

K-WANG


Motorola MVME Series IPMC712/761 I/O Module
Motorola MVME Series IPMC712/761 I/O Module
Basic Information
The installation and user manual for the Motorola MVME series IPMC712/761 I/O module introduces two multifunctional I/O modules based on the PMC (PCI Mezzanine Card) specification. The core is positioned as an extension component for MVME5100, MVME5500, and MVME6100 single board computers (SBC), providing industrial grade I/O interfaces such as SCSI, serial, and parallel, suitable for industrial control, embedded computing, and other scenarios, especially supporting backward compatibility with the old MVME761/MVME712M modules.
Module core functions and model differences
(1) Core functional positioning
IPMC712 and IPMC761 are both single width standard PMC modules, with the core function of expanding the host's I/O interface capabilities to meet the connection requirements of multiple types of devices in industrial scenarios. The common functions include:
SCSI interface: Integrated LSI SYM53C895A controller, supports Ultra Wide SCSI (16 bit bus), synchronous transfer rate up to 40MB/s (16 bit mode), 20MB/s (8-bit mode), asynchronous transfer rate 5MB/s, suitable for industrial storage devices such as hard drives and optical drives;
Serial Communication: Equipped with Z85230 ESCC (Enhanced Serial Communication Controller) and PC97307 Super I/O chip, providing multi-channel serial ports, supporting asynchronous/synchronous modes, and adapting to serial devices such as modems and sensors;
Parallel port: Supports IEEE 1284 standard, 8-bit bidirectional communication, compatible with Centronics interface devices (such as industrial printers, data collectors);
PCI-ISA Bridge: The bridge between the PCI bus and ISA bus is achieved through the Winbond W83C554F chip, supporting ISA interrupt and DMA functions to ensure legacy device compatibility;
Data storage: Onboard 256 × 8 serial EEPROM (AT24C02), used to store Vital Product Data (VPD) and record module hardware configuration information.
(2) Core differences between IPMC712 and IPMC761
The two module architectures are consistent, with the main difference being the serial port configuration and physical interface design. The specific differences are as follows:
Comparison dimension IPMC712 IPMC761
Number of serial ports: 3 asynchronous ports+1 configurable (asynchronous/synchronous) port, 2 asynchronous ports+2 configurable (asynchronous/synchronous) ports
Serial clock configuration port 4 can be set with J2/J3/J5 jumper for transmitting and receiving clocks, supporting loop back (J5 jumper). Port 3/4 can only be set with J2/J3 jumper for transmitting and receiving clocks, without loop back function
Ethernet compatibility backboard Ethernet port unavailable (needs to be extended through P2 adapter) Support backboard Ethernet port routing (needs to be coordinated with MVME761 transition module)
Typical application scenarios focus on simple serial communication extensions, such as sensor data acquisition emphasizing multi serial device connections, such as industrial bus gateways and multi node communication
Hardware architecture and key components
(1) Hardware architecture diagram
The module is designed based on the architecture of "PCI bus → bridge chip → functional subsystem", and the core components include:
PCI interface layer: connected to the host PCI bus (32-bit, 33MHz) through P11-P15 connectors, supporting PCI bus arbitration and burst transmission to ensure data transmission efficiency;
Bridge layer: Winbond W83C554F (PIB, PCI-ISA bridge) implements protocol conversion between PCI and ISA bus, supports 8259 interrupt controller and ISA DMA channel;
Functional subsystem:
SCSI subsystem: LSI SYM53C895A controller+40MHz clock, supporting wide bus and high-speed transmission;
Serial subsystem: Z85230 ESCC (2-channel synchronous/asynchronous)+Z8536 CIO (supplementary modem control signal);
Parallel subsystem: PC97307 Super I/O chip, supporting IEEE 1284 mode;
Configuration and Storage: 2 user configurable switches (S1/GPIO configuration, S2/IDSEL selection), AT24C02 EEPROM (VPD storage).
