

K-WANG


YASKAWA AC Drive G7 Series (Model CIMR-G7U)
YASKAWA AC Drive G7 Series (Model CIMR-G7U)
Basic Information and Security Core Guidelines
1. Positioning
The core technical document of the G7 series communication drive (model CIMR-G7U) covers the entire lifecycle of product safety specifications, model specifications, installation and wiring, operation modes, parameter settings, trial operation and maintenance, troubleshooting, etc. The target audience is trained authorized personnel (installers, maintenance engineers, etc.) who must strictly follow the manual guidance to ensure the safe and stable operation of the equipment.
2. Core security standards that cannot be violated
(1) Electrical safety
The iron rule for power-off operation: Before wiring, removing the cover plate (terminal cover, front cover), and touching the circuit board, all power sources must be disconnected, and the internal capacitor must be discharged (at least 5 minutes until the CHARGE indicator light goes out). After the discharge is completed, the DC bus voltage (below 50Vdc) must be measured to confirm safety and avoid electric shock.
Prohibited live operation: It is strictly prohibited to connect/disconnect wires, plug and unplug digital operators with live power, and it is forbidden to remove the protective cover when the power is turned on, otherwise it may cause electric shock or equipment short circuit.
Power matching requirements: Before powering on, it is necessary to confirm that the rated voltage of the driver is consistent with the input power supply (200-240V level/380-480V level), otherwise it may cause a fire or equipment burnout.
(2) Equipment protection and operation restrictions
Prohibition of modification and withstand voltage testing: It is not allowed to modify the driver body or circuit without authorization (modification will directly result in warranty failure), and no component shall be subjected to withstand voltage testing - the equipment contains sensitive semiconductor devices, and high voltage can cause irreversible damage.
Output terminal limitation: The output terminals (U/T1, V/T2, W/T3) must not be connected to AC power, phase-shifting capacitors, LC/RC noise filters, or electromagnetic contactors (closing the contactor during operation will generate surge current, triggering overcurrent protection) 、 .
Static electricity protection: When in contact with the control board or CMOS IC, it is necessary to follow the ESD (electrostatic discharge) process (such as wearing an anti-static wristband) to avoid static electricity damaging the circuit.
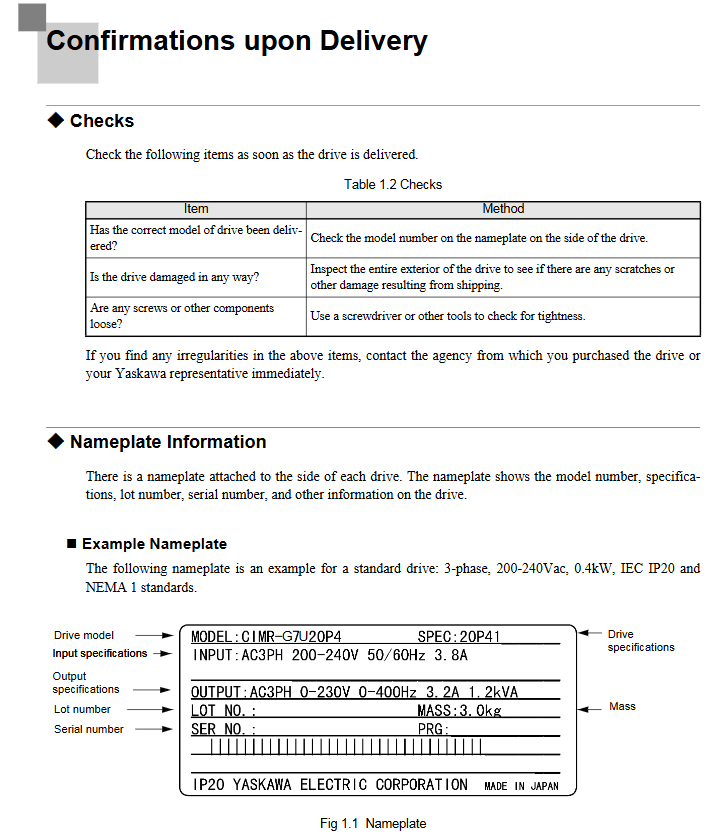
Product Model and Receipt Confirmation
1. Model system and specification classification
The G7 series drivers are divided by voltage level and protection type, covering different power requirements. The core parameters are as follows:
Classification dimension specific specification remarks
Voltage level 200-240V (3-phase): maximum motor capacity 0.4kW-110kW; 380-480V (3-phase): 0.4kW-300kW. In the model, "2" represents the 200-240V level, and "4" represents the 380-480V level (such as CIMR-G7U20P4 which has a 200V level of 0.4kW)
Protection type open enclosure (IEC IP00): to be installed inside the control cabinet; Enclosed wall mounted (IEC IP20/NEMA 1): can be directly wall mounted. Enclosed type requires the installation of a top protective cover to meet IP20 requirements
Output capacity of 200V level: 1.2kVA (0.4kW) -160kVA (110kW); 480V level: 1.4kVA (0.4kW) -460kVA (300kW) requires matching motor rated capacity (recommended 50% -100% driver capacity)
2. Receipt inspection and preparation
(1) Must check items
Model and appearance: Verify that the packaging label model matches the order, check that the drive housing is free of collisions or scratches, that the terminals are not deformed, and that the digital operator is not damaged.
