

K-WANG


ABB AFS series switches
ABB AFS series switches
Product Overview
Core positioning: A fully managed modular Ethernet switch designed specifically for the power industry (substations, distribution networks, and in plant communication), focusing on core requirements such as high reliability, electromagnetic interference resistance, and wide temperature operation in power scenarios, supporting the expansion of smart grid applications (such as renewable energy integration and distribution automation).
Product series division:
|Model series | Installation method | Core configuration differences | Number of ports | Power consumption range | Special functions|
|AFS650/655 | DIN rail (optional wall mounted) | Compact design, supports multi-mode/single-mode optical ports | Up to 10 (including 3 GbE ports) | 12-21 W | Redundant power supply (18-60VDC/48-320VDC/90-265VAC)|
|AFS670/675 | 19 inch rack | Modular design, 12 slots (2 ports/module) | Up to 28 slots (electrical/optical/SFP cage) | 10-40 W (no PoE) | Supports PoE (power type H/Z), redundant power supply (18-60VDC/77-300VDC/90-265VAC)|
|AFS677/AFR677 | 19 inch rack | Fixed port design | 16 GbE combo ports (RJ45/SFP) | 10-40 W (no PoE) | AFR677 supports L3 routing (RIPv1/v2, OSPFv2, VRRP)|
Key compliance and technical parameters
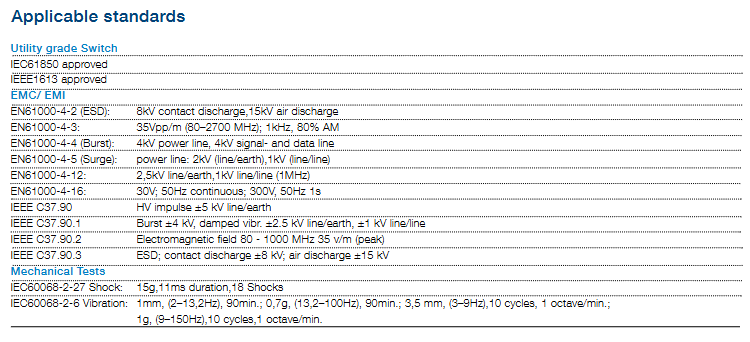
Certification and anti-interference standards:
|Standard Category | Core Standard Content|
|Industry certification | IEC61850 approval, IEEE1613 approval|
|Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC/EMI) | EN61000-4-2: 8kV contact discharge, 15kV air discharge; EN61000-4-3:35Vpp/m(80-2700MHz); IEEE C37.90.3: ± 8kV contact discharge, ± 15kV air discharge|
|Mechanical testing | IEC60068-2-27: 15g impact (11ms, 18 times); IEC60068-2-6: Vibration Test (2-13.2Hz/1mm/90min, etc.)|
|Network standards | IEEE802.1d/p/Qx/AB, IEEE802.3 series, IEEE1588 (PTP), etc|
Core technical parameters:
Working temperature: Standard 0-60 ℃, optional -40 ℃ to 85 ℃ (continuous operation)
Switching characteristics: Store and forward mode, typical switching delay of 2.7 μ s (100Mbit/s), MAC address table capacity of 8000 entries
Network function: 4042 VLANs (supporting 255 at the same time), 4 priority queues, supporting port rate limitation (kbps step), link aggregation IGMP snooping
Protection mechanism: Supports RSTP (IEEE802.1D), MRP (IEC62439), E-MRP, and fast switching of ring topology
Power specifications: AFS650/655 supports 18-60VDC (low voltage), 48-320VDC/90-265VAC (high voltage); The AFS670 series supports 18-60VDC (low voltage), 77-300VDC/90-265VAC (high voltage), all of which support redundant power supplies
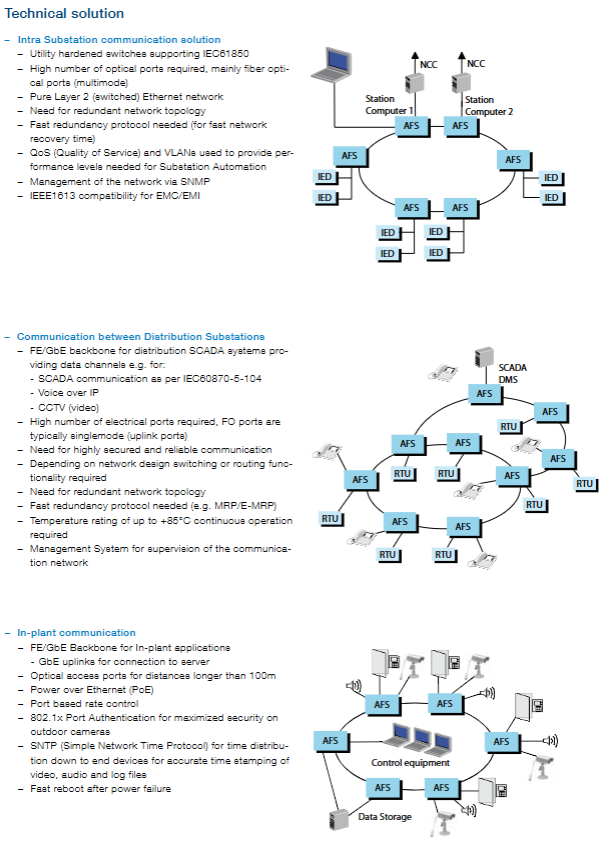
Three core application scenarios and solutions
Application scenario core requirement solution configuration
Substation automation low latency, high availability, IEC61850 compatibility, anti electromagnetic interference pure L2 switching network, redundant topology, multi-mode optical ports as the main, QoS/VLAN enabled, SNMP management supported, GOOSE message and sampling value transmission supported
Long distance transmission of power distribution communication, reliable transmission of SCADA data, multi service carrying FE/GbE backbone network, single-mode optical port (uplink), supporting IEC60870-5-104 protocol, redundant topology+MRP/E-MRP, compatible with VoIP and renewable energy data transmission
In plant communication with high bandwidth (CCTV), equipment power supply, time synchronization, high security GbE upstream connection server, PoE power supply (camera), 802.1x port authentication, SNTP time synchronization, port rate control, supporting CCTV, access control, and public address system communication
Security and management features
Security features: IEEE802.1x port authentication, SSH encryption, Radius centralized password management, multi-level user passwords, port disabling, SNMPv3 encryption authentication, VLAN isolation (IEEE802.1Q)
Management methods: SNMP V1/V2/V3, command-line interface (Telnet), web interface, port mirroring, RMON remote monitoring, LLDP topology auto discovery, SFP diagnosis, configuration recovery adapter (CRA), watchdog and rollback function
Alarm mechanism: Diagnostic LED indicator light, 2 sets of alarm contacts, local logs and Syslog reports
Customer Core Value
Power level adaptation: high EMC/EMI anti-interference ability, wide temperature working range, redundant power supply, suitable for harsh environments in substations
High availability: fanless design, high MTBF, fast switching of link failures, ensuring uninterrupted critical business operations
