

K-WANG


GE VMIVME-5565 Ultra High Speed Fiber Reflective Memory (with Interrupt Function)
GE VMIVME-5565 Ultra High Speed Fiber Reflective Memory (with Interrupt Function)
Product Overview
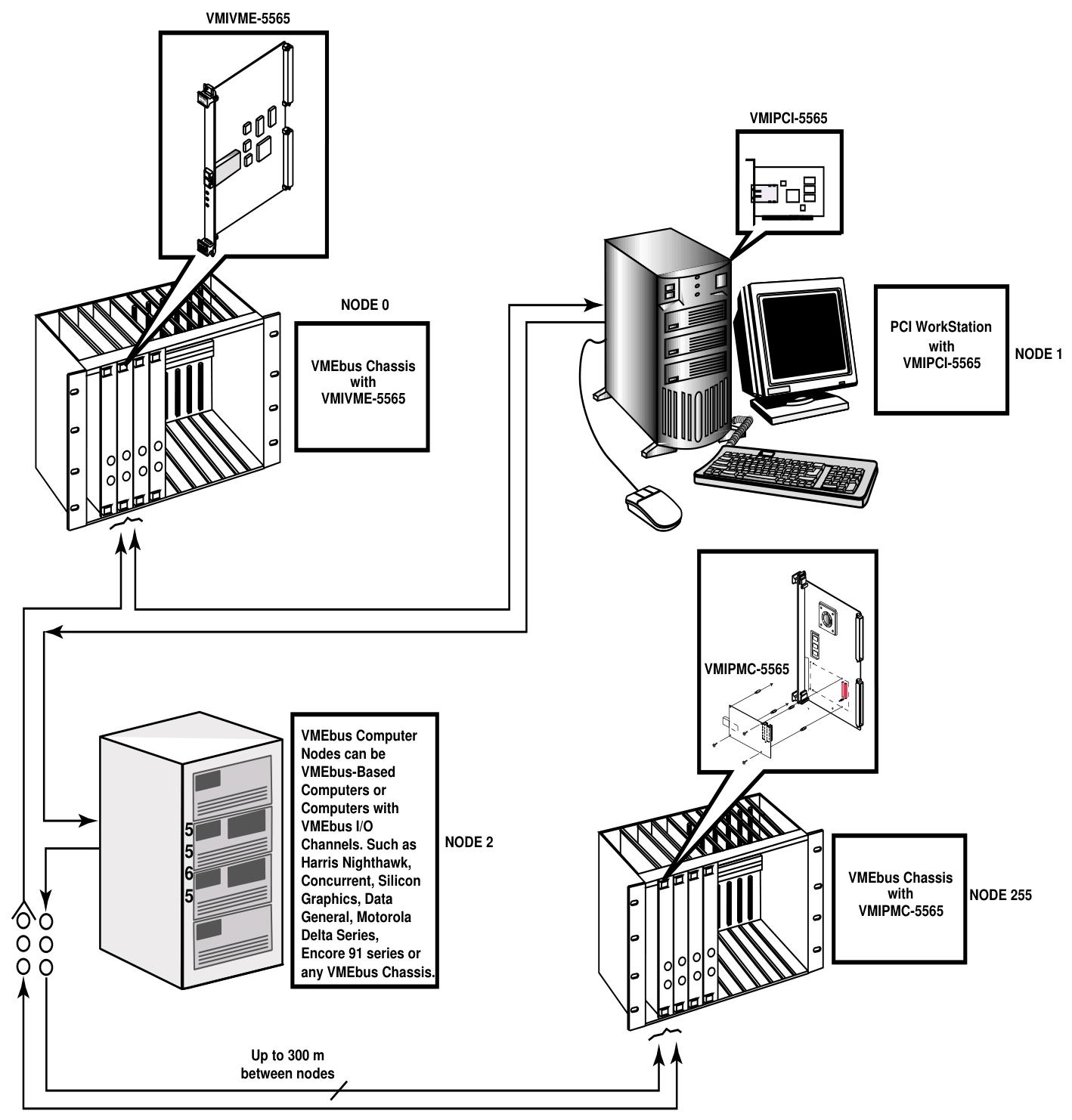
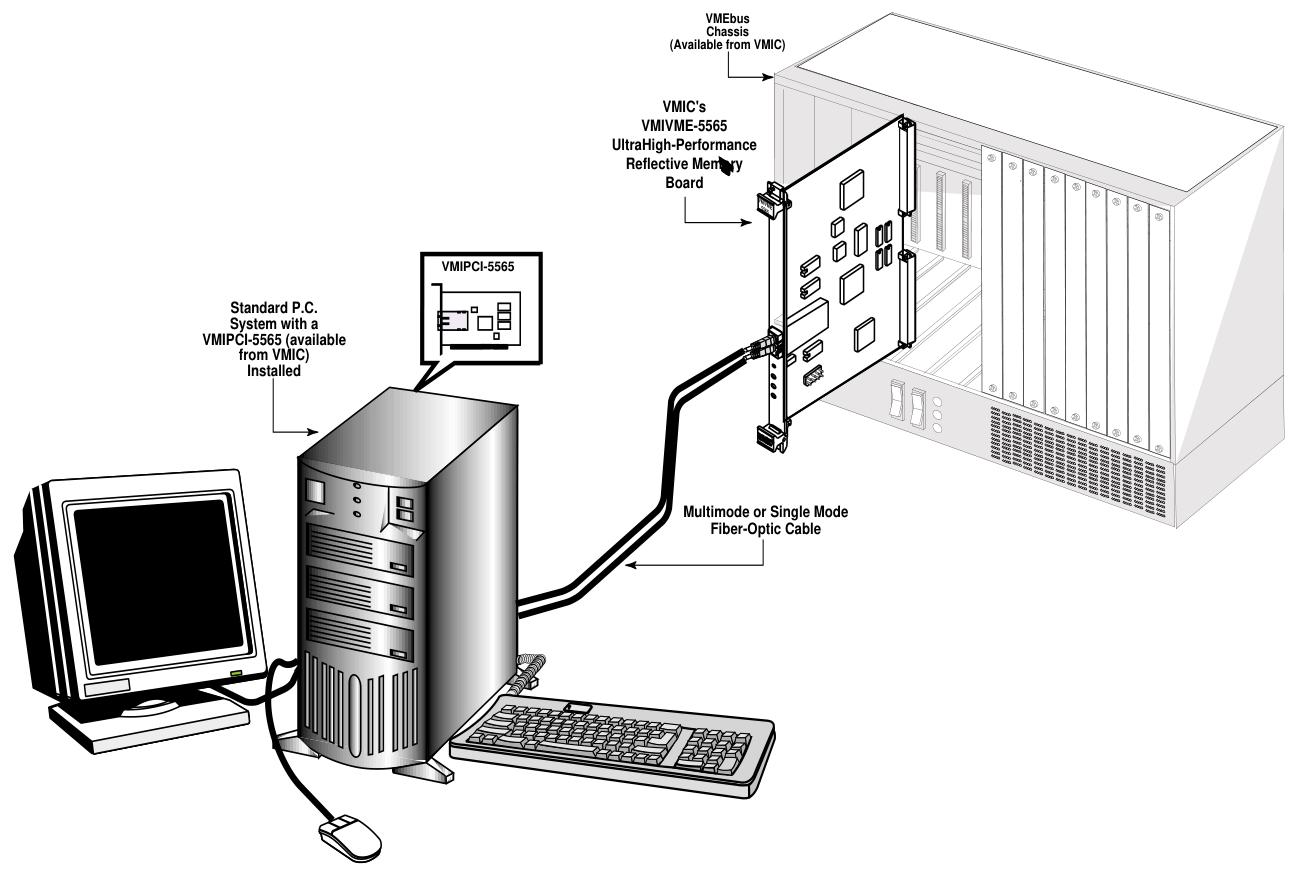
VMIVME-5565 is a member of the VMIC Reflective Memory Real time Fiber Network product series based on VMEbus. It adopts a standard 6U European card shape and can be integrated with VMIMPC-5565 and VMIPCI-5565 of the same series into networks using standard fiber optic cables. Each card in the network is called a node. It enables computers, workstations, PLCs, and other embedded controllers with different architectures and operating systems to share data in real time, with convenient operation. Data is transmitted through written memory (SDRAM), and the onboard circuit automatically transfers the data to all other nodes, almost without the involvement of any host processor or system.
Core Features
A high-speed and easy-to-use fiber optic network with a serial rate of 2.12 Gbaud.
Supports up to 256 nodes.
When using multimode fiber, the connection distance can reach 300 meters, and single-mode fiber can reach 10 kilometers.
Dynamic packet size, with each packet containing 4 to 64 bytes of data.