Component integrity: Confirm that the packaging contains the driver body, digital operator, terminal cover, fixing screws (M3/M3.5, etc.), and installation manual (1 copy in both Chinese and English). If missing or damaged, immediately contact the supplier.
(2) Preparation before installation
Tool list: Cross screwdriver (M4/# 1/# 2), straight screwdriver (blade thickness 0.4mm/blade width 2.5mm), wire stripping pliers, 6mm wrench (tightening torque of 0.5-0.7N · m for bolts), wire crimping pliers (for crimping terminals).
Environmental confirmation: The installation surface should be made of non combustible materials such as metal, kept away from oil mist, dust, radioactive substances, and corrosive gases. The environmental temperature/humidity should meet the requirements (open type: -10~+45 ℃, ≤ 95% RH; closed type: -10~+40 ℃, ≤ 95% RH).
Full process specification for installation and wiring
1. Key installation requirements
(1) Installation location and space
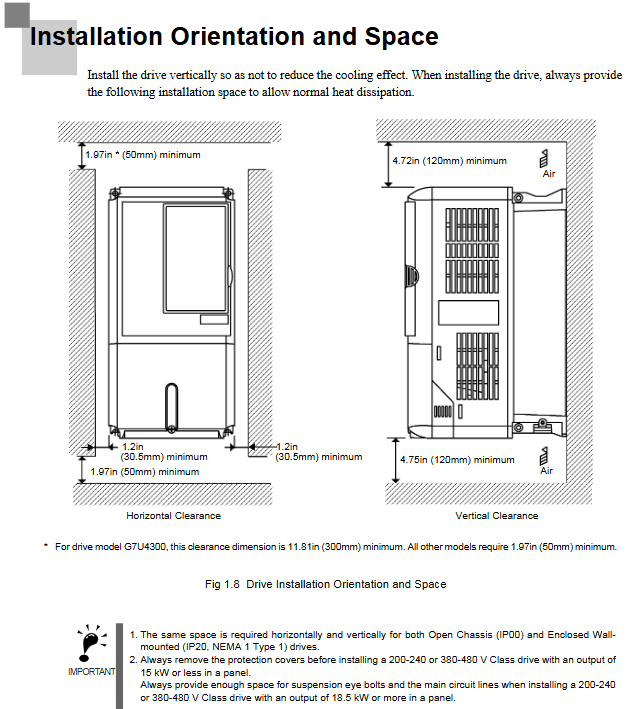
Installation direction: It must be installed vertically to avoid horizontal or inclined installation (which will reduce heat dissipation efficiency and cause overheating).
Cooling space: A minimum space of 50mm in the horizontal direction and 120mm in the vertical direction should be reserved for single installation. When multiple units are installed side by side, if the spacing is insufficient, a cooling fan or air conditioner should be installed in the control cabinet to ensure that the inlet air temperature is ≤ 45 ℃.
Special note: For models of 18.5kW and above, space for eyebolts and main circuit cables must be reserved. For enclosed installations of 15kW and below, top/bottom protective covers must be removed to meet heat dissipation requirements.
(2) Dismantling and resetting of cover plate
Terminal cover disassembly: Low power models (20P4-2015/40P4-4015): Loosen the bottom screws, press both sides and lift them up 30 ° before removing them; High power model (2018-2110/4018-4300): Loosen the top left and right screws, pull out and lift up.
Disassembly of digital manipulator: Press the side buckle of the manipulator and lift it up to remove it. When installing, the front cover should be installed first before installing the manipulator to avoid poor contact and malfunction.
