

K-WANG


TOSHIBA PRODUCT GUIDE Discrete IGBTs
Deep Analysis of Toshiba IGBT Technology Evolution and Multi Field Applications
Insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT), as the core device of modern power electronic systems, combines the high input impedance of MOSFET with the high voltage and high current driving capability of bipolar transistor, making it particularly suitable for high voltage and high current load control scenarios. As an important manufacturer in the power semiconductor field, Toshiba's IGBT products are widely used in various fields such as motor drives, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), induction heating (IH) kitchenware, plasma displays (PDP), flashlights, etc. due to their low saturation voltage drop, high switching speed, high robustness, and diverse packaging forms. This article is based on Toshiba's product guide released in 2011, systematically reviewing its IGBT technology features, product lineup, and development trends, providing reference for engineering selection and design.
Characteristics and Technical Advantages of IGBT Structure
The basic structure of IGBT is a four layer PNPN type, which achieves conductivity modulation through PNP transistors during its conduction period, thereby maintaining a low saturation voltage drop (VCE (sat)) under high voltage conditions. Compared with power MOSFETs, IGBTs have significantly reduced conduction losses at high voltages, especially suitable for medium to high voltage applications ranging from 600V to 1700V.
Toshiba IGBT has the following characteristics:
High speed switch performance: Through carrier lifetime control technology, fast switching is achieved to reduce switching losses.
Low saturation voltage drop: Even in the high current range, maintaining a low VCE (sat) is beneficial for reducing conduction losses.
Built in optimized diodes: Some models integrate fast recovery diodes (FRD) or free wheel diodes (FWD) to improve system reliability and simplify circuit design.
High input impedance, voltage driven: The driving circuit is simple and has strong compatibility.
Diversified packaging: including TO-3P, TO-220, TSON-8, SOP-8 and other packaging options to meet different installation and heat dissipation requirements.
The development trend of Toshiba IGBT technology
Toshiba IGBT has undergone multiple generations of evolution, continuously optimizing its structure, process, and materials
Flat structure IGBT: In the early days, a flat gate structure was adopted to achieve low VCE (sat) by optimizing carrier injection.
Trench Gate structure: introduced since the 4th generation to further reduce saturation voltage drop and improve switching speed.
Thinning and Fine Craftsmanship: After the 6th generation, thinner wafers and finer graphic processes were used to reduce losses and increase current density.
RC-IGBT (reverse conducting IGBT): The 6.5th generation product integrates FWD single-chip into the IGBT chip, reducing external components, lowering thermal resistance, and improving system compactness and reliability.
The following table summarizes the development trend of Toshiba's IGBT at various voltage levels:
Development direction and intergenerational characteristics of voltage levels
1200V 3rd generation: high robustness; 5th generation: trench gate structure soft switch; Generation 6.5: RC structure
900-1500V 4th and 5th generations: trench gate structure soft switch; 6th generation: Thinning; Generation 6.5: RC structure
600V 3rd generation: high robustness; 4th generation: Quick switch; Generation 6: Thinning and Fine Craftsmanship
400V 5th to 7th generation: trench gate structure, suitable for high current pulse applications such as flashlights
300-400V Generation 4-7: Used for PDP driver, gradually optimizing conduction loss and switching characteristics
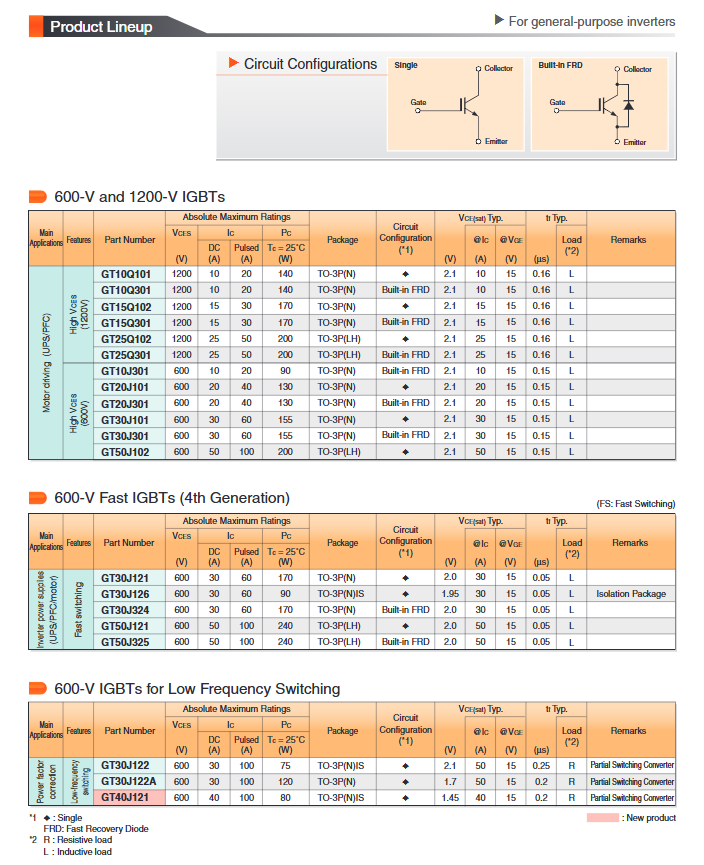
Product lineup and application selection guide
1. Universal inverter and motor drive (600V/1200V series)
Suitable for frequency converters UPS、 In servo drive and other applications, the switching frequency is generally lower than 20kHz (universal type) or up to 50kHz (fast switching type).
