

K-WANG


ABB AO2000-LS25 Laser Analysts User Manual
ABB AO2000-LS25 Laser Analysts User Manual
Product Overview
Core positioning: ABB AO2000-LS25 is a modular laser gas analyzer that operates in conjunction with the AO2000 integrated analysis system. It is based on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) technology to measure gas concentration and only detects free molecules in the gas, insensitive to bound molecules.
Composition structure:
Unit Name Core Component Function Function
The transmitter unit temperature stable diode laser, collimating optical lens group, and main electronic equipment emit laser to complete laser wavelength scanning and basic light intensity measurement
The receiver unit focuses on the lens, photodetector, and electronic device at the receiving end to receive the laser absorbed by the gas, converts the optical signal into an electrical signal, and transmits it to the transmitter unit
The voltage conversion module of the power supply unit (100-240V AC to 24V DC) provides stable power supply for the transmitter and receiver, and supports direct connection to 24V DC
Protection and explosion prevention:
Conventional protection: The protection level of the transmitter and receiver units is IP66, and the standard optical window withstand voltage reaches 5 bar (absolute pressure).
Explosion proof version:
Class I Division 2 version: CSA certified, suitable for Groups A, B, C, D environments, temperature code T4, operating temperature -20~+55 ℃.
ATEX Zone 2 version: ATEX certified, certification number Presafe 16 ATEX 8621X, II 3 G Ex nA nC IIC T5 (special application T4), operating temperature -20~+55 ℃.
Key technical parameters
Description of specific indicators for parameter categories
The measurement objects CO, CO ₂, H ₂ O, NO, NO ₂, SO ₂, O ₂, CH ₄, etc. support multi-component selection and can measure up to 2 components simultaneously
Measurement accuracy ± 1% full scale based on TDLAS technology and harmonic analysis to achieve high-precision measurement
Response speed<1 second can quickly track dynamic changes in gas concentration
Operating environment temperature: -20~+50 ℃; Pressure: 1-10 bar ABS suitable for complex industrial working conditions
Laser classification O ₂ measurement is Class 1M, others are Class 1 in accordance with IEC 60825-1 standard, laser is near-infrared light (700-2400nm)
Power supply specification input: 110V-380V AC; Output: 24V DC power supply unit outputs 24V DC, transmitter unit inputs 18-36V DC
Physical characteristics: Weight of 3.6kg, warranty period of 1 year. Lightweight design with clear after-sales support
Installation and commissioning process
preliminary preparation
Tool requirements: 2 M16 open-end wrenches, 1 5mm hex wrench, 1 2.5mm flathead screwdriver, 1 PC (386 and above).
Measurement point requirements: At least 5 times the diameter of the straight pipe section is required before the measurement point, and at least 2 times the diameter of the straight pipe section is required after the measurement point; The transmitter and receiver units need to reserve operating space, and at least 1 meter of space should be reserved outside the flange of the receiver unit.
Flanges and Openings: Two pairs of perforations with a diameter of at least 50mm need to be opened on the pipeline/chimney, using DN50/PN10 standard flanges (inner diameter 50mm, outer diameter 165mm), with a flange angle tolerance of ± 1.5 °, and alignment tolerances that meet the requirements of DN50 flange δ min ≥ 40mm and DN80 flange δ min ≥ 55mm.
Cable requirements:
Special requirements for maximum length of cable type
The receiver cable is 150m long and cannot be replaced or modified at will (within ± 20m)
Ensure that all three sets of power cables are connected for a 100m power cable to ensure even current flow
Ethernet cable 100m outdoor use requires acid and UV resistance, supporting 10/100Base-T protocol
Service PC cable 10m standard length 3m, can be extended to about 10m
Installation steps
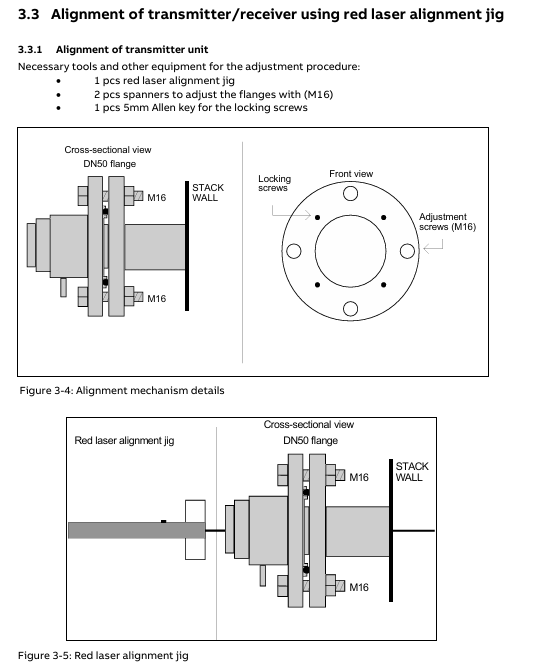
Install the alignment and blowing unit (DN50 flange) of the transmitter/receiver onto the process flange with 4 M16 × 60 bolts to ensure even compression of the O-ring.
