

K-WANG


HIMA CPU 01 Controller Module
Storage and Execution: Stores the operating system (OS) and user programs, performs core functions such as logical operations, I/O signal processing, and security self checks.
Communication management: Implement secure/non secure communication with programming and debugging tools (PADT), remote I/O, and external systems through Ethernet and fieldbus interfaces.
Status monitoring: Real time monitoring of power supply voltage, operating temperature, hardware faults, and automatic triggering of safety response in case of abnormalities (such as entering STOP state).
HIMA CPU 01 Controller Module
Product Core Positioning and Certification
1. Core functions
CPU 01 is the central processing unit of the HIMatrix F60 modular controller, responsible for three core responsibilities:
Storage and Execution: Stores the operating system (OS) and user programs, performs core functions such as logical operations, I/O signal processing, and security self checks.
Communication management: Implement secure/non secure communication with programming and debugging tools (PADT), remote I/O, and external systems through Ethernet and fieldbus interfaces.
Status monitoring: Real time monitoring of power supply voltage, operating temperature, hardware faults, and automatic triggering of safety response in case of abnormalities (such as entering STOP state).
2. Safety and compliance certification
The module is certified by multiple international standards to ensure safety and integrity:
Certification Body/Standard Certification Level/Scope Applicable Scenarios
T Ü V (IEC 61508/61511/62061) SIL 3 industrial safety controls (such as process industry, mechanical safety)
T Ü V (EN ISO 13849-1) Cat. 4, PL e Mechanical Safety Systems
T Ü V CENELEC (EN 50126/50128/50129) SIL 4 for railway and high safety industrial scenarios
CE EMC, ATEX Zone 2 EU market compliance, use of explosion hazard zone Zone 2
FM Approval Class I, DIV 2 Explosion proof Scenarios for the North American Market
PNO PROFIBUS DP Slave fieldbus compatibility certification
3. Product variants and compatibility
The module is divided into two variants, adapted to different programming tools and cannot be used interchangeably:
CPU 01: Compatible with ELOP II Factory programming tool, requiring CPU OS ≤ V6. x and COM OS ≤ V11. x.
CPU 01 SILworX: Compatible with SILworX programming tool, requiring CPU OS ≥ V7 and COM OS ≥ V12. x.
Key limitation: Projects created by ELOP II Factory cannot be edited using SILworX, and vice versa.
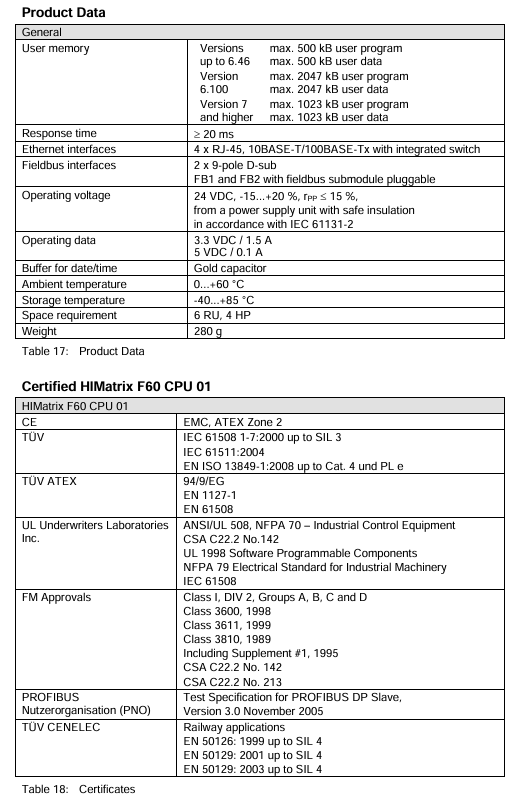
Key technical parameters
1. Hardware configuration
Category detailed parameters
Processor system dual processor architecture (uP1/uP2) with synchronization (SYNC) and watchdog functionality
Communication interface Ethernet: 4 RJ-45 ports (10BASE-T/100BASE-Tx, supporting automatic negotiation and automatic crossover);
Fieldbus: 2 9-pin D-sub interfaces (FB1/FB2, RS485, optional submodule activation required)
Storage configuration CPU OS ≤ V6. x: maximum 500kB user program, 500kB user data;
CPU OS ≥ V7: maximum 2047 KB user program, 2047 KB user data;
Date/Time Cache: Powered by Gold Capacitor
Indicator light system LED (RUN/ERR), program LED (STOP/PROG/FAULT/ORCE/OSL/BL), communication LED (Ethernet/fieldbus)
Mechanical characteristic dimensions: 6 RU (rack unit), 4 HP; weight: 280g; protection level: IP20
2. Power and environmental requirements
Power supply parameters: rated voltage 24VDC, allowable fluctuation range -15%~+20% (18~28.8VDC), ripple peak ≤ 15%; Working current: 3.3VDC/1.5A, 5VDC/0.1A.
