

K-WANG


Thermal Solutions EVS series gas regulated boilers
Key information: Released in September 2024, replacing the old version, including bilingual warning content in English/French, to be posted and kept clear and readable. Boiler model and serial number (see rated label) must be provided during maintenance.
Thermal Solutions EVS series gas regulated boilers
Product basic information
1. Core identification and certification
Product positioning: Gas driven modular regulating boiler (GAS-FIRED MODULATION BOILER), used for hot water systems, certified by AHRI, in compliance with the National Gas Code (NFPA 54/ANSI Z223.1) in the United States, the Gas Installation Code (CAN/CSA B149) in Canada, and local regulations such as Massachusetts 248 CMR 4.00/5.00.
Key information: Released in September 2024, replacing the old version, including bilingual warning content in English/French, to be posted and kept clear and readable. Boiler model and serial number (see rated label) must be provided during maintenance.
2. Model and core parameters
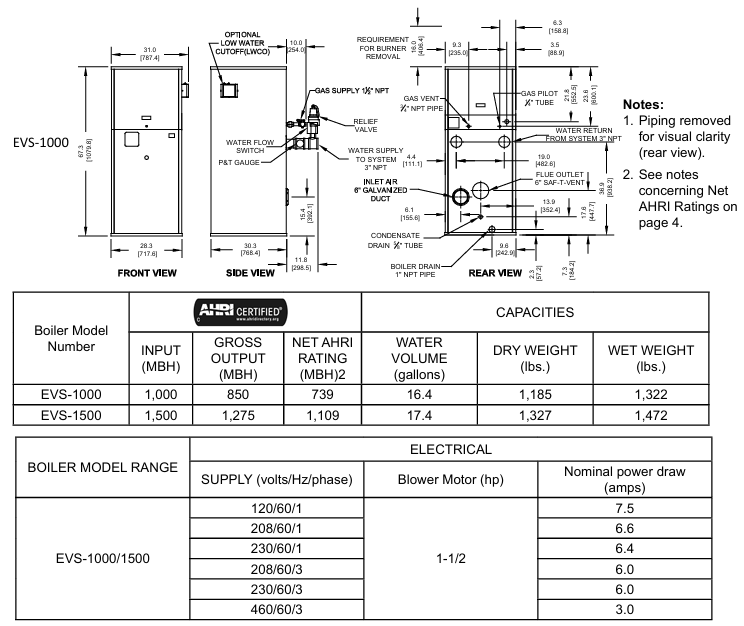
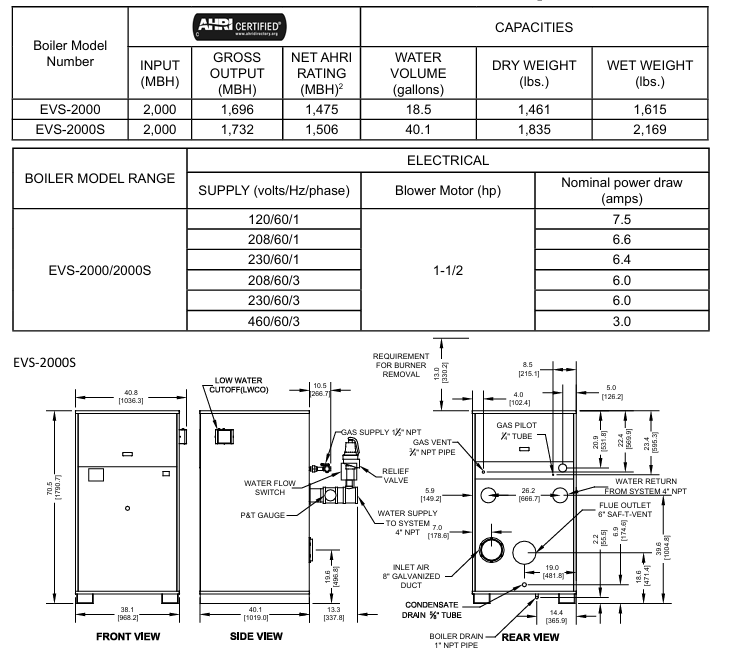
Covering 8 models (EVS-500 to EVS-3000), the core parameter differences are as follows (taking typical models as an example):
Model Input Power (MBH) Total Output (MBH) Net AHRI Rated (MBH) Water Capacity (gallon) Dry Weight (pound) Wet Weight (pound) Power Supply/Fan Power
EVS-500 500 431 375 6.1 722 823 120V/189 horsepower
EVS-1000 1000 850 739 16.4 1185 1322 120V/1.5 horsepower
EVS-2000S 2000 1732 1506 40.1 1835 2169 120V/1.5 horsepower
EVS-3000 3000 2610 2270 43.1 2193 2552 208V/2 horsepower
General restrictions: Maximum working pressure of 160 PSI, medium temperature -40~+90 ° C, ambient temperature -40~+85 ° C, condensate pH value 3-5 (requires neutralization treatment).