High robustness series (such as GT10Q101): Vces=1200V, Ic=10A, built-in FRD, suitable for motor driven U-phase circuits.
Quick switch series (FS series, such as GT30J121): adopting the 4th generation slotted gate technology, with low switching loss, suitable for high-frequency hard switching applications.
Low frequency switch models (such as GT30J122): suitable for scenarios such as some switch converters that do not require high switching frequency.
2. Soft switch application series (600V/900V/1200V)
Suitable for soft switching topologies such as induction heating (IH) kitchenware, microwave ovens, resonant switching power supplies, etc., it can significantly reduce switching losses.
900V series (such as GT15M321): IC=15A, built-in FWD, suitable for 100-120VAC input scenarios.
1200V series (such as GT40QR21): suitable for 200-240VAC input, using the 6.5th generation RC structure, with high integration.
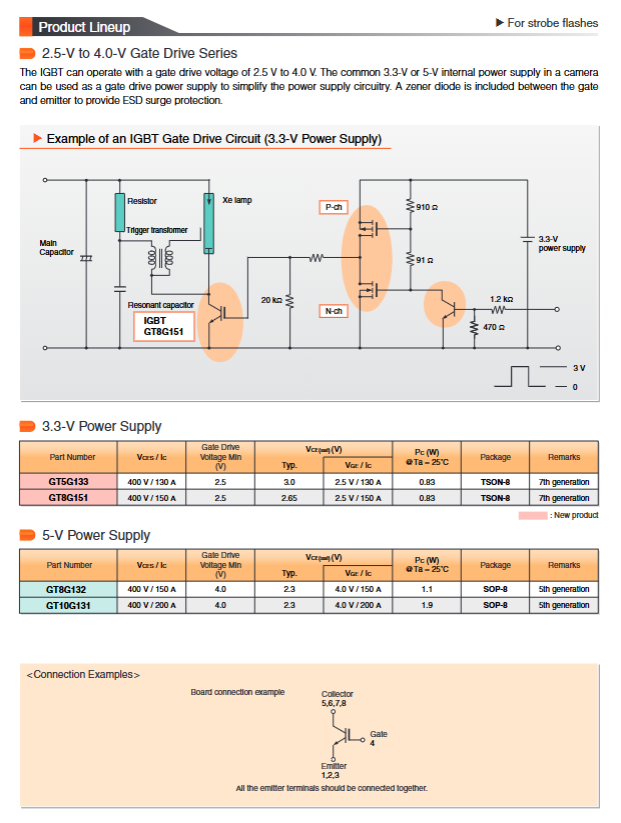
3. Flash application series (400V)
Used for digital camera flash circuits, requiring high pulse current, low gate driving voltage, and small packaging.
Low gate voltage drive series (2.5-4.0V): such as GT5G133 (Vges=2.5-3.0V), can be directly driven by the camera's internal 3.3V power supply, simplifying the circuit.
5V driver series: such as GT8G132, suitable for traditional 5V logic drivers.
4. Plasma Display Driver Series (300V/400V/600V)
Used for PDP scanning and maintenance driving, it needs to withstand high pulse current and low conduction loss.
300V series (such as GT30F124): Vces=300V, Ic=200A, using 6th generation technology with reduced conduction voltage.