Connect the blowing gas (instrument air or nitrogen), with a flange blowing flow rate of approximately 20-50 l/min, and a transmitter/receiver unit blowing flow rate of<0.5 l/min.
Install the window adapter ring (aligning with the positioning pin) and connect the transmitter/receiver unit to the adapter ring, paying attention to installing the O-ring (the transmitter side O-ring needs to be lubricated, while the adapter ring side O-ring is not lubricated).
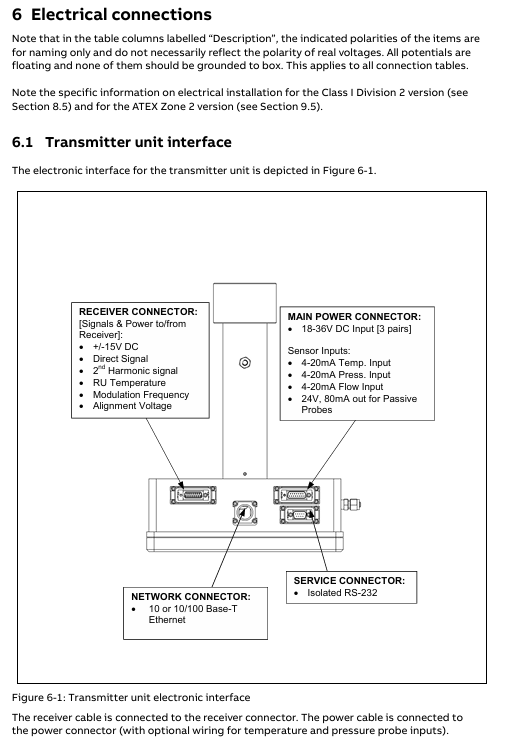
Connect the cables of each unit: the receiver cable connects the transmitter and receiver, and the power cable connects the power unit and transmitter. If an external 4-20mA temperature and pressure sensor is required, it can be connected to the corresponding terminal of the power unit or transmitter.
Debugging and alignment
Startup process: After connecting the power, the instrument enters the startup mode (about 5 minutes), and the LCD displays the firmware version, self-test status, and laser temperature stability progress. If the "Laser line up error" is displayed after startup, alignment is required.
Alignment operation:
Remove the adapter ring of the transmitter/receiver and install the red laser calibration fixture.
Adjust the M16 adjustment screw on the transmitter side flange, align the laser beam with the center of the receiver side opening, and lock the locking screw.
Move the calibration fixture to the receiver side and repeat step 2 to align with the center of the opening on the transmitter side.
Connect the alignment interface of the transmitter/receiver with a voltmeter (voltage range 0V~-3V), fine tune the flange to maximize the voltage, and ensure that the transmission rate is between 90% -100% (low dust condition).
Software operation and parameter configuration
Software composition
Built in program: integrated into the CPU board, responsible for laser temperature control, signal acquisition, concentration calculation, and self checking, without the need for user operation.
Service program: Running on Windows system, connected to instruments via RS-232 or Ethernet, used for installation, configuration, calibration, troubleshooting, supporting user mode (simplified interface) and advanced mode (full functionality, password required).
Core function operation
Parameter configuration (via the "Measurement configuration" menu):
Temperature and pressure settings: Fixed value, 4-20mA input, internal sensor or spectral measurement (temperature only) can be selected, pressure unit is bar abs (gauge pressure needs to be converted: P (abs)=1.013+P (gauge)), temperature unit is ℃ (Fahrenheit conversion: T (℃)=(T (℉) -32)/1.8).
Optical Path: Set the "Optical Path Length (Gas)" (usually the diameter of the pipeline) and "Optical Path Length (Flange)" (only required when there is a target gas inside the flange). The factory preset "Optical Path Length (inside the transmitter/receiver)" cannot be modified arbitrarily.
Concentration averaging: Set the average number of times (N), and the average time Tavg=N × Tprim (Tprim is the single measurement time, 1-4 seconds, depending on the gas type).
Calibration operation (via the "Calibrate instrument" menu):
Calibration mode applicable scenario operation requirements
PROPORTIONAL's daily calibration and process gas calibration do not require temperature and pressure control, only adjusting calibration constants. It can calibrate a single gas separately and supports automatic calibration of associated gases
GLOBAL laser parameter drift, stable temperature and pressure environment (recommended 1.013bar, 23 ℃) after replacing core components, using standard gas and test cell, password authorization required
Recommended calibration gas concentrations: HF (50-500ppm, PTFE pool), HCl (15-200ppm), CO (0.5-5% vol or 50-500ppm), NO (500-5000ppm), etc.
Data log and fault viewing:
Log function: Set the sampling interval (minimum 2 seconds) through the "Log reads" menu, record parameters such as concentration, transmission rate, temperature and pressure, and support automatic generation of new files by date.
