

K-WANG


YASKAWA GA700 series AC frequency converter
Core objective: To guide professional technicians to complete the safe installation, wiring, parameter configuration, trial operation, and fault handling of frequency converters
Applicable restrictions: limited to industrial motor control only, not used in special fields such as life support systems, nuclear industry, etc
YASKAWA GA700 series AC frequency converter
Overview
Type: YASKAWA GA700 series AC frequency converter
Core objective: To guide professional technicians to complete the safe installation, wiring, parameter configuration, trial operation, and fault handling of frequency converters
Applicable restrictions: limited to industrial motor control only, not used in special fields such as life support systems, nuclear industry, etc
Safety regulations (core focus)
1. Definition of risk level
Typical scenarios of risk level meaning
DANGER may cause death/serious injury due to live wiring and non discharge of internal capacitors during operation
Warning: May cause death/serious injury. Flammable materials near frequency converter, poor grounding
CAUTION may cause minor/moderate injury when touching high-temperature heat sinks or handling unsecured cover plates
NOTICE may cause equipment damage due to unused shielded wires and withstand voltage testing
2. Key safety requirements
Electrical safety: Power off before wiring, wait for capacitor discharge (indicator light off, DC bus voltage<50Vdc); Grounding resistance: 200V level ≤ 100 Ω, 400V level ≤ 10 Ω
Mechanical safety: Models weighing ≥ 15kg require 2 people and lifting equipment for handling, and it is prohibited to grip the front cover/terminal cover
Operation safety: Remove the motor load before Auto Tuning; 3-wire control needs to set b1-17=0 (ignore RUN command when powered on)
Installation specifications
1. Mechanical installation
Installation direction: Priority should be given to vertical installation (to ensure heat dissipation), special models can be installed on the side (please consult the manufacturer)
Distance requirement:
Single machine: Up and down ≥ 120mm, left and right ≥ 30mm, front ≥ 50mm
Side by side installation (specific model): Drive spacing ≥ 2mm, L8-35=1 needs to be set
Environmental restrictions:
Temperature: Open type (IP20) -10~50 ℃, Closed type (UL Type 1) -10~40 ℃
Altitude: ≤ 1000m (over 1000m, capacity reduction of 1% per 100m)
Pollution level: ≤ Level 2 (no dust, oil stains, corrosive gases)
2. Electrical installation
Key terminal requirements for circuit type wiring
Main circuit power line cross-section ≥ 0.75mm ² (control circuit), tightening torque 3.6-41.5N · m R/L1/S/L2/T/L3 (input), U/T1/V/T2/W/T3 (output)
Control circuit shielded twisted pair cable, up to 3m in length, with a distance of ≥ 30cm from the power line S1-S8 (multifunctional input), A1-A3 (analog input), FM/AM (analog output)
The grounding terminal on the motor side must be grounded, and the shielding layer must be grounded at one end FG (driver grounding) and the motor casing must be grounded
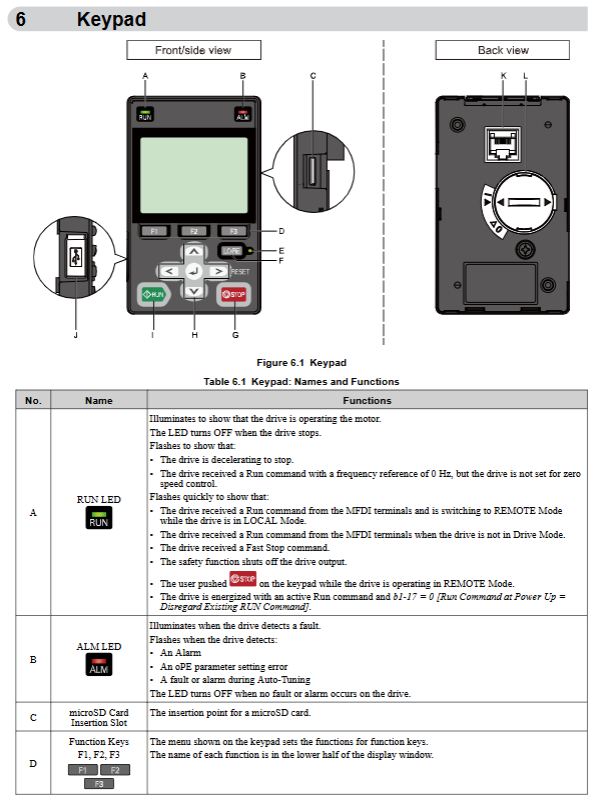
Startup and parameter configuration
1. Keyboard operation
Core components: RUN/STOP button (local start stop), LO/RE button (local/remote switch), RESET button (fault reset)
Mode description:
LOCAL mode: keyboard controls speed and start stop
REMOTE mode: External terminal or communication control (parameter b1-01/b1-02 setting)