400V series (such as GT30G124): suitable for PDP panels with higher voltage.
The 600V series (such as GT30J124) is an early 5th generation product that can still be used in some high-voltage drive applications.
5. RC-IGBT series (6.5th generation new product)
GT35MR21 (900V/35A) and GT40QR21 (1200V/40A), integrated with FWD, are suitable for soft switching and high-frequency applications, with high integration and excellent heat dissipation performance.
Packaging and selection precautions
Toshiba offers multiple packaging options, including:
TO-3P (N)/TO-3P (LH): Suitable for medium to high power, high heat dissipation applications.
TO-220SIS/SM: Suitable for medium power compact installation.
TSON-8/SOP-8: Suitable for low-power, high-density mounting, such as flash circuits.
When selecting, the following factors should be considered comprehensively:
Voltage and current levels: determined based on the system bus voltage and maximum load current.
Switching frequency: For high-frequency applications, choose the fast switch series, and for soft switch topologies, choose the corresponding low loss model.
Thermal design: Evaluate temperature rise by combining package thermal resistance (Rth) with heat dissipation conditions.
Integration requirements: If circuit simplification is needed, built-in diodes or RC-IGBT models can be selected.
Drive voltage: Choose the low Vges series for low voltage logic drive applications.
Discontinuation and replacement suggestions
Toshiba has listed some products that are in the "final stage" or have been discontinued in the product guide (such as MG30T1AL1, GT40M101, etc.), and recommends using new models as replacements. When designing, priority should be given to selecting the current mass-produced series to ensure supply and performance optimization.
Summary and Prospect
Toshiba IGBT continues to improve in terms of conduction loss, switching speed, integration, and reliability through continuous structural innovation and process evolution. From planar structures to trench gates, from discrete IGBT+diodes to single-chip RC-IGBT, its products have covered a wide range of fields from industrial motor drivers to consumer electronic flashlights.
In the future, with the development of markets such as electric vehicles, renewable energy, and high-efficiency power sources, IGBT will continue to evolve towards higher power density, higher frequency, lower losses, and higher intelligent integration. Toshiba, with its years of accumulated technology and product line, is expected to continue playing an important role in the high-end power device market.
For design engineers, understanding the technical characteristics of IGBT, correctly selecting and matching appropriate driving and cooling solutions are the key to achieving efficient and reliable power electronic systems.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
- other brands
- UniOP
-
ABB CI857K01 Communication Interface Module | ABB AC 800M Controller
-
ABB TP830 Baseplate Module | ABB S800 I/O System
-
ABB SA811F Power Supply Module | ABB Advant Controller System
-
ABB 5SGY35L4510 Motor Protection Relay | ABB Automation
-
ABB HVC-02B High Voltage Controller | ABB Automation
-
ABB UAD154A Analog I/O Module
-
ABB GCD207B101 Digital Control Interface Module
-
ABB TB820-2V2 Modulebus Terminal Base
-
ABB UDD406A Drive Control Module
-
ABB PPD113B01-10-150000 3BHE023784R1023 Control Processor Module
-
ABB 07EA90-SI Analog Input Module
-
ABB 5SHY35L4512 Power Control Module
-
ABB 3BHE021951R0124 Control System Module
-
ABB D685A1156U01 Industrial Control Module
-
ABB 07DC91C Digital Control Module
-
ABB UNS2880B-P V1 Industrial Control Processor Module
-
ABB PFEA112-20 3BSE050091R20 Tension Electronics Module
-
ABB CI810B 3BSE020520R1 Communication Interface Module
-
ABB FM9925A-E Field Module Industrial Control Module
-
MOOG 76-264 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 72-101 SER.1907R - Servo Valve
-
MOOG B52576-1 - Controls Valve Part
-
MOOG CN1000 - Servo Controller
-
MOOG CM-65-105-G-A04 - Servo Controller Evaluation
-
MOOG WSH53P32C108CS - Clamp Proportional Valve
-
MOOG ZFDRP06A4K0ASA - Check Valve
-
MOOG CCE40B64WX06A2 - Check Valve
-
MOOG CCE32B61WX06C3 - Check Valve
-
MOOG CCE25B62DAX - Check Valve
-
MOOG CCE25B61DX - Check Valve
-
MOOG CCE50C11WX06 - Hydraulic Proportional Cartridge Solenoid Valve
-
MOOG CCE50A6RH1X10 - Hydraulic Cartridge Valve HPN703404
-
MOOG CCE25B62DRX - Cartridge Valve XGB10016-000-01
-
MOOG Cce16 B6rma0v06/A12 - Throttle Valve Xeb15892-001-01
-
MOOG CB64541-001 - Crimp Connector 11+PE 24V
-
MOOG CB64539-001 - Crimp Connector 11+PE
-
MOOG RSE25BU6T2WX - Cartridge Valve HPN2946887
-
MOOG XPB10004-000-01 - Cartridge Proportional Valve
-
MOOG XEB11483-000-01 - Cartridge Proportional Valve
-