The transmission rate varies depending on the packet size, with 43 Mbytes/sec for 4-byte packets and 174 Mbytes/sec for 64 byte packets.
Up to 128 Mbyte of SDRAM reflective memory with parity check.
Supports VMEbus DMA.
Four universal network interrupts, each with 32-bit data.
Equipped with error detection function.
Standardize compliance
Compliant with the VMEbus specification (ANSI/IEEE STD 1014-1987, IEC 821 and 297), with the relevant mnemonics A32: A24; D32/D16/D08 (EO): Slave: 39/3D:09/0D。
Working principle
Basic operation: Each node in the network is interconnected in a daisy chain loop through fiber optic cables. The data transmission is initiated by the VMEbus host system writing to the onboard SDRAM. During the writing process, the onboard circuit automatically writes the data and related information into the transmit FIFO, which then forms variable length data packets ranging from 4 to 64 bytes. These packets are transmitted through the fiber optic interface to the receiver of the next board. After receiving, the relevant circuit opens the data packet and stores it in the receiving FIFO, then writes it to the corresponding position of the local onboard SDRAM, and routes the data to its own sending FIFO. This process is repeated until the data returns to the source node and is removed.
Front panel LED indicator lights: There are three LED indicator lights, with the bottom red being the status indicator light. When powered on, it defaults to "ON" and the status can be switched by writing to bit 31 of the control and status registers; The yellow color in the middle is the signal detection indicator light, which is "ON" when the receiver detects light; The green light at the top is the self data indicator light, which is "ON" when detecting the return of self data.
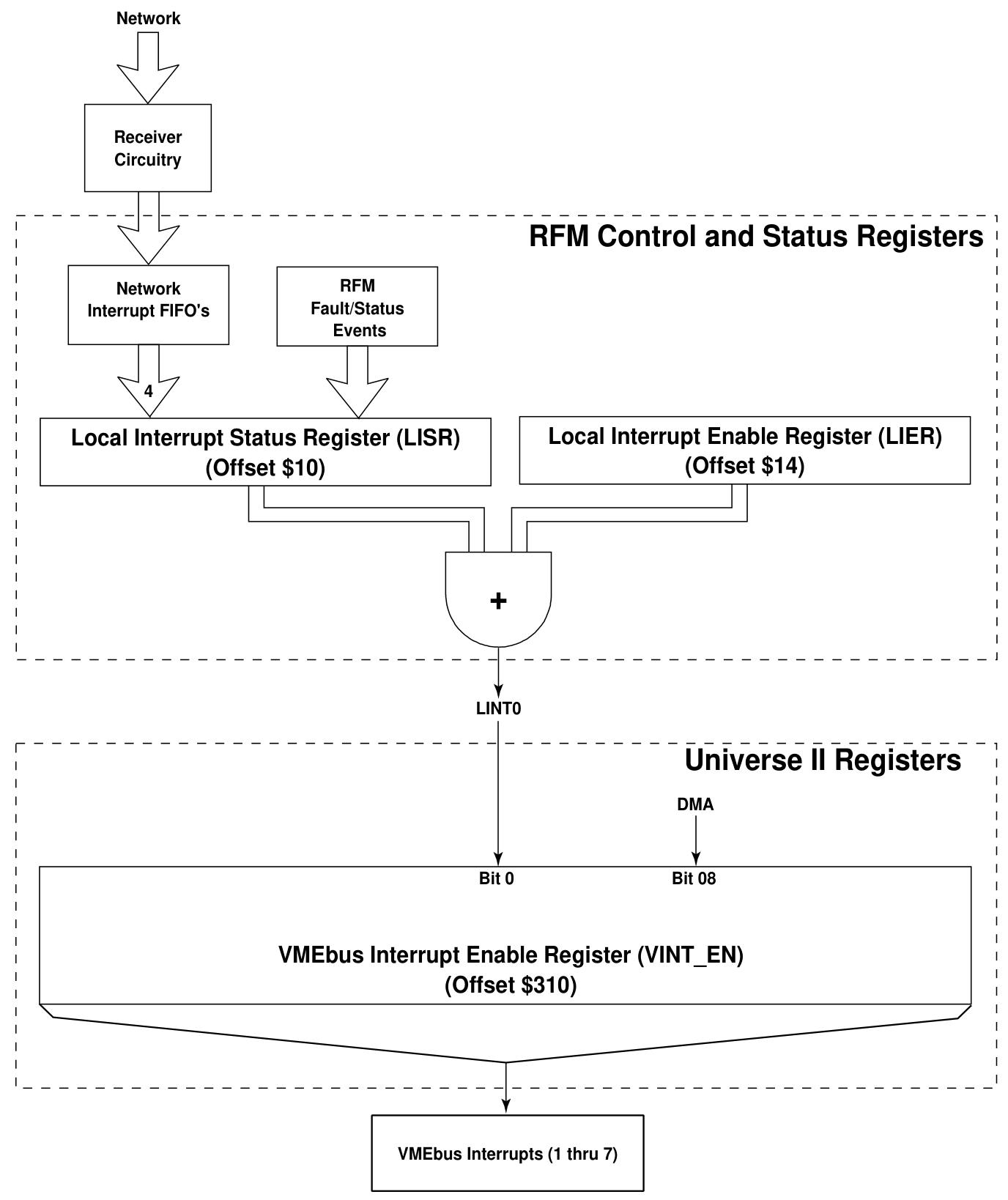
Register group: including Universe II registers (specific control and status and DMA control registers located in the VMEbus bridge, byte order in small end mode) and Reflective Memory (RFM) control and status registers (implementing unique features of the 5565 series reflective memory board).
