

K-WANG


Honeywell Safety Manager(Release 162)
Honeywell Safety Manager(Release 162)
This manual is the authoritative hardware guide for Honeywell Safety Manager Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS), applicable to industrial process safety control scenarios such as chemical, petroleum, energy, etc. The core objective is to guide engineers in completing system installation, configuration, maintenance, and troubleshooting, ensuring that the system meets SIL 1-3 safety integrity requirements and complies with international safety standards such as IEC 61508 and IEC 61511.
Basic information and security compliance in the manual
(1) Manual positioning and target audience
Core positioning: Covering the technical specifications, installation process, and maintenance methods of the entire hardware components of Safety Manager, it is the core reference for system design, debugging, and operation;
Target audience: Hardware engineers, on-site operation and maintenance personnel, system integrators, who need to have a basic understanding of PLC, industrial safety standards (such as IEC 61508), and Windows system operation ability.
(2) Safety Compliance and Certification
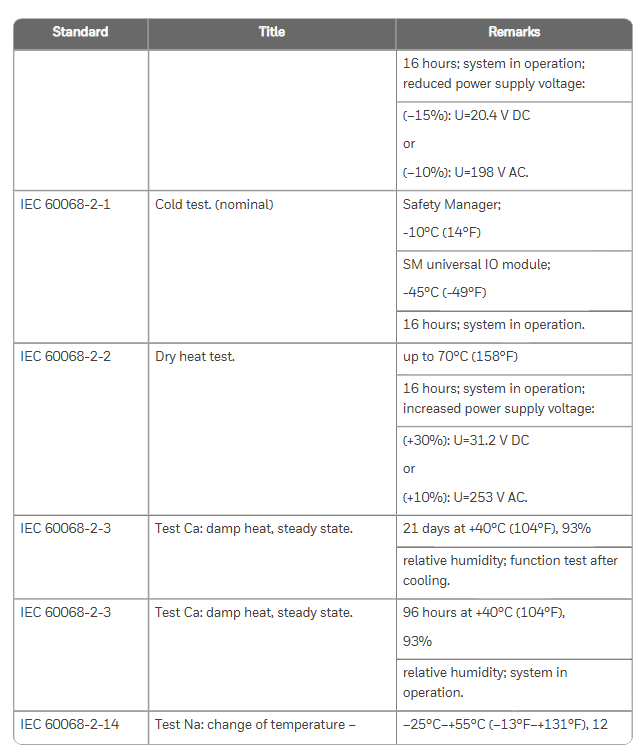
Safety standards: comply with IEC 61508 (functional safety), IEC 61511 (process industry SIS), ISO 13849-1 (mechanical safety), UL 508 (industrial control equipment), etc;
Hazardous Area Certification: ATEX, IECEx (Ex nA IIC T4, applicable to Zone 2 areas), FM 3611 (Class I/II Division 2 hazardous areas, such as chemical explosive environments);
Environmental Protection and Electromagnetic Compatibility: Compliant with RoHS Directive (Halogen Free Design) and EN 61000-6-2 (Electromagnetic Immunity in Industrial Environments), ensuring stable operation in complex industrial environments.
System hardware composition and core modules
The Safety Manager hardware system adopts a three-layer architecture of "cabinet chassis module", with core components including cabinet, controller chassis, IO chassis, power module, control processor module, input/output module, etc. The functions and technical parameters of each component are as follows:
(1) Cabinet: Physical carrier of the system
Standard configuration: Based on Rittal TS 8 series cabinets, default protection level IP20, optional IP54 upgrade; Including cooling fans (such as FANWR-24R, 24V DC with status feedback), thermostats (monitoring cabinet temperature to avoid module overheating), grounding bars (ensuring equipment grounding resistance ≤ 4 Ω), lighting fixtures (easy to maintain);
Key parameters: dimensions (such as 80 × 60 × 200cm, 80 × 80 × 200cm), weight (full load ≤ 550kg), operating temperature (-5~70 ℃, remote cabinet -40~70 ℃).
(2) Chassis: Module Installation and Signal Transmission Core
Divided into controller chassis (CPCHAS series) and IO chassis (IOCHAS series), supporting redundant/non redundant configurations to meet different safety level requirements:
Chassis type, model example, core functions, key specifications
Controller chassis CPCHAS-0001 is equipped with a control processor module to achieve system logic operations. It supports 1-2 Control processors, with a height of 4HE and a standard size of 19 inches
Non redundant IO chassis IOCHAS-0001S is equipped with non redundant IO modules, supporting 18 IO modules connected to on-site sensors/actuators, powered by 5V-R (redundant 5V)
Redundant IO chassis IOCHAS-0001R is equipped with redundant IO modules to improve system fault tolerance. It supports 9 pairs of redundant IO modules and a dual IO bus design
(3) Power Supplies: System Stable Power Supply Guarantee
Provide multiple types of power modules, supporting AC-DC conversion and redundant power supply, to meet different voltage requirements (24V/48V/60V/110V/120V DC). The core models and parameters are as follows:
Power supply model, output specifications, core characteristics, applicable scenarios
PSUNI2424 24V DC/24A, 600W dual overvoltage protection (SIL3 compatible), core controller power supply for operating temperature of -40~70 ℃
PSU-UNI2450U 25-28V DC/43-48A UL 508 certification, 100ms power-off hold, supports parallel expansion and high load IO module cluster power supply
FEEDER-24R 24V DC/63A redundant design, with status feedback relay, overcurrent protection redundant system main power feeder
(4) Control Processor Modules: The System's Brain
QPP-0002 (Quad Processor Pack): Core computing module, dual processors running synchronously, with Flash/RAM storage (battery backup, BKM-0001 module provides battery), supports Watchdog function (monitoring program execution time, memory errors), meets SIL3 requirements;
USI-0002 (Universal Safety Interface): Communication module, providing 2 channels of 10/100M Ethernet and 2 channels of universal serial communication (RS232/485), supporting interconnection with systems such as Expert PKS, with hardware firewall function;
BKM-0001 (Battery and Key Switch Module): A battery and key switch module that includes 2 lithium batteries (backup RAM data, approximately 3 months of battery life), a reset key (clear fault logs), and a forced enable key (allow IO signal forcing).
