

K-WANG


ABB Relion ® 615 series RED615 line differential protection and control device
Integrated protection function: with "line differential protection" as the core main protection, while integrating backup protection such as overcurrent, ground fault, circuit breaker failure, etc., to meet the requirements of modular protection;
Standardized communication: Deeply compliant with the IEC 61850 standard, supporting GOOSE messages (transmission delay ≤ 3ms), IEC 60870-5-103, Modbus ®、 DNP3 and other protocols, adapted for interconnection of substation automation systems;
Flexible configuration capability: Provides 3 standard configuration solutions, supports customizing signal logic through PCM600 tool, and adapts to different grounding methods (isolated neutral, resistance grounding, compensation grounding, direct grounding) of the power grid;
Full lifecycle support: Equipped with a complete documentation system (engineering, installation, debugging, operation and maintenance manuals), supporting local (LHMI) and remote (WHMI) operations, simplifying engineering and maintenance processes.
ABB Relion ® 615 series RED615 line differential protection and control device
Product basic positioning and core features
RED615 is ABB Relion ® The intelligent electronic device (IED) for line differential protection and control under the 615 series is designed specifically for public utilities and industrial power systems. Its core application is the protection and control of overhead lines and cable feeders, and it is suitable for ring and mesh power grids with or without distributed generation. Its core characteristics can be summarized as:
Integrated protection function: with "line differential protection" as the core main protection, while integrating backup protection such as overcurrent, ground fault, circuit breaker failure, etc., to meet the requirements of modular protection;
Standardized communication: Deeply compliant with the IEC 61850 standard, supporting GOOSE messages (transmission delay ≤ 3ms), IEC 60870-5-103, Modbus ®、 DNP3 and other protocols, adapted for interconnection of substation automation systems;
Flexible configuration capability: Provides 3 standard configuration solutions, supports customizing signal logic through PCM600 tool, and adapts to different grounding methods (isolated neutral, resistance grounding, compensation grounding, direct grounding) of the power grid;
Full lifecycle support: Equipped with a complete documentation system (engineering, installation, debugging, operation and maintenance manuals), supporting local (LHMI) and remote (WHMI) operations, simplifying engineering and maintenance processes.
Document and symbol specifications
(1) Document system and audience
Document positioning: This document is the "Application Manual", focusing on functional application scenarios and parameter setting guidelines. It needs to be used in conjunction with other manuals (such as the "Engineering Manual" for tool operation and the "Installation Manual" for physical installation);
Target audience: Protection and control engineers with knowledge of power engineering and communication protocols, responsible for equipment planning, preliminary engineering, and on-site debugging;
Version history: The current version is version B (released in July 2009), corresponding to product version 2.0. Compared to version A (October 2008), it has added support for DNP3 protocol, standard configuration B/C, and WHMI disturbance record upload function.
(2) Security and document symbols
Symbol Type Meaning Application Scenarios
The electrical warning icon poses a risk of electric shock and involves chapters on power wiring and terminal operation
Warning icons may pose a chain risk of personal injury caused by equipment failure, such as power grid accidents due to protection failure
Please note that icons may cause device damage, software abnormalities, parameter configuration errors, improper wiring, and other scenarios
Information icon key operation prompt function activation conditions and default parameter description
Suggestions for optimizing icon engineering, such as CT selection techniques and communication networking solutions
(3) Functional coding specification
The functional identification adopts a combination of "IEC 61850 name+IEC symbol+IEC-ANSI number", for example:
Line differential protection: LNPLDF1 (IEC 61850), 3dI>L (IEC symbol), 87L (ANSI number);
Directional grounding fault protection: DEFLPDEF1 (IEC 61850), I ₀>→ (1) (IEC symbol), 67N-1 (1) (ANSI number).
