

K-WANG


Rockwell Automation ICS AADvance Controller
Core objective: Define SIF safety application standards (mandatory) and recommendations to ensure that the system meets and maintains the required Safety Integrity Level (SIL), with a maximum support for SIL 3.
Rockwell Automation ICS AADvance Controller
Basic Information and Usage Standards
1. Scope of application and core objectives
Applicable products: AADvance controller series (T9100/T9110 processor modules, T9401/2 digital input modules, etc.) and supporting software (AADvance Workbench 1.4/2.1, AADvance Robust SIS Workstation 2.00), supporting system version 2.011.
Core objective: Define SIF safety application standards (mandatory) and recommendations to ensure that the system meets and maintains the required Safety Integrity Level (SIL), with a maximum support for SIL 3.
2. Key usage requirements
Personnel qualifications: Installation, configuration, operation and maintenance operations must be carried out by professionally trained personnel who are familiar with relevant regulations (such as IEC 61508, NFPA series standards).
Responsibility statement: If the device is used in a manner that does not comply with the manufacturer's regulations, the protective function of the device may become ineffective; Rockwell is not responsible for indirect/consequential damages, and the examples in the manual are for illustration only and do not represent actual application guarantees.
System core features and authentication
1. Core functions and security design
Application scenarios: Suitable for safety critical scenarios such as emergency shutdown (ESD), fire and gas detection, rotating machinery control, burner management, etc., while supporting non safety but business critical control requirements.
Security Capability:
Both fail safe and fault tolerant architectures are supported, and fault tolerance can be realized through two module (1oo2D) or three module (2oo3D) configurations.
Built in comprehensive diagnostic function, capable of detecting hardware/software faults. The faulty module needs to be replaced within the mean time to repair (MTTR) to avoid a decrease in SIL level.
Supports two configurations: "Power Loss Trip (DTT)" and "Power On Action (ETA)", and the number of modules needs to be selected based on SIL level and demand rate (high/low) (see Table 1).
2. Module configuration and SIL compliance requirements
Minimum module configuration for different application scenarios (simplified version of Table 1):
Application type, number of input modules, number of processor modules, number of output modules
SIL 2/3, Low/high demand, DTT 1 2 1
SIL 2, High demand, ETA 2 2 2
SIL 3, High demand, ETA 2 2 2
Note: The single channel digital output module includes a series switch. The DTT scenario supports SIL 3, while the ETA scenario only supports SIL 2; There are no three module output configuration options.
3. International certification and compliance standards
Functional safety certification: Compliant with IEC 61508 SIL 3, certified by an independent certification body.
Hazardous environment certification:
North America: Class I, Division 2, Groups A-D (UL 61010-2-201, CSA C22.2 standard).
Europe/UK: ATEX (DEMKO 11 ATEX 1129711X, Ex ec IIC T4 Gc), UKCA (UL24UKEX2993).
International: IECEx (certificate number IECEx UL 12.0032X).
Other compliance: Complies with industry standards such as EN 50156 (furnace control), EN 54 (fire alarm), NFPA 85/86/87 (boilers/ovens/fluid heaters), etc.
Safety lifecycle and management system
1. Safety lifecycle stages
The full lifecycle defined by IEC 61508 must be followed, with core stages including:
Scope definition: Clearly define system boundaries, interfaces (with processes/third-party equipment), and environmental requirements (such as temperature and power).
Hazard and Risk Analysis: Identify hazardous events, trigger sequences, and risk levels as inputs for safety requirements.
System Design and Engineering: Divide system architecture, define security requirement levels for each component, and refine hardware/software design.
Integration and Verification: The application is integrated with the controller to test and verify whether SIF meets SIL requirements (such as response time and fault handling).
Operation and Maintenance: Develop an operation/maintenance plan to ensure the SIL level is maintained during operation; Changes must be strictly controlled, and suspensions must follow safety procedures.
2. Requirements for Safety Management System
Policy and Planning: Functional safety policies need to be developed to clarify measures, responsibilities, and record management (including change control) for each stage of the lifecycle.
Personnel capability: Personnel qualifications need to be evaluated, including engineering experience, functional safety knowledge, regulatory familiarity, etc. Higher qualification requirements are required for high-risk scenarios.
Functional Safety Assessment (FSA): Led by senior personnel independent of the project, it reviews whether the entire lifecycle work meets the requirements.
System Architecture Design (SIL 2/3)
1. SIL 2 architecture
Fault safety architecture: single input (1oo1D), dual processor (1oo1D degraded), single output (1oo1D), triggering a safe state in case of a fault.
