

K-WANG


TEKTRONIX AFG31000 series arbitrary function generator
TEKTRONIX AFG31000 series arbitrary function generator
Product model and core parameters
1. Comparison Table of Model Parameters
Model, bandwidth, sampling rate, number of channels, standard memory, optional memory, pulse generator, bandwidth
AFG31021 25MHz 250MS/s 1 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 20MHz
AFG31022 25MHz 250MS/s 2 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 20MHz
AFG31051 50MHz 1GS/s 1 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 40MHz
AFG31052 50MHz 1GS/s 2 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 40MHz
AFG31101 100MHz 1GS/s 1 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 80MHz
AFG31102 100MHz 1GS/s 2 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 80MHz
AFG31151 150MHz 2GS/s 1 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 120MHz
AFG31152 150MHz 2GS/s 2 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 120MHz
AFG31251 250MHz 2GS/s 1 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 160MHz
AFG31252 250MHz 2GS/s 2 16MS/CH 128MS/CH 160MHz
2. General technical characteristics
Vertical resolution: 14 bits, ensuring waveform accuracy.
Output impedance: default 50 Ω, can be set to 1 Ω~10k Ω (resolution 1 Ω) or Infinity (>10k Ω).
Modulation types: Supports AM (amplitude modulation), FM (frequency modulation), PM (phase modulation), FSK (frequency shift keying), PWM (pulse width modulation).
Environmental adaptability: working temperature of 0 ℃~40 ℃, humidity of 5%~85% RH, working altitude of 3000m.
Safety regulations and operating taboos
1. Core security principles
Only for professional operation: Only personnel with high voltage/high frequency testing qualifications are allowed to operate, and non professionals are prohibited from contacting.
System level security: If connecting to a large system, it is necessary to comply with the security manuals of other components of the system.
Preoperative examination: Before use, verify that the device is functioning properly with a known signal source and prohibit its use for detecting dangerous voltages.
2. Key operations for preventing electric shock and fire prevention
(1) Power supply and grounding
Use designated power cords (must comply with local certification), and do not mix power cords from other devices.
The equipment is grounded through the power cord, and the grounding conductor must be connected to the ground. It is forbidden to disconnect the grounding connection.
Confirm that the power supply voltage matches the rated value of the equipment (such as 100V~240V AC) before powering on.
(2) Connection/disconnection sequence
Operation type, step purpose
Connect circuit 1. Connect the probe output to the measuring instrument → 2 Connect the probe reference terminal to the tested circuit → 3 Connect the probe input to avoid electric shock or equipment damage caused by live plugging and unplugging
Disconnect circuit 1. Disconnect probe input and reference terminal → 2 Disconnect the probe from the instrument to prevent residual voltage shock
(3) Taboos on Environment and Equipment Status
Do not use in damp, explosive, and dusty environments, and do not operate without cover plates/panels (exposing high-voltage circuits).
If the equipment falls, gets wet, or is suspected of damage, authorized personnel must inspect it before use, and it is prohibited to disassemble it by oneself.
Do not touch the exposed circuit when powered on, and keep the probe body and output line away from the tested circuit.