Reflective memory RAM: available in two sizes of 64 Mbytes or 128 Mbytes, with parity check function. The parity check function is not enabled when powered on and needs to be enabled through a specific bit setting. When enabled, only 32-bit or 64 bit writes are allowed.
Interrupt circuit: There is a programmable VMEbus interrupt output, and the interrupt source can be separately enabled and monitored through the local interrupt status register (LISR) and local interrupt enable register (LIER).
Network Interruption: capable of transmitting interrupt packets on the network, which can be directed to specific nodes or broadcasted to all nodes, including sender node ID, destination node ID, interrupt type information, and 32-bit user-defined data. The receiving node will store the relevant information in the corresponding FIFO.
Redundant transmission mode: configured through jumper E5, each data packet is transmitted twice in redundant mode, and the receiving node evaluates the transmission situation. Although this mode reduces the probability of data loss, it will lower the effective network transmission rate.
Abnormal packet removal operation: Abnormal packets refer to packets that do not belong to any node in the network. VMIVME-5565 can work as one of the two abnormal master nodes. When an abnormal packet is detected, it will be removed from the ring and relevant flag bits will be set.
Byte order: Due to the tradition of different microprocessor manufacturers, there is a distinction between big endian and small endian. The PCI to VMEbus interface of VMIVME-5565 uses Intel or equivalent bridge chips, adopts small endian byte order, and the interface has external byte order conversion logic, which can achieve independent master/slave hardware byte order conversion.
Configuration and Installation
Unpacking program: Components may be sensitive to electrostatic discharge, so attention should be paid when handling them. After unpacking, check for any damage.
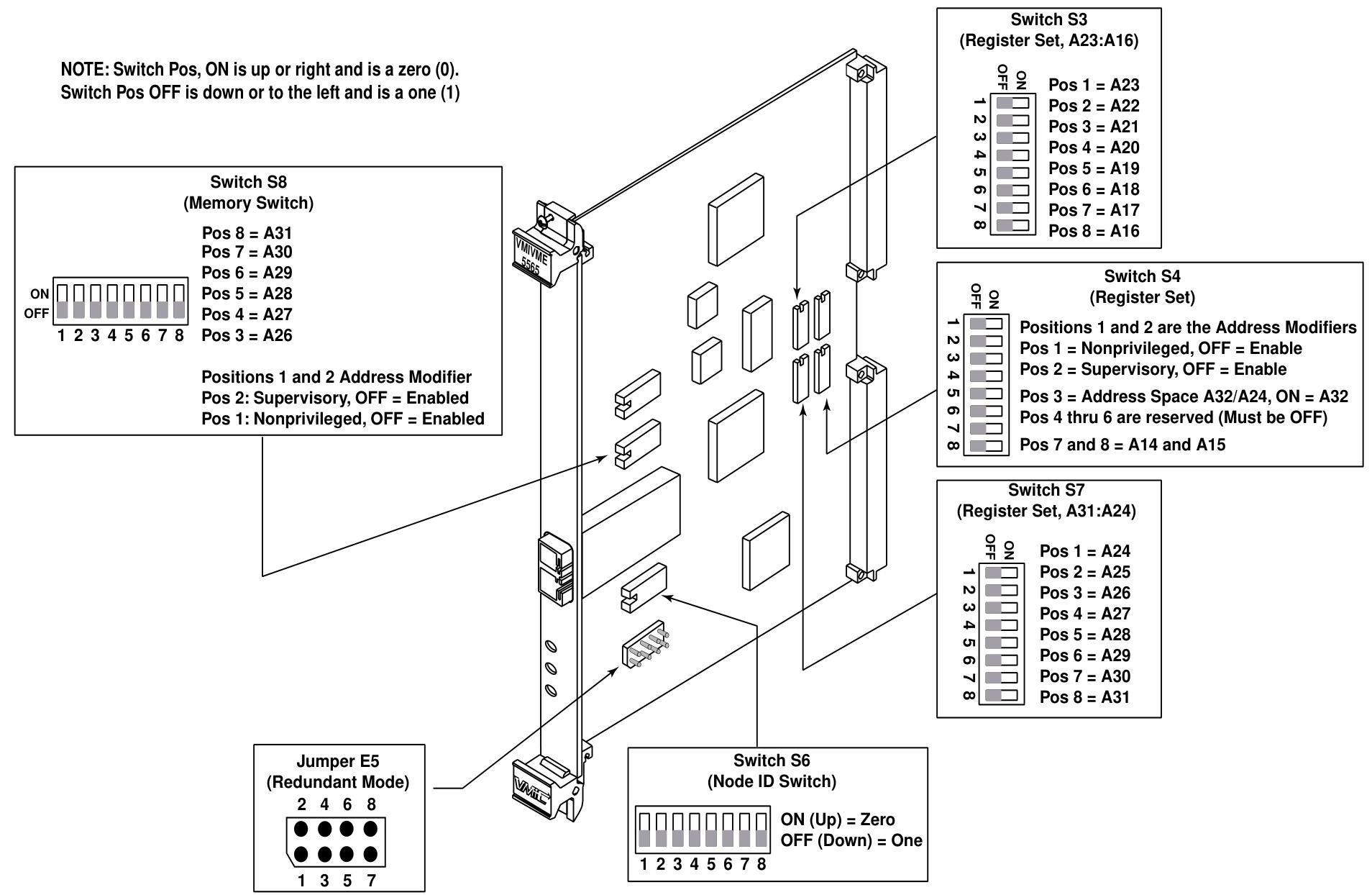
Switch/jumper configuration and position
Node ID Switch (S6): An 8-bit switch that sets the node ID within the range of 0 to 255. Each node ID must be unique, and the switch position "ON" corresponds to 0, while "OFF" corresponds to 1.
Jumper E5 (redundant mode configuration): Used to configure redundant or non redundant transmission modes and select abnormal master nodes, with different pin hopping states corresponding to different functions.