Fault tolerant input architecture: dual/triple input (1oo2D/2oo3D), dual processors, single output. When a single input module fails, it will operate in a degraded state while still maintaining safety functions.
High demand architecture: dual input, dual processor, dual output, ensuring that faulty modules are replaced within MTTR to avoid SIF shutdown.
2. SIL 3 architecture
Fault safe I/O+fault-tolerant processor: single input/output, dual/triple processor (1oo2D/2oo3D), downgraded in case of processor failure, dual fault triggers safe state.
Fault tolerant I/O architecture: dual input/output, dual processors, both input/output modules support 1oo2D degradation, suitable for high safety requirements scenarios.
TMR architecture: three inputs, three processors (2oo3D), dual outputs, with the strongest fault tolerance. A single module failure does not affect system operation. When there are two failures, it will be downgraded, and when there are three failures, it will trigger a safe state.
3. Secure network communication
SNCP protocol: SIL 3 certified "Black Channel" protocol, supports Ethernet transmission of secure data, achieves data exchange between controllers through "variable binding", and can be configured as single network (fail safe) or dual network (fault-tolerant).
Peer to Peer communication: Supports SIL 3 data transmission between AADdistance and Trusted controllers, based on master-slave mode, and recommends using redundant networks to ensure availability.
Installation and environmental requirements
1. Non hazardous environment
Environmental conditions: temperature -25 ° C~+60 ° C, pollution level ≤ 2 (IEC 60664-1, only non-conductive pollution, occasional condensation); The burner management application requires an enclosure protection level of IP40 (indoor)/IP54 (outdoor).
Installation requirements: The module should be installed vertically (ensuring natural heat dissipation), DIN rail or wall mounted, without the need for forced air cooling.
2. Hazardous environment
Special requirements:
The enclosure protection level is ≥ IP54 (IEC 60079-0/7) and must be marked with "Do not open when powered on".
Grounding wire cross-sectional area ≥ 3.31mm ², wire temperature rating ≥ 85 ° C, only supports vertical installation.
The temperature range is the same as non hazardous environments, and the pollution level is ≤ 2.
Operations and Security Assurance
1. Key daily maintenance items
Fault handling: When the processor/input/output module fails, it needs to be replaced within MTTR; If not replaced in a timely manner, the relevant SIF needs to be shut down (unless there are compensatory measures in the SRS document).
Calibration and testing: Regularly calibrate sensors/actuators, test SIF response time (≤ 1/2 of process safety time PST), and archive test records.
Backup and Update: Regularly backup system configuration (AADvance Workbench/SIS Workstation project) and test backup effectiveness; Firmware updates require the use of the ControlFLASH tool.
2. System security measures
Network security: it is forbidden to connect to the unprotected Internet; Computers need to have firewalls, antivirus software, and password protection enabled; The software license USB key needs to be properly kept.
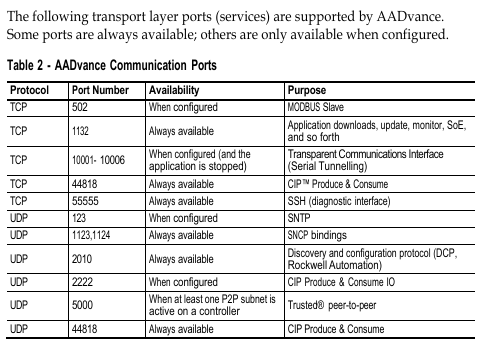
Port security: Some Ethernet ports (such as TCP 1132, UDP 2010) are open by default, and unused ports need to be closed through a firewall (refer to the configuration guide).
Program Security: The application requires password protection, and the controller needs to insert the "Program Enable Key" to modify the configuration; It is prohibited to force I/O points during operation, and it is recommended to use the program's "override" logic for maintenance.
Supporting documents and resources
1. Key related documents
Document Name Usage Description
AADvance Controller System Build Manual (ICSTT-RM448) System Assembly, Startup, and Operation Verification
AADvance PFH and PFDavg Data (ICSTT-RM449) Fault Probability (PFH/PFDavg) Data and Calculation Example
AADvance Troubleshooting and Maintenance Manual (ICSTT-RM406) System Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Repair
2. Support channels
Technical support: Get help through rok.auto/support, register an account to subscribe to product security notifications.
Document download: Download the latest manuals and firmware from Rockwell Literature Library (rok.auto/iterative) or Product Compatibility and Download Center (rok.auto/pcdc).
Key Terminology (Glossary Simplified)
SIL (Safety Integrity Level): Safety Integrity Level, levels 1-4, with SIL 3 being the highest level supported by the manual.
PST (Process Safety Time): The maximum time for triggering a hazardous event when a hazardous state exists and there is no protection. The controller defaults to PST=2500ms and needs to be adjusted based on sensor/actuator delay.
MTTR (Mean Time To Repair): The average time to repair, during which faulty modules need to be replaced to maintain SIL.
1oo2D/2oo3D: Fault tolerant configuration, 1oo2D (2 out of 1 with diagnosis), 2oo3D (3 out of 2 with diagnosis).

- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


