

K-WANG


SIEMIENS 1FK6 series three-phase servo motor
SIEMIENS 1FK6 series three-phase servo motor
Core positioning and basic information
The Siemens AG 1FK6 series three-phase servo motor (model covers 1FK6 03. -1FK6 10.) official manual in multiple languages, including English, German, French, Italian, Spanish, and Swedish, aims to provide comprehensive product usage guidance for global users. The document needs to be used in conjunction with the accompanying "Three phase Servo Motor Project Planning Guide" (order number 6SN1197-0AC20-0AP), which is applicable to the entire life cycle of motor installation, commissioning, operation and maintenance, and fault handling. The core goal is to ensure safe operation for users and stable operation of equipment, while complying with the EN 60034 series (IEC International Electrotechnical Commission standards), 73/23/EEC low voltage directive, and UL specifications (standard motor nameplate marked with "UR").
Safety Regulations: Core Risks and Protection Requirements
Safe operation is the primary focus emphasized in the document, and multiple types of risks and mandatory protective measures have been identified based on the characteristics of the motor
(1) Electrical safety risks
Voltage hazard: When the motor rotor rotates, the terminal voltage can reach up to 300V, and direct contact can cause electric shock accidents.
Operating standards:
All electrical operations must be carried out after the motor has completely stopped, and only certified electricians are allowed to operate;
Strictly follow the EN 50110-1 (DIN VDE 0105-100) standard, and before operation, follow the five step process of "power-off - isolation - electrical testing - grounding short circuit - shielding adjacent live parts";
Unauthorized modification of electrical circuits or shielding layers is prohibited to avoid short circuits or electromagnetic interference.
(2) Permanent magnet safety risks
Magnetic field hazard: The motor rotor is equipped with high magnetic flux density permanent magnets, which have strong attraction to ferromagnetic objects and can interfere with pacemakers and damage electronic data carriers (such as hard drives, USB drives, magnetic cards).
Protective measures:
It is explicitly prohibited for users of pacemakers to enter the motor disassembly area, and conspicuous signs must be posted on site;
Electronic data carriers should be kept away from the motor (especially the disassembled rotor), with a minimum safe distance of no less than 1m;
During transportation or storage, avoid close contact between the motor and ferromagnetic objects such as iron tools and steel to prevent component damage caused by adsorption and collision.
(3) Thermal safety risk
High temperature hazards: The surface temperature of the motor during operation can reach up to 140 ℃. Direct contact can cause burns, and high temperatures may damage adjacent temperature sensitive components such as wires and electronic components.
Protection requirements:
Do not touch the high-temperature surface of the motor, and install anti touch and anti protective covers if necessary;
Temperature sensitive components should be kept away from the surface of the motor to avoid direct contact;
Ensure the effective operation of the motor temperature control device to prevent damage to windings and bearings due to overheating, or demagnetization of permanent magnets.
(4) Environmental and installation safety restrictions
Prohibit the use of motors in explosion-proof areas (unless specially certified by Siemens);
During the installation, transportation, and maintenance of the motor, it is necessary to avoid severe impacts to prevent permanent magnet displacement or winding damage;
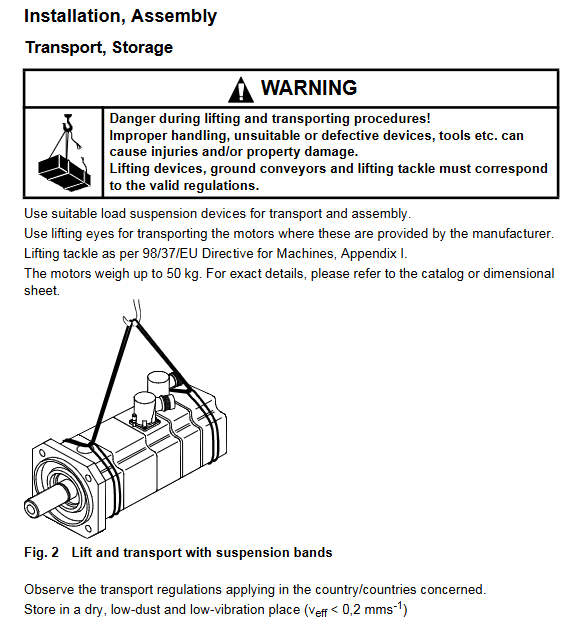
The maximum weight of the motor is 50kg, and lifting devices that comply with Appendix I of the 98/37/EEC Machinery Directive (such as lifting rings and slings) must be used for handling. It is prohibited for a single person to handle in violation of regulations.