Environmental restrictions: working temperature of 0-60 ℃, storage temperature of -40~85 ℃, pollution level II (IEC/EN 61131-2), altitude ≤ 2000m, no condensation.
Voltage monitoring: Built in voltage monitoring function, triggering an alarm (written to system variables) when<18VDC, and automatically shutting down when<13VDC.
3. Communication Protocol and Ports
(1) Support agreement
Safety related: Safe Ethernet.
Standard protocols: Modbus TCP, OPC, SNTP (time synchronization) TCP S/R; Ethernet/IP only supports CPU OS ≤ V6. x.
(2) Default network port
Port Type Port Number Purpose
UDP 8000 Programming Tool (PADT) Connection
UDP 8001 ELOP II Factory Remote I/O Configuration
UDP 8004 SILworX Remote I/O Configuration
UDP 6010 Secure Ethernet OPC
UDP 123 SNTP time synchronization
UDP/TCP 502 Modbus (user modifiable)
TCP 44818 EtherNet/IP Explicit Messaging Service
TCP 2222 EtherNet/IP data exchange

Safety operation standards
1. Electrostatic protection (ESD)
Operators must master ESD protection knowledge, wear anti-static wristbands during work, and ensure that the work area is free of static electricity interference.
When the module is idle or transported, it should be stored in the original factory anti-static packaging and direct contact with the circuit board is prohibited.
2. Installation and operation safety
Installation restrictions: Zone 2 scenarios must be placed in an enclosure with a protection level of IP54 or higher, and the enclosure must be labeled with "Only power-off operation allowed (except when explosion risk is excluded)".
Cable requirements: Signal lines and power lines should be wired separately to avoid interference; Zone 2 installation must comply with DIN EN 60079-15/14 standards (terminals, wiring, creepage distance, etc.).
Prohibited behavior: live plugging and unplugging modules or cables; Operate the reset button during module operation; Replace core components with non original parts.
3. Emergency and residual risks
Emergency response: When the module fails, it automatically enters a safe state (input processing stops, output power is cut off), and any operation that prevents the safe operation of the system is prohibited.
Residual risks: may arise from engineering design defects, user program errors, wiring faults, and need to be avoided through compliant design and regular testing.
Installation and configuration process
1. Installation steps
(1) Basic installation (inside the rack)
In the power-off state, insert the module along the upper and lower rails of the rack, align it with the backplane slot, and press the front end board until the buckle "clicks" to lock.
Secure the module with screws on both sides of the front panel to ensure a secure installation.
Connection cables: Ethernet cable (RJ-45), fieldbus cable (D-sub, requiring sub module connection), power cord (powered by power module, no direct wiring required).
(2) Zone 2 Special Installation
Additional requirements: The enclosure protection level should be ≥ IP54 to ensure heat dissipation (the basic power consumption of the module is 6.5W, and it can reach 12W when equipped with a communication submodule).
Power requirements: PELV/SILV grade safety isolation power supply must be used, in compliance with IEC 61131-2 standard.
Label pasting: The shell needs to be pasted with ATEX compliant labels, and the module comes with an "Ex113GExnA II T4X" label.
2. Configuration process
(1) Tool selection and preliminary preparation
Confirm module OS version: Select the corresponding programming tool (ELOP II Factory/SILworX) based on the model label or front-end LED.
Reference documents: HIMatrix system manual (HI 800 191 E), safety manual (HI 800 023 E), and programming tool help documentation are required.
(2) Core configuration steps
Hardware Mapping: Create a project in the programming tool and configure the CPU module (Slot 2) and I/O module (Slot 3~8) according to the rack slot. There is a slight difference in slot numbers between SILworX and ELOP II Factory (refer to the table below). |Rack slot | SILworX slot number | ELOP II Factory slot number | Module type | | --- | --- | --- | --- | | | | | | 1 | - | PS 01 power module (no configuration required) | | 2 | 0 (CPU)/1 (COM) | - | CPU/communication module (integrated) | | | 3 | 2 | 1 | I/O module | | 4 | 3 | 2 | I/O module | | | 5~8 | 4~7 | 3~6 | I/O module|
Network configuration: Set the IP address (default 192.168.0.99) and subnet mask to ensure consistency with the PADT (programming computer) network segment; If modifications are required, they can be restored to default values through programming tools or reset functions.
Programming and downloading: Write user programs using IEC 61131-3 standard languages such as Function Block Diagram (FBD), compile them, and download them to the module Flash EPROM.
Security configuration: Set the watchdog time (WDT) and security cycle time according to the security manual, and configure security communication parameters (if applicable).