Fault viewing: The "View error log" menu displays fault/warning information (including activation/deactivation time), and can save fault logs and system logs for diagnosis. Common faults include "Low transmission" (cleaning window) and "Laser line up error" (realigning).

Maintenance and troubleshooting
routine maintenance
Regular inspection: Check the transmission rate daily, test the response with standard gas every 3 months (for at least 10 minutes), and calibrate every 3-12 months.
Window cleaning: When the transmission rate is too low, use non abrasive cleaning agents/solvents to clean the optical window. If the window has cracks, it needs to be replaced (pay attention to maintaining the original angle).
Blowing optimization: The flange blowing flow rate can be adjusted according to "blowing flow rate=1/10 process gas flow rate", and the blowing effect can be verified by observing the concentration change after turning off the blowing for 30-60 seconds.
Common faults and solutions
Analysis of the causes of fault information and solutions
Low transmission (warning) Optical window contamination, transmitter/receiver alignment deviation. Clean the optical window and re align the laser
Laser line up error: The laser beam did not reach the detector and the optical path was obstructed. Check for any obstacles in the optical path, clean the window, and realign it
PLC T-read error: Temperature sensor current exceeds the range (<0.3mA or>23.7mA). Check the sensor wiring or switch to a fixed temperature setting
Low laser temp. (Error) Laser temperature adjustment malfunction, laser supercooling check transmitter heat dissipation. If it is not overheated, it may be a hardware failure. Contact after-sales service
EEPROM error: Internal memory failure. Upload backup settings file. If it occurs repeatedly, contact after-sales service
Key issue
Question 1: What are the core differences between the two calibration modes (PROPORTIONAL and GLOBAL) of ABB AO2000-LS25 laser analyzer, and which scenarios are they applicable to?
Answer: The core differences between the two calibration modes are reflected in the calibration objects, operational requirements, and applicable scenarios:
Calibration object: The PROPORTIONAL mode only adjusts the "calibration constant" and optimizes it based on the proportional relationship between the measured concentration and the standard concentration; Adjust the "calibration constant" and "linewidth parameter" simultaneously in GLOBAL mode, taking into account the reference measurement of absorbed linewidth.
Operation requirements: PROPORTIONAL mode does not require temperature and pressure environment control, does not require a password, and can be directly performed on the process site. It supports individual calibration of a single gas or automatic calibration of associated gases; GLOBAL mode requires stable temperature and pressure conditions (recommended 1.013bar, 23 ℃), uses standard gases and test cells, and requires advanced mode passwords (applied to ABB or distributors), making it more difficult to operate.
Applicable scenarios: PROPORTIONAL mode is suitable for daily calibration and adjustment when the deviation of process gas concentration is small (such as deviation<2-3%); GLOBAL mode is suitable for scenarios where laser spectral characteristics drift (such as after long-term use), core components such as laser modules/motherboards are replaced, or calibration effectiveness needs to be ensured over a wide temperature and pressure range.
Question 2: What are the key requirements for flange installation and purging system settings when installing ABB AO2000-LS25 laser analyzer, and what problems may arise if they are not met?
answer:
Key requirements for flange installation:
Flange specifications: DN50/PN10 standard flanges (inner diameter 50mm, outer diameter 165mm) are required. The diameter of the pipe/chimney opening should be at least 50mm, and the flange should be installed with perforations (in the diameter direction).
Tolerance requirements: The perpendicularity tolerance between the flange and the pipeline is ± 1.5 °, and the alignment tolerance must meet the requirements of DN50 flange δ min ≥ 40mm and DN80 flange δ min ≥ 55mm (where δ is the distance between parallel lines at the center of the flange).
Sealing requirements: During installation, it is necessary to ensure that the large O-ring between the flange and the alignment unit is evenly compressed, and the four M16 bolts need to be tightened evenly.
Consequences of failure to meet: Deviation in verticality or alignment can cause the laser to fail to align, resulting in a "Laser line up error"; Poor sealing of O-rings can lead to process gas leakage, contamination of optical windows, or pose safety risks.
Key requirements for setting up the blowing system:
Flange blowing: Use dry and clean instrument air (compliant with ISO 8573.1 Class 2-3, oil mist content ≤ 0.5mg/m ³) or nitrogen, with a flow rate of approximately 20-50 l/min and a recommended flow rate of 1/10 of the process gas flow rate.
Purging of transmitter/receiver unit: It should only be turned on under specific working conditions (such as high dust and corrosive environments), using nitrogen gas (to avoid damaging internal optical components with oil/water in the instrument air), with a flow rate of<0.5 l/min, to prevent excessive pressure inside the unit.
Failure to meet the consequences: Insufficient flange blowing flow will cause dust to deposit in the optical window, resulting in a decrease in transmission rate (warning of "Low transmission" appears); Excessive air or flow during unit blowing can damage internal optical components, affect measurement accuracy, and even lead to instrument failure.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