Product Core Information: Attributes, Applications, and Delivery
(1) Core attributes of the product
The 1FK6 series motor is a permanent magnet excitation three-phase synchronous servo motor, with a core design adapted to the "sine current principle motor control pulse inverter". Precise control of speed and torque needs to be achieved through a frequency converter, and direct connection to the three-phase power grid is prohibited (otherwise it will cause winding burnout and permanent magnet demagnetization). The motor adopts self cooling method, compact structure, suitable for high-precision driving and positioning scenarios, and has the characteristics of low noise, long life, and high protection level (IP64).
(2) Typical application scenarios
Mainly used for equipment with strict requirements for driving accuracy and response speed, including:
Machine tools (cutting, machining centers);
Automated production equipment;
Industrial robot;
Material handling devices (such as conveyors, robotic arms).
(3) Delivery scope and acceptance requirements
Delivery list: motor body (including integrated encoder, optional brake), separate product nameplate (to be attached near the equipment for reference), multilingual manual;
Acceptance criteria:
After receiving the goods, it is necessary to immediately verify the waybill with the physical object to confirm that there are no missing parts or transportation damage;
If any transportation damage is found, it is necessary to immediately claim compensation from the carrier; If there are component defects or incomplete deliveries, it is necessary to promptly contact the responsible representative of Siemens;
The instruction manual should be properly stored in an easily accessible location near the equipment for easy operation and maintenance reference.
Key technical parameters: performance and adaptation indicators
(1) Infrastructure and protection parameters
Parameter category specific indicator standard basis
Installation form standard IM B5, optional IM V1, IM V3 EN 60034-7
Protection level IP64 (dustproof, splash proof), optional IP65 (enhanced dustproof and waterproof), drive end flange can be upgraded to IP67 EN 60034-5
Cooling method: self cooling (no additional cooling device required) EN 60034-6
Design standard for shaft end: keyway free cylindrical shaft (tolerance k6); Optional: with keyway+key (tolerance k6, half key balance) DIN 748-3, IEC 60072-1
(2) Electrical and Performance Parameters
Parameter category specific indicator standard basis
Insulation class F (maximum allowable operating temperature 155 ℃) EN 60034-1
Braking parameters: normally closed holding brake (optional), power supply voltage 24V DC ± 10%, power 15W DIN VDE 0580
Speed range: Rated speed (nN) ≤ 3000rpm, maximum speed (nmax) ≤ 5300rpm, as indicated on the product nameplate
Torque parameters: Zero speed continuous torque (M0) up to 6.0Nm, rated torque (MN) up to 4.0Nm, as indicated on the product nameplate
Current parameters: Rated current (IN) up to 4.3A, zero speed current (I0) up to 3.1A, as indicated on the product nameplate
Noise level 1FK6 03./04.: ≈ 55dB (A); 1FK6 06.:≈65dB (A); 1FK6 08./10.: ≈ 70dB (A) (below 3000rpm) EN 60034-9
(3) Environmental and lifespan parameters
Parameter category specific indicator standard basis
Environmental temperature operation: -15 ℃~+40 ℃; Exceeding the range requires derating (power factor 0.92 at 50 ℃, power factor 0.82 at 60 ℃) EN 60034-1
Altitude adaptation ≤ 1000m (standard); 2000m power factor 0.942500m power factor 0.9 EN 60034-1
Bearing lifespan Rolling bearings (lifetime lubrication), reference lifespan 20000h Siemens design specifications
Radial shaft seal lifespan of approximately 5000 hours under oil lubrication conditions according to Siemens design specifications
Vibration tolerance vibration acceleration ≤ 5g, vibration level N EN 60034-14
(4) Optional configuration parameters
Encoder system: incremental encoder (sin/cos 1VPP), absolute encoder (EnDat protocol), simple absolute encoder, rotary transformer;
Additional components: planetary gearbox, normally closed holding brake;
Protection upgrade: IP65 protection level, IP67 protection for drive end flange.