Display screen: Supports multiple languages (including Chinese), displaying frequency, current, and fault codes
2. Initialization process
After powering on, enter the Initial Setup interface and set the date/time (requires installation of CR2016 battery)
Run the Setup Wizard and enter the motor nameplate parameters (rated power, voltage, current, frequency)
Execute Auto Tuning:
Rotation tuning (T1-01=0): Need to be unloaded, motor speed should be above 50% of rated frequency
Static tuning (T1-01=1): Automatically calculates motor parameters without disconnecting from the load
No load test run: Confirm the motor direction and no abnormal vibration/noise
Load and run: Verify acceleration/deceleration time (C1-01/C1-02), overload capacity
3. Core parameter configuration
Parameter code, parameter name, function description, typical settings
A1-02 Control mode selection switch V/f/OLV/EZOLV 0 (V/f, general scenario)
C1-01 Acceleration Time 1 Time from 0 to maximum frequency of 10.0s (default, adjustable according to load)
C6-01 duty mode selects constant torque/variable torque switching 0 (Heavy Duty, constant torque)
E2-01 motor rated current matching motor nameplate current entered according to actual motor parameters
L1-01 motor overload protection electronic thermal protection mode 2 (constant torque 10:1 speed range)
4. Comparison of control methods
Control mode parameter setting applicable scenarios core advantages
V/f control A1-02=0 fan, pump, multi motor linkage has strong universality and does not require motor parameters
Open loop vector (OLV) A1-02=2 high-precision speed control without speed feedback, high low-speed torque
EZ vector A1-02=8 simplified settings for ordinary variable speed scenarios, no need for fine tuning
Troubleshooting
1. Common faults and solutions
Fault code, fault name, common causes, and solutions
Check the wiring for overcurrent output short circuit, heavy load, and short acceleration time at oC, reduce load, and increase C1-01
OV overvoltage deceleration time is too short, brake resistor damage increases deceleration time, replace brake resistor, activate L3-04 (stall prevention)
Overloading of oL1 motor, overload of motor, low speed to reduce load, use of forced cooling motor, correction of E2-01 parameters
Overload of oL2 drive, insufficient drive capacity, low-speed high torque replacement with large capacity models, reducing load
GF grounding fault output side grounding short circuit, motor insulation damage inspection wiring, testing motor insulation resistance (≥ 10M Ω)
STo safety torque OFF safety input terminal disconnection inspection H1/H2/HC wiring, reset safety controller
2. Fault reset process
Remove the source of the fault (such as power-off inspection of wiring, reducing load)
Waiting for the discharge of the driver capacitor (indicator light off)
Press the RESET key on the keyboard, or power off and restart
If it repeatedly occurs, check the parameter configuration or contact the manufacturer for repair
Compliance and scrapping
Compliance standards: Complies with IEC/EN 61800-5-1, UL 508C, CSA C22.2 No.100
Scrap requirements:
Separate the battery (CR2016) and microSD card and dispose of them separately according to regulations
SD cards need to be physically destroyed or data erased to prevent information leakage
Drive body is classified and recycled according to industrial waste

- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