(2) Key electrical parameters
Parameter category specification requirements
Supply voltage+5V (± 5%), ± 12V (± 10%); Typical power consumption:+5V/0.5A,+12V/0.2A, -12V/0.1A; Maximum power consumption:+12V/0.5A, -12V/0.3A
Working temperature 0~70 ℃ (PCB working temperature), storage temperature -40~85 ℃
Isolation and anti-interference support ESD protection (compliant with IEC 61000-4-2), surge protection (IEC 61000-4-5), PCI signal level 5V standard
Connectors P11~P15 (64 pin EIA-E700 connector), supporting PCI interface and I/O signal output
Hardware configuration and installation requirements
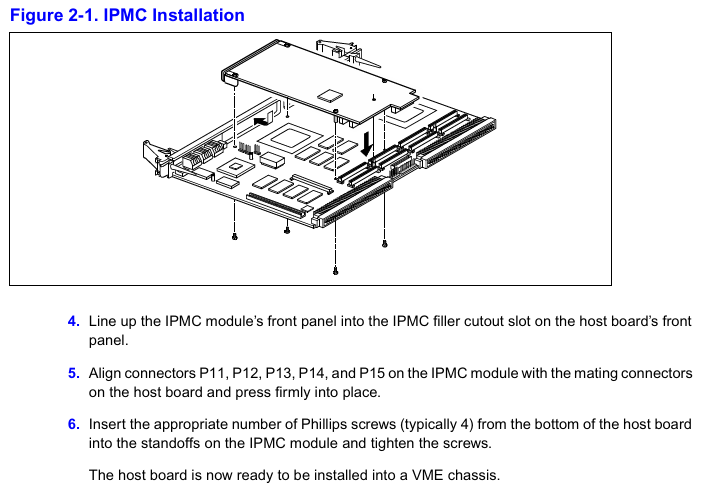
(1) Core configuration items
S1 switch (GPIO configuration): 1 × 4 switch, used to set SCSI speed and bus width:
S1-P1(GPIO2):OFF=Ultra SCSI(20/40MB/s),ON=FAST SCSI(10/20MB/s);
S1-P2 (GPO3): OFF=Wide SCSI (16 bits), ON=Narrow SCSI (8 bits);
S1-P3/P4: Not used (NC).
S2 switch (IDSEL selection): 1 × 2 switch, select the IDSEL signal connection of the PCI device according to the host model:
MVME5100/MVME5500: S2-P1=ON, S2-P2=OFF (connected to AD11);
MVME6100: S2-P1=OFF, S2-P2=ON (connected to AD16/AD21);
Prohibit simultaneous ON/OFF of two switches (to avoid abnormal device enumeration).
Jumper configuration:
IPMC712: J1 (reserved programming interface), J2/J3 (port 4 clock source), J5 (clock loop back);
IPMC761: J1 (reserved), J2/J3 (source of clock for port 3/4 transmission and reception).
(2) Installation specifications
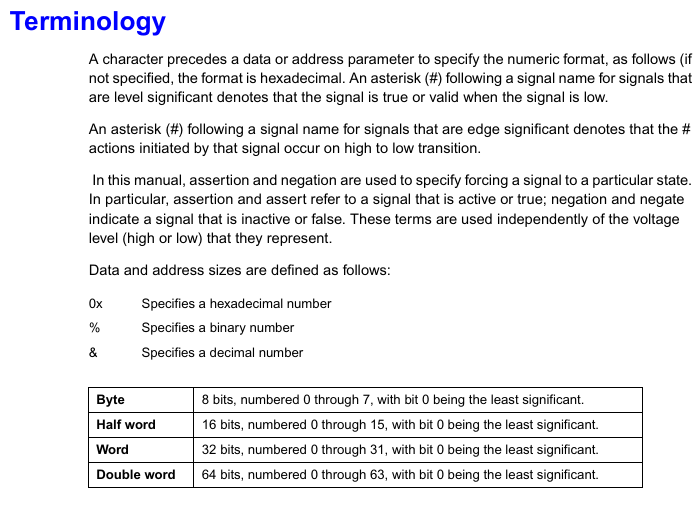
Installation position: Only supports installation in PMC slot 1 of the host. Before installation, the filler plate of the host front board needs to be removed to ensure that the module front board is aligned with the host front board;
Static protection: An anti-static wristband must be worn, and the module should be stored in anti-static packaging to avoid touching the circuit board pins;
Mechanical fixation: Fix the module on the host bracket with 4 M2 screws, ensuring that connectors P11-P15 are fully engaged with the host socket;
EMI compliance: After installation, ensure that all panel openings of the host are covered by modules or filler boards to avoid electromagnetic interference leakage.
