

K-WANG


ABB ACS800 Standard Control Procedure 7. x
Core functions: including startup configuration, control panel operation, parameter setting, fault diagnosis, communication interface, and various application macros (such as factory macros, PID control macros, torque control macros, etc.).
ABB ACS800 Standard Control Procedure 7. x
Product Overview
Scope of application: The firmware manual for the standard control program of ACS800 frequency converter is suitable for motor drive control in the field of industrial automation, supporting multiple control modes and communication protocols.
Core functions: including startup configuration, control panel operation, parameter setting, fault diagnosis, communication interface, and various application macros (such as factory macros, PID control macros, torque control macros, etc.).
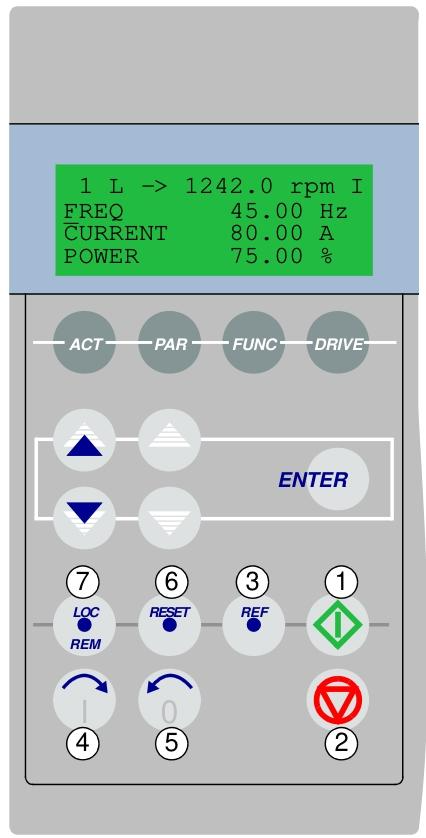
Startup and control mode
Start the process
Startup Wizard: Guide users to complete motor parameter settings (such as voltage, current, frequency, etc.) and identification run (ID Run), supporting both standard and simplified identification modes to ensure motor control accuracy.
Basic startup: Manually input parameters, suitable for quick configuration scenarios without the need for a wizard.
control model
Local control: Directly operated through the control panel, supporting start, stop, steering, and speed settings.
External control: Receive commands through digital/analog inputs or fieldbus (such as PROFIBUS, Modbus), supporting dual control switching between EXT1 and EXT2.
Core functional modules
Program Function
Given signal processing: supports multi-source given signals such as analog input, digital input, fieldbus, etc., and can combine given signals through mathematical operations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and taking the maximum value).
Speed and torque control:
Speed control: supports PID regulation, acceleration/deceleration ramp setting, and dangerous speed avoidance.
Torque control: Suitable for scenarios that require precise torque output, such as elevators and conveyor belts.
Braking control: Supports DC brake, magnetic flux brake, and mechanical brake, with configurable braking delay and torque threshold.
Application Macro Program
Factory macro: default mode, suitable for general speed control scenarios, supports 3 constant speed options.
PID control macro: used for process control (such as pressure and flow closed-loop), integrating sleep function to optimize energy consumption.
Torque control macro: directly controls motor torque, supports switching with speed control mode.
User macro: allows storage of two sets of custom parameters, facilitating quick switching between different motors or operating conditions.
Communication and Interface
Fieldbus support: compatible with protocols such as PROFIBUS, Modbus RTU/TCP, PROFINET, etc., and supports redundant communication configurations.
I/O expansion module: can connect digital/analog expansion modules, expand input and output channels, support motor temperature measurement, encoder interface, etc.
Parameters and actual signals
Parameter group division:
Startup data (99 sets): motor nameplate parameters, control mode, identification of operating configuration.
Given options (11 groups): Define the source of speed/torque given (such as analog input, fieldbus).
Limit values (20 sets): Setting operating limits such as speed, current, torque, etc.
Fault function (30 sets): Protection parameters for overcurrent, overvoltage, underload, etc., supporting automatic reset and alarm threshold setting.
Actual signal monitoring: Real time display of speed, current, torque, DC bus voltage, etc., supporting custom display combinations and filtering processing.
Fault diagnosis and maintenance
Fault codes and reset
Locate faults through control panel LED indicators or fault codes (such as overcurrent, overheating, communication interruption), and support manual or automatic reset (parameter configuration required).
Fault records store the last 6 events, including timestamps and fault types, to assist in quick troubleshooting.
Maintenance suggestions
Regularly check the matching of motor parameters, encoder connections, and the operating status of the cooling fan.
The communication module should pay attention to grounding and anti-interference, and avoid parallel wiring of high-voltage lines and signal lines.
Safety and Standards
Electrical safety: Ensure that grounding complies with NEC standards, avoid modifying parameters with motors, and prevent accidental start-up.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC): Sensor cables need to be shielded and grounded at one end, and isolated from high-voltage lines.
Compliance certification: Complies with IEC standards and supports explosion-proof applications in hazardous environments (requires corresponding module configuration).

