

K-WANG


MOTOROLA MVME162 Embedded Controller
MOTOROLA MVME162 Embedded Controller
The complete user guide for the Motorola MVME162 series embedded controller (model 001-043) is developed from eight dimensions: manual basic information, hardware specifications, hardware configuration installation, operating instructions, functional modules, serial port interconnection, security compliance, and supporting resources. It is the core reference for the design, use, and development of this controller. The following is a detailed summary of the points:
Core hardware specifications
MVME162 is a dual high VME module, divided into 21 models (001-043). The core configuration revolves around a 25MHz 32-bit MC68LC040/MC68040 processor, both of which include 8KB cache and MMU. MC68040 also comes with a floating point coprocessor (FPU). The differences in core capacity among different models are DRAM capacity and whether they have SCSI/Ethernet/VMEBus interfaces. The core hardware specifications are shown in the table below:
table
Hardware Category Core Configuration Key Parameters/Remarks
Processor MC68LC040/MC68040 25MHz, 32-bit, former without FPU, latter with FPU
Main storage DRAM 1/4/8MB optional, with programmable parity check, 1MB for non interleaved architecture, 4/8MB for interleaved architecture
Static storage SRAM 512KB, with battery backup, worst-case backup for 200 days, no parity check
Read only/flash EPROM+Flash 4Mbit EPROM slot (JEDEC 32 pin PLCC); 1MB Flash (1 old board with 28F008SA, 4 new boards with 28F020)
Non volatile storage NVRAM+TOD clock Thompson MK48T08, 8K × 8 NVRAM with battery backup, TOD clock supports seconds/minutes/hours/days/months/years, BCD 24-hour clock
Timer/watchdog MCchip+VMEchip2 MCchip: 4 32-bit programmable timers (1 μ s resolution)+1 watchdog; VMEchip2: 2 32-bit programmable timers+1 watchdog
Power requirement: DC power supply+5V (± 5%): 3.5A typical, 4.5A maximum; +12Vdc (± 5%): 100mA maximum; -12Vdc (± 5%): 100mA maximum
Physical dimensions of dual height VME board: Board size: 233mm × 160mm × 17mm; with connector/panel: 262mm × 188mm × 20.32mm
Working environment temperature/humidity Working temperature: 0-70 ℃ (forced air cooling outlet temperature); Storage temperature: -40-85 ℃; Relative humidity: 5% -90% (non condensing)
Hardware configuration and installation
This chapter provides a detailed explanation of the unpacking, jumper configuration, and module installation steps for MVME162. The core operations must be carried out in a power-off state to avoid static electricity damage to the circuit. The core content includes:
Requirements for unpacking: If the packaging box is damaged, the carrier's agent must be present to unpack and inspect it, retain the packaging materials for storage/transportation, and avoid touching the integrated circuit area;
Jumper configuration: The board contains multiple configurable jumper caps, which are factory default configurations and can be modified according to needs. The core jumper functions are shown in the following table:
|Jumper number | Function | Factory configuration | Optional configuration|
|J1 | System Controller Selection | 1-2 Short Circuit (for VMEbus System Controller) | Remove Jumper (for Non System Controller)|
|J11 | Serial port 1/console clock | No jumper (asynchronous communication) | 1-2, 3-4 short circuit (synchronous external clock)|
|J12 | Serial port 2 clock | No jumper (asynchronous communication) | 1-2, 3-4 short circuit (synchronous external clock)|
|J20 | SRAM backup power supply | 1-3, 2-4 short circuit (VMEbus+5V backup power supply) | 3-5, 4-6 short circuit (onboard battery)|
|J21 | EPROM Capacity Selection | 2-3 Short Circuit (4Mbit, Only Available Specification) | -|
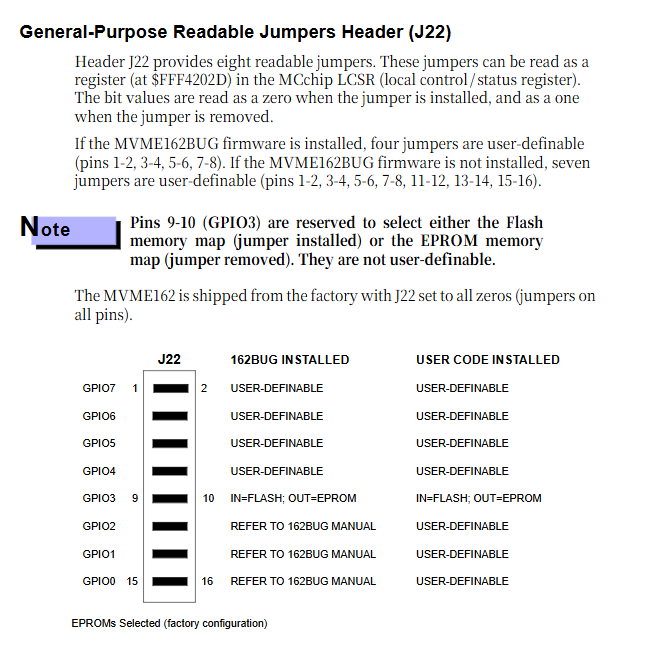
|J22 | Universal readable jumper | Fully short circuited (all 0) | Partially removed, corresponding register value is 1, GPO3 (9-10) is used to select Flash/EPROM|
SIM serial port module: Serial port 2 (Port B) is equipped with a SIM module through the J10 interface, supporting four types of DTE/DCE: EIA-232D/EIA-530. The module can be plugged and replaced, and the core model is SIM05-SIM08;
Module installation
IP modules: up to 4 can be installed, corresponding to J2/J3, J7/J8, J13/J14, J18/J19 interfaces, supporting dual size IP modules;
MVME162 board: If it is a system controller, it needs to be installed in slot 1 on the leftmost side of the VME chassis. The IACK/BG jumper in the slot needs to be removed and firmly connected to the P1/P2 backplane connector;
Transition module: MVME712 series transition module is required, only its serial ports 2/4 can be used, and 1/3 and printer ports are prohibited. This module cannot be used when configuring EIA-530;
System supporting requirements: To complete the MVME162 system setup, it is necessary to provide the system console terminal, disk drives and controllers, operating system, MVME712 transition module+P2/LCP2 adapter board and cables.
