

K-WANG


SIEMENS SIMATIC S7 300/400 operates MICROMASTER 4 (MM4) frequency converter through Profibus DP
Set value transmission: Loop the speed set value in the form of percentages from * * -100% to+100% * *, and any changes will take effect in real-time.
Status feedback: Output signals such as motor rotation direction (O-Right/O-Left), actual frequency (O-Actual_frequency, range -100% to+100%), and shutdown status (O-STOP).
SIEMENS SIMATIC S7 300/400 operates MICROMASTER 4 (MM4) frequency converter through Profibus DP
Core purpose and value of functional blocks
inverter control
Implement motor start stop: supports regular start stop (dependent on P1120 ramp up time, P1121 ramp down time) and quick stop (dependent on P1135 OFF3 ramp down time).
Set value transmission: Loop the speed set value in the form of percentages from * * -100% to+100% * *, and any changes will take effect in real-time.
Status feedback: Output signals such as motor rotation direction (O-Right/O-Left), actual frequency (O-Actual_frequency, range -100% to+100%), and shutdown status (O-STOP).
Automatic debugging
Batch/Replacement Scenario Adaptation: When debugging multiple MM4 units in bulk or replacing a single faulty unit, there is no need for PG/PC or professional debugging software. The PLC can automatically complete the parameter configuration of the new MM4.
Simplified debugging process: including quick debugging (P0010=1), motor recognition (requires motor cold state), and saturation characteristic recognition (only supported by MM440).
parameter management
Full parameter read and write: Read and write all parameters of MM4 through PKW communication, and the OP (operation panel) only supports parameter reading.
Parameter backup: Store the debugged parameters in the PLC's parameter DB (data block) for easy recovery in the future.
Diagnostic function
Multi dimensional error monitoring: covering MM4 faults/alarms, Profibus DP errors, parameter transmission errors, and automatic debugging errors.
Historical data recording: stores the latest and historical fault/alarm information (such as the fault codes and values of the last 3 faults), supports fault reset (I_RESET_Corr).
Scope and Limitations of Application
3.1 Applicable Equipment
Equipment type, specific model/specification
MM4 frequency converter MM411 V1.10, MM420 V1.17, MM430 V2.00, MM440 V2.05
Controller SIMATIC S7 300 (CPU 313-2DP and above) S7 400、C7、SINUMERIK
3.2 Not Applicable Devices and Limitations
Not applicable to controllers: SIMATIC S7 200, SIMATIC S5.
Function limitation: The system does not monitor whether the startup signal (I_Enable) meets safety conditions, and users need to provide additional protection in the program.
Installation and configuration process
4.1 Scenario without Drive ES Basic and Starter
Hardware configuration: Set the Profibus DP address of MM4 (no need to reset to factory settings).
HW Config operation:
Start HW Config in Step 7 and configure PLC hardware.
Select "MICROMASTER 4" in the "PROFIBUS-DP/SIMOVERT Catalog" and specify the DP address.
Select slot 1 and configure PPO type as PPO1 (4 PKW+2 PZD).
Program loading:
Save and compile HW Config, download to PLC module.
Copy the program blocks and symbol table from the functional block example to the user program, adapt them, load them into the PLC, and start them.
Debugging startup: Call the MM4 diagnostic interface of OP to troubleshoot DP errors, enter the debugging interface to enter motor data, start automatic debugging (set I2 Enable=0, I2 Enable QC=1, IOU_ Parameters=1), and execute motor recognition after completion.
4.2 Scenarios with Drive ES Basic and Starter
Hardware configuration: Follow step 1 of section 4.1 to set the DP address of MM4.
HW Config operation:
Configure PLC and MM4, select the corresponding MM4 version (refer to the equipment nameplate, such as "A01/2.05" corresponding to version 2.0x).
Pre allocate PPO type as PPO1 (PKW+PZD-2/2), fill in the I/O address of MM4 (PKW starting address, PZD address is PKW address+8).
Program and OP adaptation:
Load the program block and symbol table in step 3 of section 4.1.
Install OP project and adapt to "MM4" and "ParameterDB" text lists.
Debugging startup: The first debugging can be completed through Starter, and the parameters can be entered into the parameter DB; or the OP debugging interface can be directly called, and the subsequent process is the same as step 4 in 4.1.