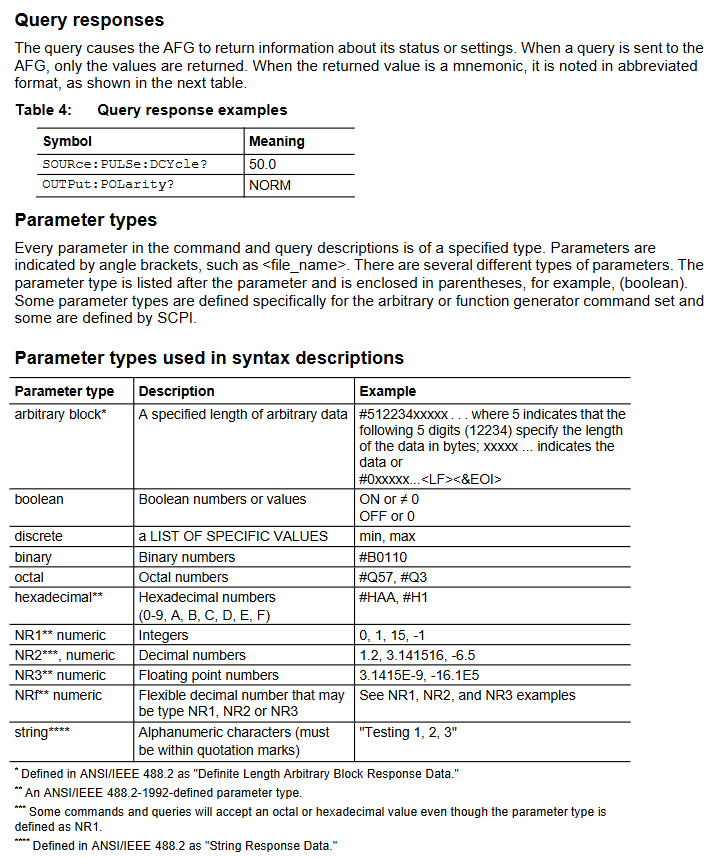
Remote control interface and instruction system
1. Interface configuration
(1) GPIB interface
Requirements:
Each device must have a unique address (1-30) and must not be duplicated;
The bus can connect up to 15 devices, with a total cable length of ≤ 20m and at least 1 device per 2m;
Power on devices account for ≥ 67%, support star/linear topology, and prohibit parallel/ring topology.
Address setting: Enter the address through the panel "Utility → I/O Interface → GPIB Address" (* RST command cannot initialize the address).
(2) VISA interface
TekVISA software (official website download) needs to be installed, supporting GPIB, RS-232, Ethernet remote control, and complying with VISA 2.2 standard.
Applicable development environment: Windows system, supporting ADE (Application Development Environment) such as LabVIEW and VB.
2. Instruction system and syntax
(1) Instruction classification
Example Function of Instruction Type
IEEE 488.2 General Command * CAL? 、 *CLS, * RST self calibration, clear register, reset
SCPI command SOURce1: FUNCTION SIN, OUTPut1: STATe ON. Set the waveform of channel 1 to sine and enable the output of channel 1
(2) Core Grammar Rules
Abbreviation: Commands can be abbreviated (uppercase is required, lowercase can be omitted), such as DISPlay: BRIGhtness can be abbreviated as DISP: BRIG.
Chain command: Multiple commands are separated by semicolons, and prefixes can be omitted for the same root node, such as TRIGger: CLOPe POS; SOURce SIN (assuming the trigger slope is positive and the source waveform is sine).
SI units: support voltage (V/mV), frequency (Hz/kHz/MHz), time (s/ms/μ s/ns), etc., such as Frequency 10MHz (assuming frequency 10MHz).
Parameter type: Supports Boolean values (ON/OFF), numerical values (NR1/NR2/NR3), and strings (quotation marks required), such as MMEMory: DELete "U:/TEST. TFWX" (remove the TEST. TFWX file from USB).
Detailed explanation of core functions and instructions
1. Waveform generation and output control
(1) Waveform type and parameter settings
Supporting waveforms: 13 types including sine (SINusoid), square wave (SQUare), pulse (PULSe), ramp (RAMP), noise (PRNoise), arbitrary wave (EMEMory/EFILe), etc.