Register and memory configuration switch: VMIVME-5565 occupies two independent address spaces on VMEbus. The control and status register spaces can be set as extended address space (A32) or standard address space (A24), and the SDRAM memory space can be set as extended address space (A32). When configuring, address overlap should be avoided. The switch "ON" corresponds to address bit 0, and "OFF" corresponds to address bit 1.
Physical installation: Power off installation, ensure correct switch settings, fix after installation on the chassis, and connect fiber optic cables according to the ring topology.
Front panel description: Optical transceiver, "RX" for receiver, "TX" for transmitter, using "LC" type fiber optic cable, with three LED indicator lights as described earlier. When operating, pay attention to dust prevention and avoid looking directly at the transmitter.
Cable configuration: There are multi-mode or single mode fiber optic interfaces, and cables and connectors have specific specifications.
Connectivity: Nodes are connected in a circular manner.
Programming
RFM Control and Status Register: Located at a specific offset address, it includes local control and status registers, local interrupt status registers, local interrupt enable registers, etc. Each register has different functions and bit definitions.
RFM network registers: including Network Target Data Register (NTD), Network Target Node Register (NTN), Network Interrupt Command Register (NIC), as well as various interrupt sender IDs and data FIFOs, used for generating and receiving network interrupts.
Example of network interrupt handling: including the steps for setting interrupt programs and serving network interrupts.
Universe II registers: divided into Universe II control and status registers and Universe II DMA registers, each with different offset addresses, functions, and bit definitions, which can be used to control and monitor interrupts and DMA transfers.
DMA source and destination addresses: determined by specific registers, transfer direction determined by L2V bits, alignment requirements for addresses, adjustable transfer size and data width, DMA command packet pointer pointing to command packet, DMA startup, VMEbus ownership, completion, and termination all have corresponding operations and mechanisms.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