Flexible Expansion: Port density can be expanded (8-28), supporting FE/GbE, PoE, L3 routing (AFR677), and adapting to different scale requirements
Integrated solution: integrated into ABB's power communication ecosystem, supporting multi business integration such as SCADA, IEC61850, voice, etc
Key issues
Question 1: What are the specific power level characteristics of ABB AFS series switches reflected in? Why can it adapt to the harsh environment of substations?
Answer: The power level characteristics are mainly reflected in three aspects: ① Environmental adaptation: supporting standard working temperature of 0-60 ℃, optional wide temperature range of -40 ℃ to 85 ℃, fanless design+optional normal coating, and can withstand extreme temperatures; ② Anti interference capability: certified by IEEE1613, compliant with EN61000-4 series (ESD 8kV contact/15kV air discharge, surge 2kV line to ground) and IEEE C37.90 series standards, resistant to strong electromagnetic interference; ③ Reliability design: Supports redundant power supply (AC/DC wide voltage input, such as AFS650 supporting 48-320VDC), fast protection mechanism (MRP/E-MRP, ring topology fast switching), high MTBF guarantee, avoiding single point failure. These characteristics enable it to directly adapt to harsh environments such as severe electromagnetic pollution, large temperature fluctuations, and high requirements for continuity in substations.
Question 2: What are the core differences between different models of ABB AFS series? How to choose the appropriate model based on the application scenario?
Answer: The core differences are concentrated in three dimensions: installation method, port configuration, and functional expansion. The selection logic is as follows:
Model Series Core Differences Adaptation Scenarios
AFS650/655 DIN rail installation, up to 10 ports, no L3 routing for small substations, distribution terminals, and distributed equipment communication within the factory (limited space, low port requirements)
AFS670/675 19 inch rack, modular design (up to 28 ports), supporting PoE for large-scale substation automation, requiring high port density distribution communication backbone network (multi device access, requiring PoE power supply for cameras/terminals)
AFS677/AFR677 19 inch rack, 16 GbE combo ports, AFR677 supports L3 routing (RIPv1/v2, OSPFv2) for cross regional power distribution communication and complex networks requiring routing functionality (multi subnet interconnection, backbone network hierarchical architecture)
Question 3: What are the key technical measures for ABB AFS series switches to ensure the reliability of critical business in the power industry, such as IEC61850 data transmission?
Answer: Key technical measures include: ① Fast protection mechanism: supporting MRP (Media Redundancy Protocol), E-MRP, and RSTP, which can achieve fast switching in case of link failure in ring topology, reducing the interruption time of IEC61850 GOOSE message and sampling value transmission; ② Network isolation and priority: Supports 4042 VLANs (255 at the same time) and 4 priority queues, isolates different services through IEEE802.1Q VLANs, ensures QoS guarantees priority transmission of IEC61850 critical data, and avoids bandwidth preemption; ③ Hardware redundancy: supports redundant power input to avoid equipment shutdown caused by power failure; ④ Management and monitoring: Real time monitoring of network status through SNMP V3, RMON, LLDP topology discovery, combined with alarm contacts and Syslog reports, to quickly locate faults; ⑤ Protocol compatibility: Native support for IEC61850 protocol ensures seamless integration with intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), reducing latency and fault risks caused by protocol conversion
- YOKOGAWA
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Energy and Gender
- Covid-19
- man-machine
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- Industrial information
- xYCOM
- Motorola
- architecture
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
ABB REF610 Protection and Control Relay
-
ABB DSQC633 Robot Control Interface Module
-
ABB DSQC332A Robot Control Module
-
ABB F362 Industrial Interface Module
-
ABB SK616001-A Industrial Control Module
-
ABB 3HAC0977-1 Robot Control Interface Module
-
ABB S503X Industrial Protection and Switching Device
-
ABB BC25 Industrial Automation Communication Interface
-
ABB DSQC504 Robot Servo and Control Module
-
ABB DSQC509 Robot I/O and Control Interface Module
-
ABB DSQC346B Robot Motion Control Board
-
ABB 3HAB8859-1/03A Industrial Robot Control Interface Board
-
ABB 3HAB9271-1/01B Robot Controller Communication Module
-
ABB 3HAC5497-1 Robot Control Processing Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