Installation specifications (key requirements)
1. Pre requirements
Installation qualification: It is required to be operated by a certified Plumber/Gas Fitter (mandatory in Massachusetts). Before installation, local regulations must be confirmed to ensure a safe distance from combustible materials (6 inches left/right/back, 24 inches front, 18 inches for flue connections, and 24-36 inches for maintenance spacing depending on the model).
Space and ventilation: Determine whether a "non confined space" (≥ 50 ft ³/1000 Btu/h) or a "confined space" based on the space volume and total gas input. A confined space requires two permanent ventilation openings (within 12 inches at the top and 12 inches at the bottom, with a minimum diameter of 3 inches); Sealed combustion engine models can be exempted from indoor ventilation, but the intake pipe needs to be installed according to regulations.
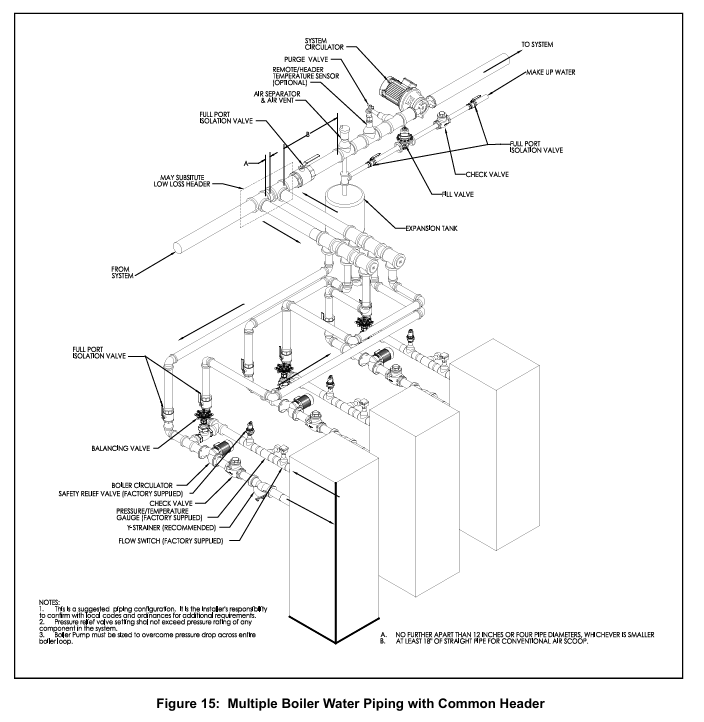
2. Core system installation
(1) Ventilation system
Type: Supports positive pressure ventilation (side wall/vertical, maximum equivalent length of 50 feet, non confluent) and negative pressure ventilation (traditional chimney, requiring a vertical height of 15 feet or more and double acting air pressure dampers), ventilation ducts require AL29-4C ® Wait for condensation resistant materials, tilt the horizontal section at least 1 inch every 4 feet, and keep the terminal away from doors and windows (below 4 feet/horizontal 4 feet/above 1 foot) and gas meters (4 feet).
Special requirements: Massachusetts sidewall ventilation requires the installation of carbon monoxide detectors with backup batteries (1 per floor) and 8-foot high signage ("GAS VENT DirectLY BELOW. KEEP CLEAR").
(2) Water system
Water quality requirements: hardness ≤ 8.5 grains (150 ppm), pH 8.8-9.2, requiring professional water treatment (anti oxidation, scaling), ethylene glycol usage not exceeding 50%, and rust inhibitor needs to be added; The new pipe needs to be cleaned with trisodium phosphate (TSP), and the old system needs to be equipped with a filter at the return water end.
Pipeline specifications: The supply/return water diameter should be 2-4 inches (depending on the model), and the flow rate should comply with Table 2 (such as EVS-500 minimum 22 gpm, maximum 43 gpm). The return water temperature should not be lower than 130 ° F (anti condensation), and the temperature difference should not exceed 40 ° F (anti heat exchanger damage); Safety valves (not shut-off valves), exhaust devices, and expansion tanks need to be installed.
(3) Gas system
Pressure requirements: The minimum inlet pressure for natural gas is 4-9 inches of water column (depending on the model), for propane it is 8 inches of water column, and for maximum pressure it is 14 inches of water column. For overpressure, an additional pressure regulator must be installed (no multiple boilers can share one); Gas pipes need to undergo leak testing (using soapy water, no open flames), and install sediment traps and manual shut-off valves.