MOOG XCB10235-000-00 - Cartridge Valve
-
MOOG C43285-203 Rev. D - Control Board and Coil
-
MOOG BS23-28FC-04CHP - Servo Motor
-
MOOG G631-3005A - Servo Valve
-
MOOG BN34-35CD-04CHEP - Servo Motor
-
MOOG BN34-25CD-01LH - Servo Motor
-
MOOG BN23-28EF-01CHG - Servo Motor
-
MOOG BI160D - Servo Drive Evaluation
-
MOOG B97012-024 - Hydraulic Servo Valve D-71034
-
MOOG B80HXAGGNSF2 - Servo Valve Component
-
MOOG B64569-2V - 10 Micron Hydraulic Filter Element
-
MOOG B48333-801 - Hydraulic Component
-
MOOG B35829-008A - Linear Actuator
-
MOOG API090E - Servo Evaluation Component
-
MOOG SM23205D-DN-F1 - Animatics Smart Motor Servo
-
MOOG AC6023-24C - Servo Valve Component
-
MOOG AC4598-6 - Servo Valve Component
-
MOOG A72068-1 - Hydraulic Component
-
MOOG A32179-1 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG A11592 - Hydraulic Servo Valve D635-606C
-
MOOG A076-795 - ServoCon Valve A076795
-
MOOG A076-506 - Servo Valve A076506
-
MOOG A076-401R - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG A076-103HRI-10 539 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG A076-102 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG A076-101A - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG A05891-1 - Hydraulic Component
-
MOOG 963.364.8011A - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 963.364.8011 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 897012-024 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 7WEFS42P06C88B - Hydraulic Proportional Servo Valve
-
MOOG 79.212 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 79.211 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 78.5113 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 78 Series - Servo Valve Series
-
MOOG 771F232 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 771-117 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 770-147E - Valve Assembly G2761AM002
-
MOOG 77-703 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 77-553 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 77-159 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 77-123 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 761-5077B - Electro-Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 761-4088B5 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760N1181B - Electro-Hydraulic Servo Valve 3000psi
-
MOOG 760N1087A - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760N1085A - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760K645B - Electro Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760C461A - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760C262A - Servo Valve MOD 252.23C-01
-
MOOG 760A509A - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760A508A - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760A191A M3741851 - Flow Control Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760-851A - Servo Hydraulic Valve
-
MOOG 760-795A - Attica Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760-748A - Directional Control Valve
-
MOOG 760-508A - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 760-101 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 76-263C - Hydraulic Valve
-
MOOG 76-185 M2021851 - Flow Control Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 76-100 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 74937-1 - Hydraulic Control Valve
-
MOOG 744F007 - Servo Valve 2019 Model
-
MOOG 744F006 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 744 Series - Servo Valve Evaluation
-
MOOG 743-003D - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 743 Series - Servo Valve Evaluation
-
MOOG 730Y218-H P5 - Servo Valve
-
MOOG 73-797 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 73-744 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 73-233 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 73-104 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 73-103 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 73-101 - 2 Stage Flow Control Servo Valve
-
MOOG 720B210062554 - Electronic Control Unit
-
MOOG 72-516 - 72 Series Servo Valve
-
MOOG 72-101 - Servo Valve 1906R
-
MOOG 642-515A - Proportional Valve T654R
-
MOOG 641-229B - Proportional Directional Control Valve
-
MOOG 631F172F5 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 631-3015B - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 631 SERIES - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 630-1283D - Servo Valve S30HOGB4NNL
-
MOOG 62F120 - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 62-321 - Electro-Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 62-314A - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 62-134 - Hydraulic Control Valve
-
MOOG 60B401H - Hydraulic Servo Valve
-
MOOG 60B023H - Hydraulic Servo Valve

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