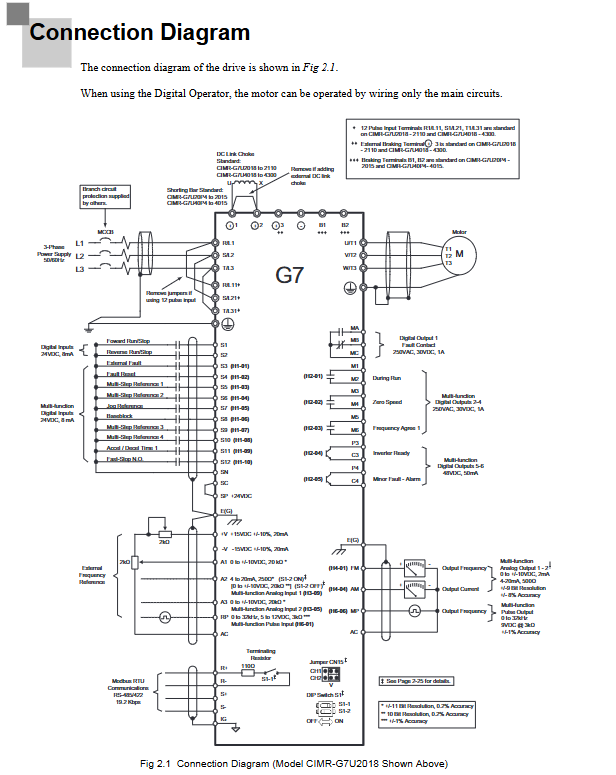
2. Wiring specifications (main circuit+control circuit)
(1) Main circuit wiring
Cable specifications: Select the appropriate cable according to the model (for example, 2mm ² (14AWG) cable is recommended for the main circuit of the 200V level 0.4kW model, and 325mm ² cable is required for the 480V level 300kW model), using UL certified copper wire (75 ℃ temperature resistance).
Terminal torque: The torque of different terminal screws varies, such as M4 screws with a torque of 1.2-1.5N · m and M8 screws with a torque of 9.0-10.0N · m. Loosening can easily cause heating and fire, while tightening can easily damage the terminals.
Grounding requirements: The grounding resistance for 200V level should be ≤ 100 Ω, and for 480V level it should be ≤ 10 Ω. The grounding cable should be independent (not shared with welding machines or power tools) and the length should be as short as possible. Multiple drivers should be grounded to avoid forming loops.
(2) Control circuit wiring
Cable requirements: Use shielded twisted pair cables (recommended 0.75mm ²/18AWG), separate them from the main circuit cables (spacing ≥ 30cm), and connect the shielding layer to the driver grounding terminal (E (G)).
Terminal function: The digital input terminals (S1-S12) are 24Vdc/8mA optocoupler isolated and used for forward and reverse rotation, fault reset, etc; Analog input terminals (A1-A3) support 0- ± 10V/4-20mA signals; The capacity of relay output terminals (MA/MB/MC, etc.) is 250VAC/30VDC/1A.
Wiring inspection: After completion, it is necessary to confirm that there are no broken wires touching other terminals, no foreign objects remaining, and screws tightened. It is prohibited to use a buzzer to detect the control circuit.
Operation mode and digital manipulator
1. Core operating mode
The drive includes 5 core modes, covering requirements such as parameter settings, operation monitoring, and self-tuning:
Mode Name Core Function Operation Scenario
Drive mode monitors operational data (frequency, current, voltage), checks fault information, performs start stop operations, daily operation monitoring, and troubleshooting
Quick programming mode (Quick) sets basic parameters (control mode, frequency reference source, acceleration and deceleration time, motor rated parameters) for the first trial run, quickly configuring core parameters
Advanced Programming Mode (Adv) for viewing/modifying all parameters (PID, torque compensation, carrier frequency, etc.) in complex application scenarios (such as PID control, multi-stage operation) that require fine tuning of parameters
Verify mode only displays parameters that are different from the factory default values to confirm the modification results and avoid missing them
Before vector control, ensure that the driver matches the motor characteristics (by disconnecting the motor load) in the self-tuning mode (A. Tune) for automatic calibration of motor parameters (rotation self-tuning/static self-tuning)
2. Use of digital manipulators
(1) Key function
The core buttons include: LOCAL/REMOTE (switch local/remote control), MENU (mode selection), ESC (return to previous level), JOG (jog operation), FWD/REV (forward/reverse selection), RUN/STOP (start/stop), DATA/ENTER (confirm input).
Fault reset: When the drive reports a fault, press the Shift/RESET key to reset (the cause of the fault needs to be confirmed first).
(2) Meaning of indicator lights
FWD/REV: lit up indicates that the current command is forward/reverse; ALARM: Constant illumination indicates a fault, while flashing indicates an alarm; RUN: Constant light indicates running, flashing indicates decelerating; STOP: Constant light indicates a stop, while flashing indicates a frequency lower than the minimum output frequency.