3. Reset operation (restore default settings)
Applicable scenario: Forgetting administrator account password or IP address conflicts with PADT.
Operation steps:
Disconnect the module power supply and unplug all fieldbus connectors (to avoid interfering with other devices).
Insert a needle shaped insulating material into the reset hole of the front end board, press and hold for ≥ 20 seconds, and at the same time, turn on the power to restart the module.
Reset effect: The IP address is restored to 192.168.0.99, the system ID (SRS) is restored to 6000.0.0, and only the default administrator account (empty password) is activated.
Note: In COM OS versions ≥ 10.42, after resetting, it is necessary to reconfigure the connection parameters and account before downloading the program/OS.
Operation and Diagnosis
1. Running status indication (LED interpretation)
The LED status of the module varies slightly with the CPU OS version, and its core meaning is as follows:
(1) System LED
Meaning of LED color status (CPU OS ≥ V8)
RUN green constantly on and running normally (STOP/RUN status)
RUN green Blinking1 (600ms on/off) is loading a new operating system
RUN green off, non RUN state
ERR red constant light lacks additional function authorization and testing mode
ERR red Blinking1 fault shutdown (hardware/voltage/configuration failure), requiring PADT restart
ERR red goes out without any malfunction
(2) Program LED
STOP (red): Always on=STOP/valid configuration; Blinking=STOP/Invalid configuration.
PROG (yellow): Always on=loading configuration/OS, modifying WDT/safe time/SRS.
Fault (yellow): Blinking=OS damage, invalid configuration, I/O failure.
FORCE (yellow): constantly on=forced function preparation; Flashing=forced function activation.
(3) Communication LED
Ethernet (next to RJ-45): Green=Full Duplex; Yellow=connection is valid; Flashing=data transmission/conflict.
Fieldbus (FB1/FB2): yellow=interface activated; Synchronized flashing=emergency loader activated.
2. Basic operating procedures
(1) Start the process
Confirm that the module is securely installed, the cable connections are correct, and there is no risk of static electricity.
Connect the power module to supply power, and the module will automatically perform LED self-test (all LEDs will briefly light up).
Start the programming tool and establish a communication connection with the module (via IP address).
Download user programs and configuration files to verify the validity of the configuration.
Switch the module to RUN state and confirm normal operation through LED and programming tools.
(2) Shutdown process
Normal shutdown: Use programming tools to switch the module to STOP state, and disconnect the power after the program stops.
Emergency stop: When the module fails, it automatically enters the ERROR STOP state, and after troubleshooting, it restarts through PADT.
3. Diagnostic methods
First level diagnosis: Determine the fault type based on the status of the front-end LED (such as ERR flashing=system fault, FAULT flashing=I/O fault).
Secondary diagnosis: By using programming tools to read diagnostic logs and system variables (such as power status and temperature status), locate specific fault points.
Common diagnostic items: communication failure (port/protocol configuration), invalid configuration (slot mapping error), hardware failure (voltage/module damage).
Maintenance and troubleshooting
1. Daily maintenance
Regular maintenance: Conduct a Proof Test every 10 years, refer to the HIMatrix Safety Manual (HI 800 023 E).
System update: Use downtime to upgrade the operating system through programming tools (first place the module in STOP state), and confirm the compatibility of the new version before upgrading.
Cleaning requirements: Wipe the outer shell with a dry soft cloth, and do not clean with water or chemical solvents; Regularly check that the cooling vents are unobstructed.
2. Fault handling
(1) Common faults and solutions
Possible causes and solutions for the fault phenomenon
The module cannot be started, ERR is constantly on and the voltage is too low. Check the power supply voltage (≥ 18VDC) for hardware faults and replace the module
Communication failure, Ethernet LED off, IP address conflict, cable damage investigation, IP conflict (communication LED synchronously flashing=conflict), replace network cable
Program cannot be downloaded, invalid PROG flashing configuration, incompatible OS version, verification slot mapping and configuration parameters, upgrading/downgrading OS
I/O unresponsive, FAULT flashing. I/O module fault, wiring error. Check the I/O module connection, rewire and test
There is no communication on the fieldbus, and the FB LED is off. The fieldbus submodule has not been installed, and a compatible fieldbus submodule has been installed
(2) Module replacement process
Disconnect the power supply module and unplug all connecting cables (Ethernet, fieldbus).
Loosen the module fixing screws and remove the module from the rack rail through the bottom handle.
Fix the new module according to the installation steps, connect the cables, and ensure that the wiring is consistent with the original module.
Connect the power, download the original configuration and program, and verify that it runs normally.
Attention: Only modules of the same model or HIMA authorized substitute models can be replaced, and mixing different variants (CPU 01/CPU 01 SILworX) is prohibited.

- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