Product hardware and operating interface
(1) Hardware structure
The RED615 hardware consists of a "plug-in unit+chassis", and the core plug-in modules and functions are as follows:
Plug in module slot ID core function key parameters
Auxiliary power supply/BO module X100 provides auxiliary power supply, output trip/signal contact power input: 48-250V DC/100-240V AC; Including 2 sets of PO contacts and 1 set of SO contacts
Binary I/O module X110 binary input/output with 8 BI and 4 SO contacts
Analog input/BI module X120 collects current/voltage signals, expands BI 3-channel phase current (1/5A), 1-channel zero sequence current (1/5A or 0.2/1A), and 1-channel zero sequence voltage (configuration B exclusive)
Optional BIO module X130 expansion I/O with 6 BI and 3 SO contacts
Communication module X000 protocol communication supports Ethernet (100BASE-TX), RS-485, and fiber optic (ST interface)
(2) Operation interface
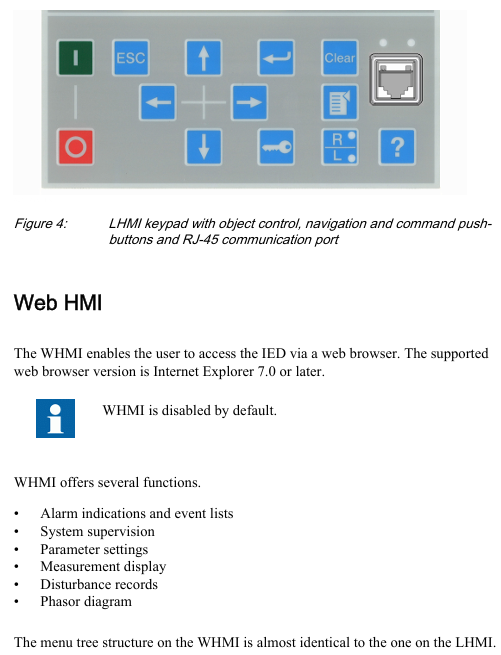
Local HMI (LHMI)
Display unit: LCD supports two character sizes (small characters: 5 rows x 20 columns; large characters: 4 rows x 8 columns), divided into four display areas: "title, icon, content, and scrollbar";
LED indicator lights: 3 fixed protection lights (Ready/Start/Trip)+11 programmable alarm lights (such as differential protection action, CT fault);
Key functions: navigation key (switching menu), control key (circuit breaker opening and closing), function key (alarm confirmation, reset, local/remote switching).
Web HMI(WHMI)
Access method: accessed through IE 7.0+browser, disabled by default, requires manual activation;
Core functions: parameter configuration, real-time measurement value viewing, disturbance record download, phasor diagram display, menu structure consistent with LHMI;
Access range: Local (connected to laptop via front-end RJ-45 port) or remote (via LAN/WAN).
(3) User Authorization
Four types of user permissions are preset, with authorization disabled by default (WHMI mandatory), and passwords can be changed by administrators:
Typical operations within the scope of username permissions
VIEWER read-only view of measurement values and alarm logs
OPEROTOR control and status switching, local/remote mode switching, alarm reset
ENGINEER configuration and testing modify parameters, clear disturbance records, enter testing mode
Administrator full permission to change password and restore factory settings
Core functions and standard configurations
(1) Three standard configuration schemes
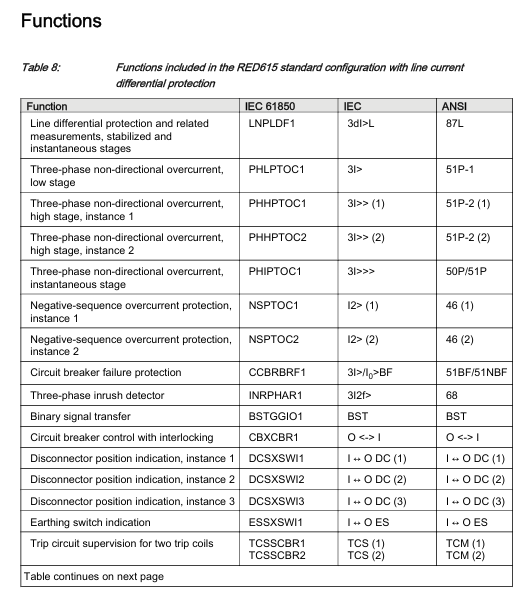
RED615 provides three predefined configurations that cover different ground fault protection requirements, with the following core differences:
Configuration Type Core Protection Function Applicable Scenarios Key Modules
Configure A (line differential protection), including line differential protection (87L), three-phase overcurrent protection (50P/51P), negative sequence overcurrent protection (46), and circuit breaker failure protection (51BF), for cable feeders. In scenarios where ground fault protection is not required, there is no zero sequence voltage input and the CT synthesis of zero sequence current is relied upon
Configuration B (including directional grounding fault protection) Configuration A: All functions+directional grounding fault protection (67N), transient/intermittent grounding fault protection (67NIEF), automatic reclosing (79). For overhead lines/cable mixed lines, it is necessary to distinguish the fault direction of the power grid (such as multi power distribution network), including zero sequence voltage input (U ₀), and adapt to the compensation grounding system