Detailed explanation of key functions
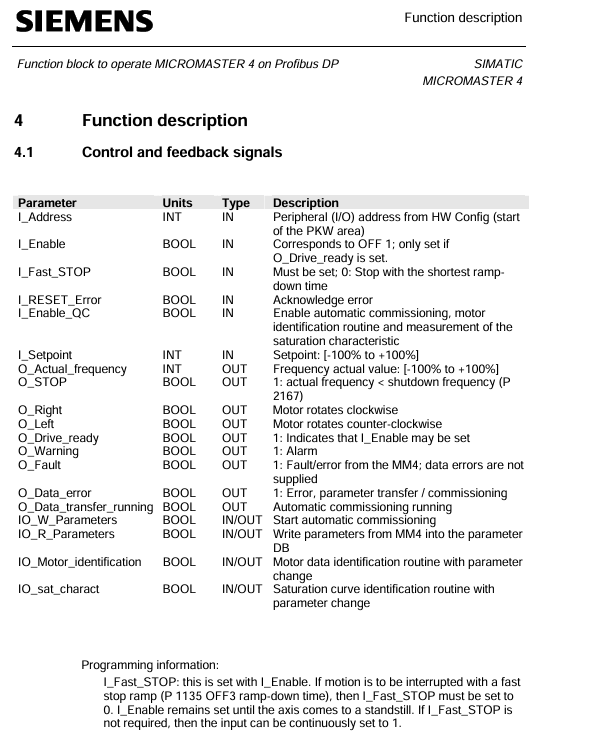
5.1 Definition of Control and Feedback Signals
Parameter Name Type Direction Unit/Range Description
The starting I/O address of the PKW area configured in the I-Address INT IN - HW Config
I-Enable BOOL IN - Variable frequency drive enable signal, can only be set when O-Drive-ready=1
I-Fast-STOP BOOL IN - Fast Shutdown Signal: 0=Fast Shutdown (using P1135), 1=Normal Shutdown (default can be set to 1)
Setpoint INT IN -100~+100 speed setting value (percentage)
Actual operating frequency INT OUT -100~+100 (percentage)
O-Drive-ready BOOL OUT - Inverter ready signal: must meet the requirements of "shutdown, I-Fast-STOP=1, no faults, no debugging in progress"
O-Fault BOOL OUT - MM4 fault signal (excluding data transmission errors)
O-Data_ error BOOL OUT - Parameter transmission/automatic debugging error signal
IOU_ Parameters BOOL IN/OUT - Start automatic debugging signal (user set 1 to start, clear 0 after FB is completed)
5.2 Automatic Debugging Process
5.2.1 Parameter DB adaptation
Motor data area: Enter the required parameters for quick debugging (P0010=1), using motor dataset 0 by default; Multiple parameter DBs need to be created for multiple datasets, which can be specified through Z_Sotor_data_SBNr.
Technical data area: Enter other parameters that are not quick debugging, support sub parameters (sub parameter 0 is the first, such as data [2] indicating the presence of sub parameters 0 and 1), and match the data type of the parameters.
5.2.2 Parameter input method
Operation steps for input method
Method 1: The frequency converter has been debugged and set to I2 Enable=0 and I2 Enable QC=1;
2. Set IOUR_Parameters=1 to start data reading;
3. O-Data_transfer_running=1 indicates that the transfer is in progress, and after completion, IOUR_Parameters will automatically clear 0.
Method 2: 1. Enter parameters directly on the OP interface (only display the parameters that need to be changed);
2. Use initial values for other parameters and support leaving the DB list empty (for easy OP indirect addressing).
5.2.3 Automatic Debugging Steps
Restore MM4 to factory settings.
Perform quick debugging (transfer motor data area parameters).
Transmission technology data area parameters.
Save the parameters to the EEPROM of MM4.
After debugging is completed, perform motor identification (ensuring that there are no errors during debugging and the motor is in a cold state).
5.3 Parameter transmission mechanism
Communication method: Based on PKW communication, it supports three parallel parameter read/write requests (Job_1~Job_3), which are executed in the order of Job_1 → Job_2 → Job_3.
Request block structure (taking Job_1 as an example):
|Parameter Name | Type | Initial Value | Description|
|Job_1. Parameter-N | INT | 0 | Target parameter number (e.g. 1002 represents fixed frequency 2)|
|Job_1. Index | INT | 0 | Sub parameter number (set 0 when there is no sub parameter, set the last sub parameter number when there are multiple sub parameters)|
|Job_1. Identifier | Byte | B # 16 # 0 | Operation type: 1=Read single parameter, 2=Write RAM, 3=Write EEPROM, 11=Read multiple sub parameters, etc|
|Job_1. Value_2~2 | DINT | L # 0 | Transferred parameter values (used as needed, such as using only Value_0 for a single parameter)|
Control signal: Job.RWRequest_1~3 are request trigger signals (user set 1 to start, clear 0 after FB is completed); Data_fault.Job.RWRequest_1~3 are error signals corresponding to the requests.
5.4 Diagnostic mechanism
5.4.1 Classification of Error Sources
Malfunctions/alarms of MM4 (such as overcurrent and overvoltage).
Fault of standard FC (SFC14/SFC15).
The functional block itself is malfunctioning.
Parameter transmission and automatic debugging errors.
