

K-WANG


ABB KOFA12D3 Indoor current transformers
ABB KOFA12D3 Indoor current transformers
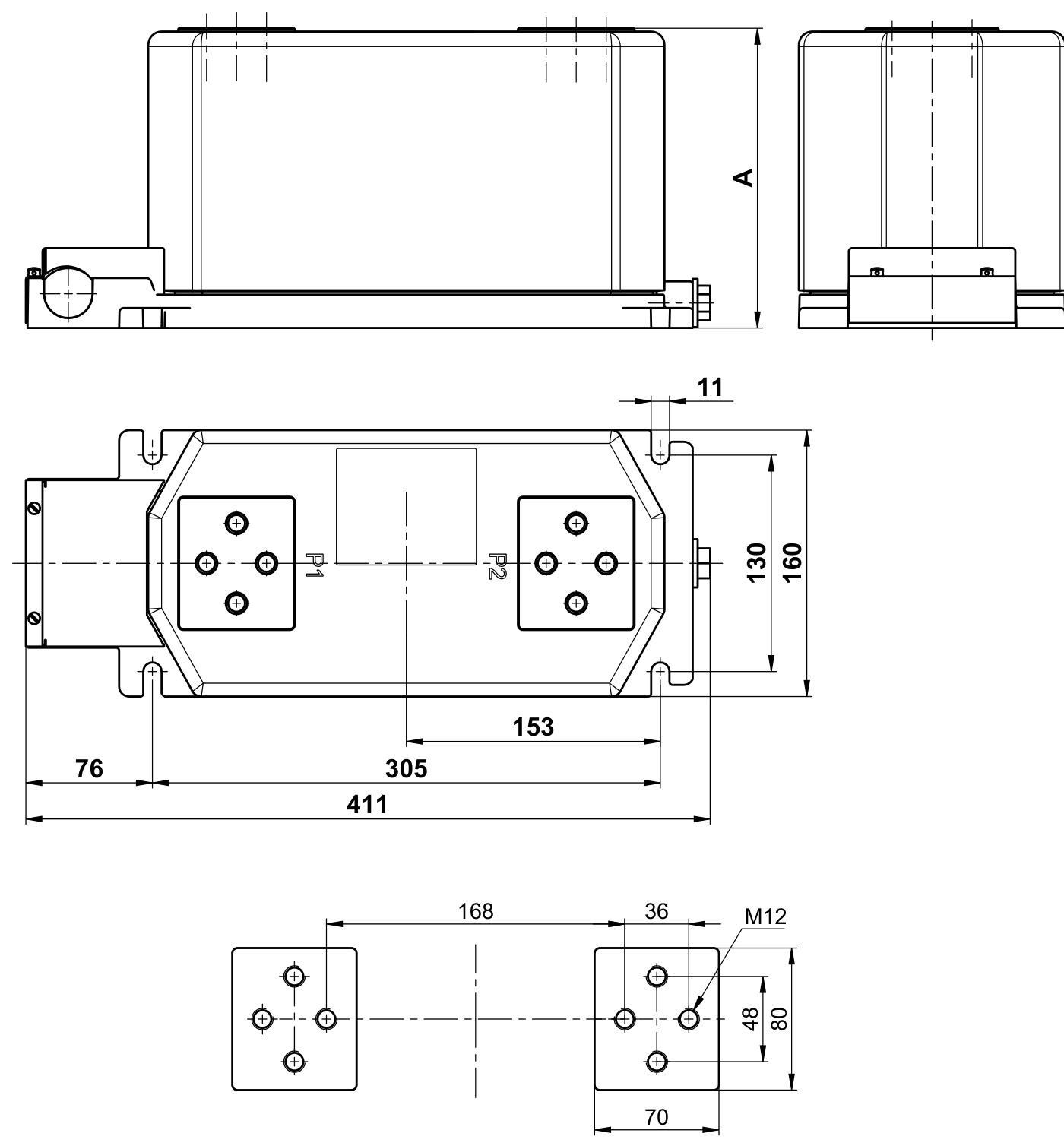
Technical parameters
Rated frequency: 50Hz and 60Hz.
Rated secondary current: 5 (1.2) A.
Rated load: 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30VA.
Accuracy levels: 0.2, 0.5, 1, 5P10, 5P20.
Mechanical strength of one terminal: 5kN.
Standards: Compliant with IEC, BS, ANSI and other standards, other data can be provided as required.
Structure and Design
Winding and packaging: The primary winding, iron core, and secondary winding are encapsulated by epoxy resin casting.
Secondary conductor:
The fixing screws on the light alloy base are also easily accessible from above.
The conduit used for the secondary conductor can be fixed at the U-shaped slot entrance of the secondary junction box to prevent the secondary conductor from entering the junction box through the entrance hole.
According to the order requirements, the junction box can be equipped with threaded entrances for cable terminal accessories.
One 2.5-10mm ² or two 2.5-6mm ² (one 2.5-6mm ² for three-phase transformers) conductors can be directly connected to the secondary terminal. The terminal cover can be sealed and the enclosure protection level is IP30.
Primary terminal: The primary terminal uses M12 screws, and the connection can be changed without removing the installed primary conductor.
Environmental and altitude requirements
Operating environment:
Suitable for indoor installation, IEC recommends an ambient temperature between -5 ℃ and+40 ℃, and can actually be used at temperatures as low as -40 ℃.
Transformers must prevent the deposition of large amounts of dust or similar pollutants, as well as avoid direct sunlight.
Altitude impact:
The altitude in mountainous areas may be higher than the elevation (1000m) used as a design standard in IEC standards.
The thin air in high-altitude areas can affect the cooling of transformers, as well as the creepage distance and air gap between ground and phases. In this case, the manufacturer should be consulted.
The issues of creepage distance and air gap can be solved by selecting transformer types designed for higher voltages. For the operating voltage used, it is best not to exceed the normal level of impulse test voltage (BIL level), as this may have a negative impact on the available output on the secondary side.
Insulation level
The insulation levels of KOFA models are 12/28/75kV, 17.5/38/95kV, and 24 (25)/50/125kV.
Preferred current transformer
Advantages:
The factory has prepared documents and materials for the most commonly used ratings, which can provide short delivery times for urgent needs.
Simplify the selection and ordering process by providing specific order codes for each standard current transformer.
Model examples: KOFA 12 D2 (12kV), KOFA 24 D2 (24kV).
Parameters: Secondary current of 5A, 2 iron cores, weights of 17kg and 19kg respectively, in compliance with international standard IEC 60044-1.
Ordering example: If the requirement is 6.6kV, in accordance with IEC 60044-1 standard, with a primary current of 100-200/5/5A, iron core 1 is 15VA, class 0.5, iron core 2 is 15VA, class 10P10, frequency 50Hz, the ordering code is KOFA 12 D2-L01.
Customized design transformer
One time and type selection table:
The table displays the available short-circuit strength and rated primary current for 12, 17.5, and 24kV, as well as the iron core selection symbol. The larger the iron core symbol, the smaller the size of the iron core and transformer. For transformers with two primary connections, this meter is suitable for lower rated currents, and at double the rated current, the thermal and dynamic intensity will also double.
The type selection table provides transformer types and weights corresponding to different numbers of iron cores at 12, 17.5, and 24kV.
Core selection table: Determine the core size based on rated load, accuracy level, etc.
Working principle
1、 Basic principles
Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Induction