Operation instructions
This chapter introduces the front-end panel operations, memory mapping rules, software initialization, and reset operations of MVME162, which are the core basis for device use and program development
Front panel controls
Buttons: ABORT (S1) (Generate programmable interrupt after software enable, return 162Bug), RESET (S2) (Reset all devices on the board, if it is a system controller, drive SYSRESET *);
8 LED indicator lights: FAIL (red, BRDFAIL * activated), STAT (yellow, processor paused), RUN (green, local bus cycle executed), SCON (green, for VMEbus system controller), LAN (green, LAN chip is local bus master device), FUSE (green, LAN transceiver power is normal), SCSI (green, SCSI chip is local bus master device), VME (green, using VMEbus);
Memory mapping: divided into two types: local bus memory mapping and VMEbus memory mapping. The local bus address range is
00000000−
FFFFFFFF, The core partition includes programmable DRAM/SRAM/IP memory areas
FF800000−
FF9FFFFF's Flash/EPROM area
FFF00000−
FFFEFFFF's local I/O device area (including various registers)
FFFF0000−
VMEbus A16 area of FFFFFFFF; The local I/O device area includes core registers such as VMEchip2, MCchip, SCC, LAN, SCSI, IPIC, TOD clock, etc. The manual provides detailed definitions of the addresses, bit widths, and functions of each register;
BBRAM/TOD clock mapping: The 8KB NVRAM of MK48T08 is divided into user area, network area, system area, debugging area, configuration area (256B), TOD clock area (8B). The configuration area stores key information such as card serial number, Ethernet address, SCSI ID, etc., and the last byte is the checksum;
Software initialization: The 162Bug debugging firmware completes the default configuration of most control registers during power on/reset. If custom configuration is required, please refer to the M68040 manual and MVME162 programming reference guide; In a multi MPU system, only one MPU control register is allowed at a time to avoid conflicts;
Reset operation
System reset (SYSRESET *): triggered by the reset button, power on, watchdog timeout, and VMEchip2 LCSR bit, lasting at least 200ms and complying with the VMEbus specification;
Local Reset (LRST): a subset of system reset, with 5 triggering methods (watchdog timeout, reset key, GCSR bit, etc.) SYSRESET*、 Power on), the VMEbus master device can reset the local bus through GCSR, which carries risks and is only used in case of device failure.