(5) I/O Modules: Field Signal Interaction
Input module: supports digital/analog signal acquisition, with fault self detection function, core models such as SDI-1624 (24V DC 16 channel digital input), SAI-1620m (16 channel analog input, 0-4V), SDI-1608 (16 channel digital input with ground fault monitoring);
Output module: supports safe digital/analog output, with short-circuit protection, core models such as SDO-0824 (24V DC 8-channel digital output), SAO-0220m (2-channel analog output, 4-20mA);
Converter module: such as BSAI-0420mI (converts 4-20mA to 0-2V, compatible with SAI-0410 module), to achieve matching between on-site signals and module inputs.
Key processes for system installation and maintenance
(1) Hardware Installation Specification
Cabinet installation: Horizontal/vertical installation should meet the requirement of heat dissipation gap (such as reserving 100mm above and below the fan), and grounding should be independent (protective ground and signal ground should be separated);
Module installation: IO modules need to press the "Key Coding" corresponding slot (such as SDI-1624 corresponding to A5/C5 hole positions) to avoid damage caused by incorrect insertion; Redundant modules need to be installed in pairs to ensure synchronous communication;
Cable connection: System interconnection cables (SIC) and communication cables (such as CCI-HSE-01 Ethernet cables) should be wired according to pin definitions to avoid reverse polarity (such as 24V DC power supply "+" connected to pin d8, "0V" connected to pin d10).
(2) Regular maintenance plan
Daily maintenance (daily/weekly): Check the LED indicator light (green normal, red fault), fan operation status, and cable joint tightness; Backup historical data (to USB drive/server);
Regular maintenance (monthly/quarterly): clean the cabinet filter (to avoid dust blockage causing overheating), test the power supply voltage (fluctuation should be ≤± 5%), and measure the cable insulation resistance (≥ 10M Ω);
Annual maintenance: Full module calibration (using original calibration tools such as 9100 calibrator), battery replacement (BKM-0001 module lithium battery replaced every 5 years), firmware upgrade (downloading the latest version from GE Digital official website).
(3) Troubleshooting and Solutions
Based on the "internal system exception" error mentioned in the Nexinstrument document, supplement the general troubleshooting logic of Safety Manager, and organize common troubleshooting solutions in the manual:
Possible causes and solutions for fault phenomena
System error "internal exception": 1. Control processor program crashes; 2. Power supply voltage fluctuations; 3. Module communication interruption: 1. Check the QPP-0002 module's Status LED (red indicates hardware failure and needs to be reset or replaced); 2. Use a multimeter to measure the 24V DC power supply (within the range of 20.4-31.2V); 3. Check the communication light of USI-0002 module (Tx/Rx light does not light up, network cable needs to be unplugged again)
IO module has no signal input 1. Sensor failure; 2. Cable breakage; 3. Module calibration expired. 1. Replace sensor for testing; 2. Use a multimeter to measure the continuity of the cable (such as the signal at pin d12 of SDI-1624 module); 3. Recalibrate the module (refer to SAI-1620m calibration process)
Power module alarm (red light on) 1. Overvoltage/undervoltage; 2. Fan malfunction; 3. Overload 1. Check the input voltage (e.g. PSU-UNI2450U input needs to be between 93-253V AC); 2. Check the fan speed (FANWR-24R speed should be ≥ 1500 RPM); 3. Reduce the number of parallel modules to avoid overloading
Communication interruption (with upper computer): 1. IP address conflict; 2. Protocol mismatch; 3. Network cable failure: 1. Reconfigure the USI-0002 module IP (to avoid conflicts with Expert PKS); 2. Confirm the communication protocol (such as Modbus TCP); 3. Replace the network cable and test the link (using a cable tester)
System configuration and expansion
Model coding rules: The hardware model includes a prefix (FS - non coated, FC - coated, FA - explosion-proof), module type (such as SDI-1624), and suffix (version number, such as V1.1), for example, "FC-SDI-1624" represents a coated 24V DC 16 channel digital input module;
Scalability: Supports adding IO channels through IO expansion modules (such as IO-0002), improving power supply reliability through redundant power supplies (such as RUSPSU-R), and achieving on-site signal terminal switching through FTA modules (such as IOTA-R24).
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