Example of Key Instructions:
Let the waveform of channel 1 be sine: SOURce1: FUNCTION SIN
Assuming a frequency of 10kHz: SURce1: Frequency 10kHz
Set amplitude to 2Vpp: SURce1: VOLTage: Amplitude 2VPP
Set offset 1V: SURce1: VOLTage: OFFSet 1V
(2) Output control
Turn on/off output: OUTPut1: STATe ON/OFF
Output polarity reversal: OUTPut1: Polarity Inverted (default NORMAL)
Output impedance setting: OUTPut1: Impedance 50OHM (default 50 Ω, can be set to 1 Ω~10k Ω)
2. Modulation function (AM/FM/PM, etc.)
Taking AM (amplitude modulation) as an example, the key instructions are as follows:
Example of functional instructions
Set modulation depth SOURce1: AM: DEPTh SOURce1: AM: DEPTh 50PCT (50% depth)
Set the internal modulation frequency SOURce1: AM: INTernal: FREQuency SOURce1: AM: INTernal: FREQuency 1kHz
Set modulation source SOURce1: AM: SOURce1: AM: SOURce INTernal (internal source)
Turn on AM SOURce1: AM: STATe SOURce1: AM: STATe ON
3. Sequence control (advanced mode)
Support defining 256 sequence elements to achieve waveform looping, jumping, and waiting for triggering. Core instructions:
New sequence: SEQueen: NEW
Set sequence length (10 elements): SEQuence: LENGth 10
Let element 1 loop 100 times: SEQuence: ELEM1: LOOP: COUNT 100
After triggering element 1, jump to element 6: SEQuence: ELEM1: GOTO: INDex 6; GOTO:STATe ON
Running sequence: SEQControl: RUN: IMMediate
4. Data storage and management
(1) Virtual Disk Definition
Disk identification, storage location, permission usage
U: USB flash storage for reading and writing user waveforms/settings files
M: Internal flash read-write storage commonly used waveforms/settings
P: Internal predefined area read-only storage factory preset waveforms (such as sine and square waves)
(2) Store/load instructions
Save channel 1 waveform to USB: MMEMory: STORe: TRACe EMEMory1, "U:/WAVE1. TFWX"
Loading settings from USB to memory 1: MMEMory: LOAD: STATe 1, "U:/SET1. TFS"
Delete USB file: MMEMory: DELete "U:/OLD. TFWX"
Status and Event Management
1. Status register system
Compliant with IEEE 488.2 and SCPI standards, the core registers are as follows:
Meaning of register name function key bits
Status Byte Register (SBR) summarizes device status OSB (operational status), ESB (event status), MAV (message available)
The Standard Event Status Register (SESR) records core events OPC (operation completed), CME (command error), EXE (execution error)
The operating condition register (OCR) records the operating status CAL (calibration in progress), SWE (scanning in progress), WTRIG (waiting for trigger)
2. Error code system
Error codes are divided into "standard errors" (-100~-499) and "device specific errors" (1~32767). Common examples include:
Error code type description
-100 command errors command syntax errors (such as spelling errors)
-222 execution error parameter out of range (e.g. frequency set to 1000MHz, exceeding the upper limit of 250MHz)
-350 device error error queue overflow (more than 64 events)
1101 calibration error CH1 internal offset calibration failed
2305 self-test error CH1 output gain self-test failed
3. Error query
Search for the next error: SYSTem: ERRor: NEXT? The return format is -222, "Data out of range"
Maintenance and troubleshooting
1. Maintain standards
Cleaning: Wipe the outer surface with a dry lint free cloth or 75% isopropanol. Do not use water/solvents/abrasives, and do not allow moisture to enter the interior of the equipment.
Repair restriction: There are no user repairable parts, and only DC offset can be adjusted for serial numbers C019999 and below. Other faults need to be returned to the factory.
2. Common fault handling
Troubleshooting steps for possible causes of fault phenomena
No waveform output turned on, parameter out of range 1. Execute OUTPut1: STATe? Confirm the output status; 2. Check if the frequency/amplitude is within the device range
GPIB no response address conflict, cable fault 1. Confirm that GPIB address is unique; 2. Replace GPIB cable; 3. Restart the device and controller
Calibration failed due to excessive temperature and humidity in the environment, hardware malfunction. 1. Confirm that the environment is 0 ℃~40 ℃/5%~85% RH. 2. Execute DIAGnostic? Self inspection; 3. If errors 1101-1216 are reported, return to the factory for repair
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