Function module analysis
This chapter analyzes the working principles, interface specifications, and timing performance of each core module of MVME162 from the perspective of hardware architecture. The core content includes:
Local bus architecture: 32-bit synchronous bus, based on MC68040 bus, supports burst transmission and listening, bus arbitration is priority arbitration, and the priority of the main device from high to low is LAN (82596CA)>SCSI (53C710)>VMEbus>MPU;
Core storage module
DRAM: Controlled by MCchip, with programmable base address and capacity, parity errors can trigger interrupts/bus exceptions, requiring at least 10 initialization cycles;
SRAM: 512KB 32-bit, powered by Dallas DS1210S for battery backup, supporting dual backup of VMEbus+5V backup power supply and onboard battery. The onboard battery is RAYOVAC FB1225 (two BR1225 lithium batteries), which can be backed up for at least 2 years in a 40 ℃ power outage state;
Flash/EPROM: Bus conversion from 8-bit to 32-bit is implemented by MCchip, and reset code reading source (Flash/EPROM) is selected through GPIO of J22;
Communication and Expansion Interface
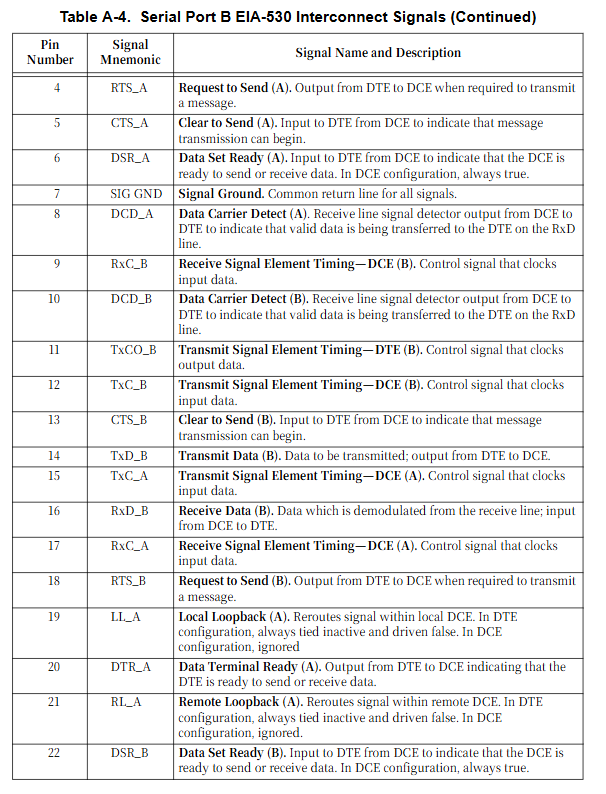
Dual serial ports: controlled by Zilog Z85230, serial port 1 is EIA-232-D DCE, and serial port 2 can be selected from EIA-232-D/EIA-530 DTE/DCE, supporting asynchronous (110B/s-38.4KB/s) and synchronous (SDLC/HDLC) protocols, and supporting CTS/DCD/RTS/DTR control signals;
Ethernet: controlled by Intel 82596CA, with 32-bit local bus DMA, the unique Ethernet address of the board is $08003E2xxxxx, stored on BBRAM and board labels, LAN DMA cannot access VMEbus to avoid buffer overflow;
SCSI: Controlled by NCR 53C710, with 32-bit local bus burst DMA, supports SCSI bus, and requires correct termination at both ends of the bus. The adapter board provides a termination resistor slot and fuse;
Industry Pack: Controlled by IPIC ASIC, supports 4 IP interfaces with 3M connectors, programmable memory/I/O space, and supports interrupt control;
VMEbus: Implemented by VMEchip2 ASIC, factory optional configuration, does not support on-site installation, supports A24/A32 addresses, D8/D16/D32 data, supports DMA burst transfer (D64/MBLT), provides system controller, interrupt handling, bus arbitration and other functions;
Local resources
Programmable timers: 4 MCchips+22 VMEchips, 32-bit, 1 μ s resolution, capable of generating periodic interrupts;
Watchdog timer: 1 each for MCchip and VMEchip2, working independently, timeout can trigger SYSRESET *, local reset, and board fault signals;
Hardware interrupts: VMEchip2 provides 8 software programmable hardware interrupts that can be triggered by software;
Local bus timeout: Both VMEchip2 and MCchip provide timeout function, with a timeout value of 8/64/256 μ s/infinite. After timeout, a TEA signal is sent to the main device. MCchip implements this function for boards without VMEbus;
Timing performance: The core is DRAM read and write cycles, with non interleaved DRAM read cycles of 4,2,2,2, interleaved DRAM read cycles of 4,1,1,1, and write cycles of 3,2,2 at 25MHz; EPROM/Flash cycle is 3-10 bus clock/byte, programmable configuration; The SCSI DMA transfer rate is 44MB/s (25MHz, no checksum, interleaved DRAM), and the LAN DMA transfer rate is 20MB/s (25MHz, no checksum).
Serial port interconnection specification
This chapter provides a detailed definition of the interconnection standard for MVME162 dual serial ports, supporting two specifications: EIA-232-D and EIA-530. The core content includes:
EIA-232-D: Single ended signal, DB25 interface, defined signal function for 25 pins, core uses TxD/RxD/RTS/CTS/DSR/DCD/DTR/SG, suitable for short distance transmission (recommended ≤ 15m), total load capacitance ≤ 2500pF, manual defines the electrical characteristics of transmitter/receiver (minimum output voltage ± 8.5V, input threshold ± 2.25V/± 0.75V);
EIA-530: Supports balanced/single ended signals, DB25 interface, upgraded to EIA-232-D, supports higher transmission rates, core signal is differential signal (such as TxD_A/TxD_B), manual defines the electrical characteristics of transmitter/receiver (differential output voltage ≥ 2.0V, input threshold ± 200mV);
Grounding requirements: The signal ground (Pin7) must be connected to complete the circuit loop; Use with caution the chassis ground (Pin1) to avoid current and data interference caused by different device ground potential differences. Only connect the signal ground to the chassis ground at one location (recommended on the computer side).
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