Programming and Compatibility
(1) Core points of programming
PCI device configuration:
The onboard PCI device includes a SCSI controller (vendor ID 0x1000, device ID 0x0012) and a PCI-ISA bridge (vendor ID 0x10A, device ID 0x0565), which require setting interrupt and DMA parameters through the PCI configuration space;
IDSEL address mapping: Ensure device enumeration uniqueness based on the host model corresponding to AD11 (MVME5100/5500) and AD16/AD21 (MVME6100).
Interrupt and DMA configuration:
Interrupt routing: SCSI interrupts (IRQ14) and serial/parallel interrupts (IRQ3/4/7/9/10) are bridged to the host MPIC (Multiprocessor Interrupt Controller) through PIB, with different interrupt pin assignments for different hosts (such as IRQ0/9 for MVME5100 and MPP5/16 for MVME6100);
DMA channels: Supports 7 ISA DMA channels, with channels 0/1/5/6 for serial port transmission and reception, channels 2/3 for parallel ports, and channel 4 for internal cascading.
VPD access: Access the onboard EEPROM (address 0xA4) through the I ² C bus to read configuration information such as module model and hardware version. The host needs to access it through the I ² C controllers of Hawk (MVME5100), GT-64260 (MVME5500), and MV64360 (MVME6100).
(2) System compatibility
Adaptation host: Only supports MVME5100, MVME5500, and MVME6100 single board computers, and S2 switch and interrupt mapping need to be configured according to the host model;
Backward compatibility: Supports replacing old MVME761/MVME712M modules and achieving I/O signal compatibility through P2 transition cables, but attention should be paid to some PMC I/O routing restrictions (such as IPMC712 not supporting backplane Ethernet);
Software support: Compatible with Motorola PowerPlus II architecture programming specifications, requiring the use of firmware tools such as MOTLoad and PPCBug for configuration and debugging.
Environmental adaptability and compliance certification
(1) Environmental parameters
Environmental category specification requirements
Temperature operation: 0~70 ℃ (compliant with IEC 60068-2-1/2); Storage: -40~85 ℃ (compliant with MIL-STD-810G)
Humidity 20%~95% (40 ℃ without condensation, in accordance with IEC 60068-2-78)
Vibration and shock operation vibration: 5~60Hz (0.137mm), 60~150Hz (1.0G, in accordance with IEC 60068-2-6); Storage impact: 15G (11ms, compliant with IEC 60068-2-27)
The protection level module body is IP20 (compliant with IEC 60529) and needs to be installed in control cabinets with a protection level of IP54 or higher
(2) Compliance certification
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC): compliant with EN 55022 Class B, EN 61000-6-2/4, resistant to ESD (± 8kV air discharge), surge (± 2kV communication port);
Safety certification: CSA ordinary area certification, Class I Division 2 Groups A-D hazardous area (non flammable);
Environmental Compliance: Compliant with RoHS Directive (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE Directive (Electronic Waste Recycling).
Precautions for use
SCSI signal conflict: When installing other modules in host PMC slot 2, it is important to note that there may be conflicts with the SCSI signal (P15 connector), and the redundant signal should be disconnected through a 0 Ω resistor (R92-R100);
Clock configuration: The serial port clock source needs to be strictly matched through jumper wires (such as distinguishing between "module driver" or "external input" for IPMC712 port 4 clock) to avoid communication abnormalities;
Firmware and documentation: The module needs to be used in conjunction with the host firmware (such as the Hawk ASIC firmware of MVME5100). It is recommended to refer to the host manual to confirm the details of interrupt and DMA configuration.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