- YOKOGAWA
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Energy and Gender
- Covid-19
- man-machine
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- xYCOM
- Construction site
- Siemens
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Motorola
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
-
Kollmorgen S33GNNA-RNNM-00 - Brushless Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen 6sm56-s3000-g-s3-1325 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM52K-CCCN2-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen PSR3-230/75-21-202 - Power Supply
-
Kollmorgen akm24d-anc2r-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM22E-ANCNR-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen S60300-550 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen B-204-B-21 - Servomotor
-
Kollmorgen AKM21E-BNBN1-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen TT2953-1010-B - DC Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen pa8500 - Servo Power Supply
-
Kollmorgen BDS4A-210J-0001-207C2 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen TTRB1-4234-3064-AA - DC Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen MH-827-A-43 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM24D-ACBNR-OO - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen 00-01207-002 - Servo Disk DC Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM21C-ANBNAB-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen PSR3-208/50-01-003 - Power Supply
-
Kollmorgen 6SM56-S3000 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen DBL3H00130-B3M-000-S40 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen 6SN37L-4000 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM65K-ACCNR-00 - Servo motor
-
Kollmorgen 6SM56-L3000-G - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKMH43H-CCCNRE5K - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen PSR4/52858300 - Power Supply
-
Kollmorgen KBM-79H03-E03 - Direct Drive Rotary Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM33E-ANCNDA00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen U9M4/9FA4T/M23 - ServoDisc DC Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM13C-ANCNR-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM43L-ACD2CA00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM54K-CCCN2-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen M-605-B-B1-B3 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKD-P00606-NBAN-0000 - Rotary Drive
-
Kollmorgen 6SM-37M-6.000 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen A.F.031.5 - Sercos Interface Board
-
Kollmorgen 918974 5054 - Servo PWM
-
Kollmorgen U12M4 - ServoDisc DC Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKD-B00606-NBAN-0000 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen MV65WKS-CE310/22PB - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen 65WKS-CE310/22PB - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen EM10-27 - Module
-
Kollmorgen S64001 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen CR03200-000000 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen 6SM57M-3000+G - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen BDS4 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen AKD-P00306-NBEC-000 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen AKD-B01206-NBAN-0000 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen STP-57D301 - Stepper Motor
-
Kollmorgen 6SM37L-4.000 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen 44-10193-001 - Circuit Board
-
Kollmorgen PRDR9SP24SHA-12 - Board
-
Kollmorgen PRD-AMPE25EA-00 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen DBL3N00130-0R2-000-S40 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen S406BA-SE - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen AKD-P00607-NBEI-0000 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen AKD-P01207-NBEC-0000 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen CR03550 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen VSA24-0012/1804J-20-042E - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen N2-AKM23D-B2C-10L-5B-4-MF1-FT1E-C0 - Actuator
-
Kollmorgen 04S-M60/12-PB - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen H33NLHP-LNW-NS50 - Stepper Motor
-
Kollmorgen A-78771 - Interlock Board
-
Kollmorgen AKM43E-SSSSS-06 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKD-P00607-NBEC-0000 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen E21NCHT-LNN-NS-00 - Stepper Motor
-
Kollmorgen cr10704 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen d101a-93-1215-001 - Motor
-
Kollmorgen BDS4A-203J-0001-EB202B21P - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen MCSS23-6432-002 - Connector
-
Kollmorgen AKD-P01207-NACC-D065 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen CK-S200-IP-AC-TB - I/O Adapter and Connector
-
Kollmorgen CR10260 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen EC3-AKM42G-C2R-70-04A-200-MP2-FC2-C0 - Actuator
-
Kollmorgen BDS5A-206-01010-205B2-030 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen s2350-vts - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen AKM24D-ANC2DB-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen E31NCHT-LNN-NS-01 - Stepper Motor
-
Kollmorgen PRD-0051AMPF-Y0 - Servo Board
-
Kollmorgen TB03500 - Module
-
Kollmorgen 60WKS-M240/06-PB - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen M21NRXC-LNN-NS-00 - Stepper Motor
-
Kollmorgen H-344H-0212 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen MCSS08-3232-001 - Connector
-
Kollmorgen AKM33H-ANCNC-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen PA-2800 - Power Supply
-
Kollmorgen MTC308C1-R1C1 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen PRDR0091300Z-00 - Capacitor Board
-
Kollmorgen BDS4A-206J-0024/01502D79 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen S20330-VTS - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen S20250-CNS - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen SBD2-20-1105-WO - Servo Drive Board
-
Kollmorgen M405-C-A1--E1 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen PRD-PB805EDD-00 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen 6SM57S-3.000-J-09-HA-IN - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen AKM33H-ANCNDA-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen PCB-00030200-04 - PCB
-
Kollmorgen H22SSLB-LNN-NS-02 - Stepper Motor
-
Kollmorgen BJRL-20012-110001 - Module
-
Kollmorgen BDS4A-206J-0001404A - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen H-342-H-0802 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen CR10561 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen BDS5A-206-00010-205B2-030 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen BDS5A-206-00010-207B-2-030 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen mcss08-3224-001 - Connector
-
Kollmorgen M-207-B-23-B3 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen PRD-0041200Z-S0 - Encoder/Resolver Card
-
Kollmorgen MH-225-G-61 - Motor
-
Kollmorgen MT308B1-T1C1 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen BDS4A-240J-0001604C83 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen 6SM57-S-3000 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen N-T31V-15-5B-6-MF3-FT1E-C251 - Actuator
-
Kollmorgen PRD-0051AMPA-X0 - Servo Board
-
Kollmorgen CF-SS-RHGE-09 - Cable
-
Kollmorgen DIGIFAS7204 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen S30101-NA - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen DIGIFAS7201 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen PRD-0051AMPA-Y0 - Servo Board
-
Kollmorgen AKM23D-EFCNC-00 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen SE10000 - Servo Drive
-
Kollmorgen PSR4/5A-112-0400 - Power Supply
-
Kollmorgen AKM31H-ANCNC-01 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen M-203-B-93-027 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen CP-SS-G1HE-05 - Connector
-
Kollmorgen AKM42G-ASCNR-02 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen DBL4N00750-B3M-000-S40 - Servo Motor
-
Kollmorgen R3-BK23-152B-12-PL-ASE-BS115 - Actuator
-
Kollmorgen MH-427-B-61 - Motor
-
Kollmorgen cr06902 - Servo Drive