When current passes through a winding, alternating magnetic flux is generated in the iron core. According to the law of electromagnetic induction, the secondary winding will induce electromotive force due to changes in magnetic flux, thereby generating current in a closed secondary circuit. The secondary current is directly proportional to the primary current, and the phase is basically the same. Through this proportional relationship, high current measurement and transformation can be achieved.
The relationship between primary and secondary sides
A winding with few turns (or even a single turn) is directly connected in series in the tested circuit, passing through a high current; The secondary winding has a large number of turns and is connected in series with measuring instruments or protective devices, with a small current (usually 5A or 1A).
2、 The support of key structures for principles
Winding and iron core design
Primary winding: usually a single conductor or a few turns, carrying the current of the tested main circuit and generating an alternating magnetic field.
Core: High permeability materials (such as silicon steel sheets) are used to concentrate magnetic field lines and improve electromagnetic induction efficiency. The change in magnetic flux directly affects the induced electromotive force on the secondary side.
Secondary winding: With a large number of turns, it outputs a secondary current proportional to the primary current through induced electromotive force for subsequent equipment use.
Insulation and encapsulation
As mentioned in the document, the KOFA series uses epoxy resin casting encapsulation for the primary winding, iron core, and secondary winding, which not only ensures electrical insulation but also fixes the structure to prevent iron core vibration from affecting electromagnetic induction stability.
3、 Job characteristics and application points
The relationship between accuracy and load
The load connected to the secondary side (such as instrument internal resistance, wire resistance, etc.) will affect the accuracy of the current transformer. The document mentions that the rated load range is 2.5-30VA, and excessive load may lead to increased errors. Therefore, it is necessary to select the appropriate rated load based on the parameters of the secondary equipment (such as accuracy levels of 0.2 and 0.5 corresponding to different load requirements).
For example, level 5P10 indicates that under rated load, when the primary current is 10 times the rated value, the composite error does not exceed 5%.
The impact of short-circuit current
When a short circuit occurs on the primary side, a high current will generate a strong magnetic field, which may cause the iron core to saturate and distort the secondary current. The document emphasizes the short-circuit strength parameters (such as short-time current I th, impulse current I dyn), and the design should ensure that the transformer can withstand the thermal and electrodynamic effects of short-circuit current to avoid damage or error exceeding the limit.
The danger of open circuit on the secondary side
The secondary winding must not be open circuited, otherwise when there is current on the primary side, the magnetic flux of the iron core will increase dramatically, and high voltage (up to thousands of volts) will be induced on the secondary side, endangering equipment and personnel safety, and possibly damaging the insulation of the transformer.
4、 Combining with KOFA series in the document
The Implementation of Principles in Structural Design
The KOFA series uses epoxy resin to encapsulate and fix windings and iron cores, reducing external interference and ensuring the stability of electromagnetic induction; The primary terminal is connected with M12 screws, which is easy to install and ensures good electrical contact, avoiding contact resistance affecting the conduction of primary current.
5、Parameter matching and application scenarios
The rated frequency of 50/60Hz is suitable for different power grid requirements, and the secondary current of 5A (1.2A) meets the standard measurement circuit requirements.
For high-altitude areas, by selecting models with higher voltage levels (such as 24kV instead of 12kV), increasing the creepage distance and air gap, preventing insulation breakdown, and ensuring the reliable application of electromagnetic induction principles in special environments.

- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