Configuration C (including non directional grounding fault protection) Configuration A: All functions+non directional grounding fault protection (50N/51N), automatic reclosing (79), radiation type distribution network, no need to distinguish fault direction scenarios (such as single power supply feeders) rely on CT synthesized zero sequence current, no zero sequence voltage input
(2) Detailed explanation of key protection functions
Line differential protection (LNPLDF1, 87L)
Core function: As the main protection, it realizes unit protection of the line and quickly cuts off internal faults;
Features: Contains stable low order (can be locked by CT fault detection) and instantaneous high order (can dynamically adjust the action value through remote circuit breaker status);
Communication dependency: It is necessary to establish protective communication with the remote IED, which will automatically lock in case of communication failure to avoid misoperation.
Earth fault protection
Directional (configuration B): Based on the phase of zero sequence current (I ₀) and zero sequence voltage (U ₀), the fault direction is determined, suitable for multi terminal power grids, divided into low order (sensitive section) and high order (fast section);
Non directional (configuration C): Based solely on zero sequence current amplitude action, suitable for single ended power grids, divided into low order, high-order, and instantaneous order.
Automatic reclosing (DARREC1, 79, configuration B/C optional)
Starting condition: triggered by protection action signals (such as overcurrent, ground fault);
Locking logic: The circuit breaker spring is not storing energy, the gas pressure is low, and it is locked when manually opening;
Status indication: LED5 is lit during the reclosing process, and an alarm is triggered when it fails.
Circuit breaker related protection and monitoring
Circuit breaker failure protection (CCBRBRF1, 51BF/51NBF): When the circuit breaker is not opened after the protection action, a trip command is sent to the upstream circuit breaker;
Trip Circuit Monitoring (TCSSCBR1/2, TCM): Monitor 2 sets of trip coil circuits, and lock the monitoring function when the circuit breaker is opened;
Circuit breaker status monitoring (SSCBR1, CBCM): Based on current and contact status, the mechanical characteristics of the circuit breaker are determined, and an alarm is triggered when there is an abnormality.
Communication and Networking
(1) Protocol support
Protocol type, functional scope, physical interface
IEC 61850 monitoring, control, parameter configuration, disturbance record upload (COMTRADE format), GOOSE message (trip level delay ≤ 3ms) Ethernet (RJ-45100BASE-TX)
IEC 60870-5-103 Protection signal upload, telemetry and remote signaling RS-485 or Ethernet
Modbus RTU/ASCII third-party device interconnection (such as PLC, SCADA) RS-485 or RS-232
DNP3 telemetry, remote signaling, remote control, supporting TCP/IP or serial Ethernet or RS-485
(2) Precautions for Communication Networking
GOOSE application: supports the highest performance level (transmission delay ≤ 3ms), meets the tripping requirements of distribution substations, and can simultaneously send events to 5 clients;
Client limitation: A single IED can support up to 5 concurrent clients. After PCM600 occupies 1, the remaining 4 can be allocated to other protocol clients;
Time synchronization: Line differential protection requires remote station time reference synchronization, which is recommended to be implemented through IEC 61850 or SNTP.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