Pipe diameter selection: Refer to Table 4 (such as the equivalent length of 10 feet for a 1-inch SCH40 pipe with a capacity of 514 ft ³/h), and consider the equivalent length of the pipe fittings (Table 6, such as the equivalent length of 1.55-20.2 feet for a 90 ° elbow).
(4) Electrical system
Power supply: requires independent circuit and fuse switch, voltage 120/208/230/460V (depending on model), grounding in accordance with NFPA 70; Do not connect the boiler and circulating pump to the same fuse switch. Isolation relays are required for low voltage control (24V), and short circuiting of safety controls is prohibited.
Operation and debugging process
1. Check before startup
Confirm that the installation of ventilation, water, gas, and electrical systems is compliant, turn off all power sources and gas valves, empty the air in the gas pipeline (wait for 5 minutes), check for no gas leaks, and then open the gas valve.
2. System startup steps
Water injection and exhaust: Close the boiler water supply valve, exhaust in zones (drain to no bubbles for 30 seconds in each zone), fill the system to working pressure, and check for water leakage.
Power on and debugging: Turn on the power, confirm the direction and flow switch function of the circulation pump, and set TSBC ™ Controller (see Chapter 9), check the fan direction (test during pre blowing).
Flame debugging: Verify the ignition flame (blue stable, signal 1.5-5.0 VDC) and the main flame (uniform orange), adjust the air-fuel ratio (high flame O ₂ 4-6%, low flame O ₂ 5.5-7%) to ensure CO ≤ 400 ppm.
3. Conventional operations
Ignition command: via TSBC ™ Activate the controller or external thermostat, manual ignition is prohibited; When you smell gas, turn off all electrical appliances, stay away from the building, and contact the gas supplier/fire department.
Operation monitoring: Real time monitoring of outlet temperature, modulation rate, flame signal to ensure that safety controls such as safety valves, high limit temperature controllers (manually reset), and low water level cut-off devices are functioning properly.
Maintenance and troubleshooting
1. Maintenance cycle and content
Operational requirements for periodic maintenance projects
Daily inspection around the boiler, instrument readings, and flame observation to ensure that there are no flammable materials and no abnormal flames
Weekly igniter, flame signal, gas valve leakage testing, fuel valve closure testing, safety shutdown time
Monthly flue/condensate drainage, gas pressure interlock testing to clean condensate water and ensure pressure is within normal range
Half year instrument calibration, air filter replacement, circulation pump maintenance, filter cleaning with soapy water, pump maintenance according to manufacturer's specifications
Annual heat exchanger inspection, air-fuel ratio re inspection, safety valve testing, disassembly panel inspection for corrosion, and safety valve testing in accordance with ASME specifications
2. Common fault handling
Possible causes and solutions for alarm information
Low Water Level: The low water level cut-off device triggers a manual reset to check the water replenishment system
Low Water Flow circulation pump malfunction or pipeline blockage, confirm pump operation, clean filter
Fuel Limit gas pressure too high/too low reset pressure switch, check regulator/gas pipeline
High Temp Limit: If the water temperature exceeds the safe value, manually reset the high temperature controller and check the load/circulation system
FSG Fault Flame Protection Device Fault Reset Device, Check Igniter/UV Sensor
3. Spare parts and maintenance
Spare parts ordering: obtained through Thermal Solutions distributors (Lancaster warehouse), providing model and serial numbers; Key spare parts such as heat exchanger (EVS-500:103530-01), fan (EVS-750:81156018), and gas valve (V4295A series) require original factory parts.
Maintenance taboos: Do not disassemble the burner (easily damaged). Before electrical maintenance, all power sources must be cut off and locked. Replacement of controls must be consistent with the original factory model.
TSBC ™ Thermal Solutions Boiler Control
1. Core functions
Support boiler modulation control, multi boiler master-slave linkage (up to 8 units, RJ11 networking), outdoor temperature reset (adjust water temperature according to outdoor temperature, energy-saving), domestic hot water priority (DHWP), fault diagnosis (store 10 alarm records).
2. Key settings
Basic parameters: Warm Season Shutdown (WWSD) set point at 70 ° F, master-slave start triggering 90% modulation rate, stop triggering 25%, rotation period of 168 hours (balanced wear); The default PID parameters are local P=20, I=30, and remote P=20, I=30 (adjustable as needed).
Operation modes: manual mode (setting modulation rate from 0-100%), automatic mode (controlled by outlet/remote temperature), automatic switching to standby mode in case of sensor failure (such as remote sensor failure → outlet sensor control).
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