Core content of parameter settings
1. Required basic parameters
First use requires priority configuration of the following parameters to ensure the normal operation of the device:
Parameter number, parameter name, function description, factory default value (200V level 0.4kW)
A1-02 Control mode selection: 0=V/f control, 2=open-loop vector control 1 (default), 3=flux vector control 2
B1-01 frequency reference source selection 0=digital operator, 1=control terminal (analog input) 1
B1-02 Run Command Source Selection 0=Digital Operator, 1=Control Terminal (Contact Signal) 1
C1-01 Acceleration Time 1 Acceleration time from 0 to maximum frequency (seconds) 10.0s
C1-02 Deceleration time 1 Deceleration time from maximum frequency to 0 (seconds) 10.0s
E1-01 Input Voltage Setting Driver Rated Input Voltage (200V for 200V level, 400V for 480V level) 200V
E2-01 motor rated current The rated current on the motor nameplate (ampere) is 1.90A
L1-01 motor overload protection selection 1=standard fan cooling motor protection (default), 3=vector motor protection 1
2. Key Explanation of Functional Parameters
Self tuning parameters (T1 series): Set T1-01 to 0=rotational self-tuning (motor no-load operation calibration), 1=static self-tuning (motor does not rotate, only partial parameters are measured), and input the motor nameplate parameters (power, voltage, frequency, number of poles).
PID control parameters (b5 series): b5-01 set 1=PID enable, b5-02=proportional gain (default 1.00), b5-03=integration time (default 1.0s), used for closed-loop control of pressure, flow, etc.
Torque compensation parameter (C4 series): C4-01=torque compensation gain (default 1.00), increases when low load vibration occurs, and increases when low-speed torque is insufficient.
Trial operation and maintenance
1. Trial operation process
(1) No load trial operation
After confirming that the wiring is correct, turn on the power and check that the digital operator displays normally (without any fault codes);
Switch to LOCAL mode, set the low frequency (such as 5Hz), press the RUN button, and confirm that the motor rotates correctly (if reversed, swap any two output terminals U/T1, V/T2);
Gradually increase the frequency to the rated value, monitor the output current (there should be no abnormal fluctuations), and press the STOP button to confirm that the deceleration is normal.
(2) Load trial operation
Connect the motor and load after power failure to ensure that the mechanical system is unobstructed;
Starting from low frequency (10% rated frequency), check the stability of the load operation and ensure there are no abnormal noises or vibrations;
Gradually increase to the operating frequency and confirm that the output current is ≤ the rated current of the motor. If overcurrent/overload occurs, adjust the acceleration/deceleration time or check the load.
2. Maintenance and upkeep
(1) Daily inspection
Check the drive for any abnormal noise or odor, and ensure that the cooling fan is running normally;
Confirm that the digital operator displays normally without any fault/alarm codes;
Check that the terminal screws are not loose and the cables are not aged or damaged.
(2) Regular maintenance (every 6 months to 1 year)
Clean the dust inside the drive (using compressed air, pressure ≤ 0.3MPa);
Check the wear of the cooling fan bearings (replace if there is any abnormal noise);
Measure the capacitance of the main circuit (if it is lower than 80% of the initial value, it needs to be replaced).
Common fault handling
Fault code, fault cause, and solution measures
OC output short circuit, motor overload, short acceleration time. Check whether the output cable is short circuited, reduce the load, and extend the acceleration time (C1-01)
The UV input voltage is too low, the capacitor discharge is incomplete, and the power supply fluctuation confirms that the input voltage meets the requirements. Wait for the capacitor to fully discharge (≥ 5 minutes) and install a voltage regulator device
OL1 motor overload (exceeding thermal protection time), reduce load, check motor heat dissipation, adjust L1-02 (overload protection time)
PGO PG (encoder) disconnection, wiring error check PG cable connection, confirm PG model matches parameter F1-01 (PG pulse number)
- YOKOGAWA
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Energy and Gender
- Covid-19
- man-machine
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- Industrial information
- xYCOM
- Motorola
- architecture
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
ABB REF610 Protection and Control Relay
-
ABB DSQC633 Robot Control Interface Module
-
ABB DSQC332A Robot Control Module
-
ABB F362 Industrial Interface Module
-
ABB SK616001-A Industrial Control Module
-
ABB 3HAC0977-1 Robot Control Interface Module
-
ABB S503X Industrial Protection and Switching Device
-
ABB BC25 Industrial Automation Communication Interface
-
ABB DSQC504 Robot Servo and Control Module
-
ABB DSQC509 Robot I/O and Control Interface Module
-
ABB DSQC346B Robot Motion Control Board
-
ABB 3HAB8859-1/03A Industrial Robot Control Interface Board
-
ABB 3HAB9271-1/01B Robot Controller Communication Module
-
ABB 3HAC5497-1 Robot Control Processing Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