Installation and Connection: Specifications and Key Requirements
(1) Transportation and Storage Standards
Transportation requirements:
Use appropriate lifting devices (such as slings and rings) to avoid tying the motor shaft or flange directly with ropes and prevent damage to components;
During transportation, it is necessary to fix it firmly, avoid severe bumps or impacts, and prevent the permanent magnet from shifting;
Comply with local transportation regulations, clarify that the motor is a "strong magnet containing equipment", and avoid magnetic interference issues during air transportation.
Storage conditions:
The storage environment needs to be dry, low dust, and low vibration (effective vibration speed)v eff<0.2mm/s);Avoid direct sunlight or high temperature and humidity environments to prevent the winding from getting damp or the performance of the permanent magnet from deteriorating;
Before storage, remove the rust inhibitor at the shaft end (using commercial solvents) to avoid affecting subsequent installation.
(2) Mechanical installation requirements
Installation gap: At least three sides of the motor need to reserve a 100mm heat dissipation gap to ensure self cooling effect;
Fixed specifications:
Use hexagon socket head screws with a strength grade of ≥ 8.8 to fix the flange, and tighten them evenly (to avoid flange deformation);
The screw torque must meet the equipment requirements, and excessive tightening is prohibited to cause thread damage;
Load limit:
Motors with integrated brakes are prohibited from bearing axial forces, and radial forces must strictly follow the requirements of the project planning guidelines;
When installing vertically (with the shaft end facing upwards), protective measures should be taken to prevent liquid from seeping into the upper bearing;
Balance requirements:
Motors with keyways are already balanced with half keys when they leave the factory. After installing output components such as couplings and gears, they need to be rebalanced according to ISO 1940 standards;
Do not strike the motor shaft or bearings. Special tools (such as a puller) should be used to install/remove the output components. If necessary, the output components can be heated (to avoid high temperature conduction to the inside of the motor).
(3) Electrical Connection Specification
Cable selection:
Pre assembled shielded cables recommended by Siemens must be used (not within the scope of delivery), and power cables and signal cables must be laid separately to avoid electromagnetic interference;
The cable should be compatible with the rated voltage and current of the motor, and have sufficient mechanical strength to avoid pulling and damaging it;
Plug connection:
The plug types are divided into power plug (P) and signal plug (S), and the wiring must strictly follow the drawing (Fig.5), and misconnection is prohibited;
The plug torque must comply with the specifications (power plug: 12Nm/20Nm, signal plug: 12Nm), and excessive twisting is prohibited;
The direction of the plug can be adjusted up to 10 times (when equipped with a matching socket) to avoid cable fatigue damage;
The inside of the plug should be clean and free of residue and moisture, and the sealing surface should be intact to ensure an IP64 protection level;
Grounding and shielding:
The protective conductor (PE) must be reliably grounded, and the grounding resistance must comply with local electrical regulations;
The cable shielding layer needs to be grounded at both ends to reduce high-frequency harmonic radiation and avoid electromagnetic interference (EMC);
Special requirements:
The encoder and temperature sensor are electrostatic sensitive components, and touching their connection terminals with hands or tools with static electricity is prohibited;
The temperature sensor can only cope with conventional overheating scenarios, and an additional thermal overload relay needs to be configured when the motor is stationary and overloaded.
Start up, operation and maintenance, and troubleshooting
(1) Pre startup inspection
Electrical connection inspection: Confirm that all plugs are securely fastened, the wiring is correct, and there are no loose or short circuit hazards;
Mechanical state inspection: manually rotate the motor output component to confirm that there is no jamming or friction noise, and that the keyway (if any) is fixed;
Protection device inspection: Motor overload protection, temperature protection and other devices have been activated and function normally;
Environmental condition inspection: The installation environment temperature and altitude meet the requirements, and the heat dissipation gap is sufficient;
Auxiliary equipment inspection: The supporting equipment such as frequency converter and encoder have been debugged and the parameters are adapted to the characteristics of the motor.
