division 1 (Groups A-D) and EEx ia IIC, suitable for explosive gas environments.
Static protection: When operating the module, wear an anti-static wrist strap and store it in a conductive bag to prevent static electricity from damaging the circuit board.
Maintenance warning: When hot plugging modules, ensure that the rack is powered off to avoid the risk of short circuit or electric shock caused by live operation.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