5.4.2 Key diagnostic signals and displays
Parameter Name Type Direction Description
When there is an alarm for O-Warning BOOL OUT, it is 1
O-Fault BOOL OUT MM4 fault is 1 (excluding data errors)
Resetting signal: clearing MM4 fault and data error display, interrupting debugging process (without interrupting parameter transmission)
Data_fault.Nr. INT STAT error number (e.g. 0=illegal parameter number, 17=request execution not allowed in running state)
Data_fault.DP_Add_info HEX STAT DP error details (e.g. 8090=no module specified address, corresponding to SFC14/SFC15 error)
Error code description
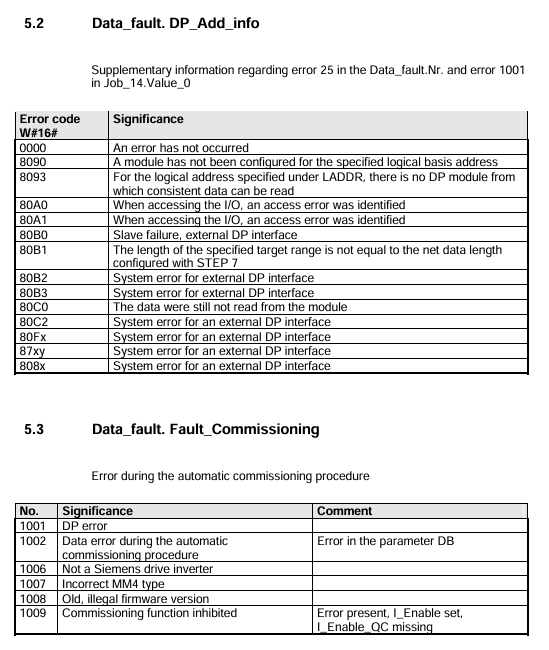
6.1 Data_fault.Nr. (Parameter transmission and debugging errors)
Error Number Meaning Remarks
0 Illegal Parameter Number (PNU) parameter does not exist in MM4
The parameter value cannot be modified. This parameter is a monitoring type parameter and can only be read
17. Due to operational status, the task cannot be executed. The current MM4 status does not support this request (such as changing motor data during operation)
25 DP error needs to be viewed in conjunction with Data_fault.DP_Add_info for details
Parameter number 1001 is currently not activated and depends on the running status of MM4. It can be operated after activation
6.2 Data_fault.DP_Add_info (DP Error Supplement)
Meaning of Error Code (W # 16 #)
8090 specifies logical address without configuration module
80A0 recognized access error while accessing I/O
The target range length of 80B0 does not match the network data length configured in Step 7
6.3 Data_fault.Fault_Commission
Error Number Meaning Remarks
1001 DP error needs to be investigated for Profibus DP connection and address configuration
1002 automatic debugging data error parameter DB has errors (such as parameter values exceeding the range)
1007 MM4 model incorrectly configured MM4 model does not match the actual connected device
Functional Block Technical Data
Project specifications
Block type FB
Block Name MM4
Generate language STL
Local data 36 bytes
MC7 code length 3166 bytes
Load memory requirement 4244 bytes
Working memory requirement 3202 bytes
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
- other brands
-
ABB PFEA113-20 Tension Measurement Module
-
ABB GDD471A001 Drive Control Board
-
ABB UCD224A103 Control Unit Module
-
ABB PDD205A1121 Power Drive Control Module
-
ABB DSPC454 Processor Module
-
ABB 81EU01E-E Excitation Control Module
-
ABB TK457V050 Control Cable Assembly
-
ABB DSRF197K01 I/O Interface Module
-
ABB TK802F Communication Cable Assembly
-
ABB 3BHE039203R0101 Control Interface Module
-
ABB 3BHB004027R0101 Power Control Board
-
ABB 3BHB003154R0101 Power Control Board
-
ABB PM864AK01-eA AC 800M Processor Unit
-
ABB CI868K01-eA Communication Interface Module
-
ABB 5SHY35L4520 IGCT Power Semiconductor Module
-
ABB UNS0119A-P V101 Control Interface Module
-
ABB GCC960C103 Control Communication Board
-
ABB GVC736CE101 Voltage Control Module
-
ABB PCD244A101 Control Processor Module
-
ABB GFD212A Ground Fault Detection Module
-
ABB PPD513 A2A‑11165 Industrial Automation Controller
-
ABB PDD200A101 Digital Processing Device
-
ABB SPIET800 Industrial Automation Interface Module
-
ABB SPAD346C3 Protection and Automation Device
-
ABB FPX86-9329--C Power Interface Board
-
ABB ARCOL0339 Precision Power Resistor
-
ABB 5SDF0860H0003 Phase Control Thyristor Module
-
ABB KUC720AE01 Drive Control Module
-
ABB UFC718AE01 Control Interface Unit
-
ABB 5SHX2645L0004 IGCT Power Semiconductor Module
-
ABB SPHSS03 High-Speed Signal Processing Module
-
ABB CB801 Communication Backbone Module
-
ABB DSAI130D Analog Input Module
-
ABB 086345-504 Industrial Interface Control Module
-
ABB PFCL201C 10KN Tension Measurement Module
-
ABB 3HAC17484-8108 Industrial Control Module
-
ABB 5SHY3545L0009 IGCT Power Semiconductor Module
-
ABB NPCT-01C Control Processing Module
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