(2) Start the process
Brake test (with brake motor): Apply 24V DC ± 10% voltage to brake pins BR and BR2 to confirm that the rotor can rotate freely without friction noise;
Inverter startup: Start the system according to the instructions of the inverter (such as SIMODRIVE, MASTERDRIVES MC), and the initial speed should be lower than the rated speed;
Operation monitoring: Observe the operation status of the motor, confirm that the speed and torque meet the requirements, and there is no abnormal vibration, noise, or overheating;
Positioning test (positioning scenario): Verify that the encoder signal is normal and the motor positioning accuracy meets the standard;
Emergency stop test: Trigger the emergency stop button, confirm that the brake and frequency converter are linked normally, and the motor can quickly stop.
(3) Daily maintenance and cycle requirements
Cleaning and maintenance: Regularly clean the dust and oil stains on the surface of the motor to ensure effective heat dissipation. Power off during cleaning to prevent water or cleaning agents from seeping into the interior of the motor;
Status check:
Regularly inspect cables and plugs for damage, aging, and loose fasteners;
Monitor the operating temperature, vibration, and noise of the motor, and promptly shut down for troubleshooting if any abnormalities are found;
Periodic maintenance reference:
Bearing: The reference life is 20000 hours. If there is abnormal noise or increased vibration during operation, it should be replaced in a timely manner;
Radial shaft seal (oil lubrication): with a reference life of 5000 hours, regularly check for leaks and replace if necessary;
Special maintenance: After disassembling the motor, the encoder system must be recalibrated, otherwise it will affect the positioning accuracy.
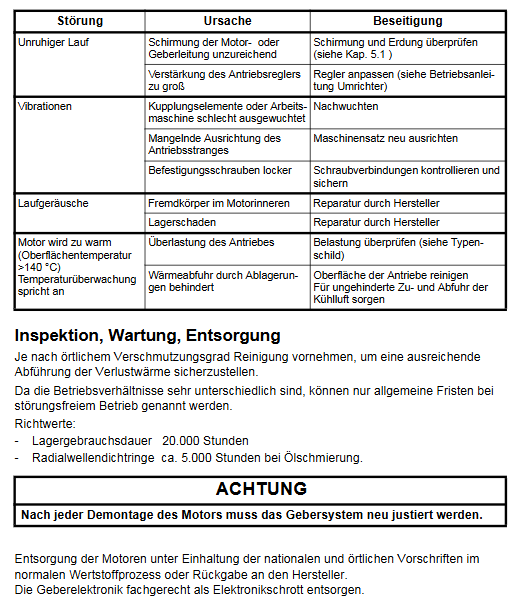
(4) Common faults and solutions
Core causes of fault phenomena and solutions
Irregular motor operation: 1. Insufficient shielding of motor/encoder cables, electromagnetic interference; 2. The gain of the frequency converter controller is too high. 1. Check if the grounding of the cable shielding layer is reliable; 2. Reduce the controller gain according to the frequency converter manual
Severe motor vibration: 1. Coupling/load imbalance; 2. Poor alignment of the drive chain; 3. Loose fixing screws. 1. Rebalance the load and coupling components; 2. Calibrate the coaxiality of the drive chain; 3. Check and tighten all fasteners
Abnormal operating noise (abnormal noise): 1. Foreign objects enter the interior of the motor; 2. Bearing wear or damage; 3. Permanent magnet displacement: 1. Stop the machine for inspection and remove foreign objects; 2. Replace the bearings; 3. Contact Siemens for professional maintenance
Motor overheating (surface temperature>140 ℃) 1. Load exceeding rated torque; 2. Insufficient heat dissipation gap or surface dust; 3. Temperature sensor malfunction: 1. Reduce the load to the rated range; 2. Clean the surface dust and increase the heat dissipation gap; 3. Repair or replace the temperature sensor
Encoder signal abnormality: 1. Encoder wiring error; 2. The encoder is subject to electromagnetic interference; 3. The encoder is damaged. 1. Check the wiring diagram and rewire it; 2. Strengthen cable shielding and grounding; 3. Replace the encoder and calibrate it
(5) Equipment Disposal Standards
When the motor is scrapped, it should be classified and recycled according to national/local regulations, or returned to Siemens for disposal. It is prohibited to dispose of it at will;
Encoders, brakes, and other electronic components need to be disposed of separately as electronic waste to avoid environmental pollution;
Before disposal, it is necessary to remove the permanent magnets inside the motor (operated by professionals) to prevent strong magnetic fields from causing harm to disposal personnel or equipment.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


