

K-WANG


YASKAWA Machine Controller MP2000 Series
Adaptive controller: MP2000 series machine controller (MP210M, MP2200, MP2300, MP2500MD)
Core functions: Support multi protocol industrial communication, data transmission between devices, engineering debugging and maintenance, and adapt to various interfaces such as RS-232C, Ethernet, DeviceNet, etc
YASKAWA Machine Controller MP2000 Series
Core positioning
Applicable products: JAPMC-CM23 model communication module, including 6 sub models: 218IF-01, 218IF-02, 217IF-01, 260IF-01, 261IF-01, 215AIF-01
Adaptive controller: MP2000 series machine controller (MP210M, MP2200, MP2300, MP2500MD)
Core functions: Support multi protocol industrial communication, data transmission between devices, engineering debugging and maintenance, and adapt to various interfaces such as RS-232C, Ethernet, DeviceNet, etc
Hardware specifications and installation configuration
1. Core parameters of the module
Module model, communication interface, key specifications, protection level, weight
218IF-01 RS-232C+Ethernet (10Base-T) serial port up to 19.2kbps; Ethernet 10Mbps, TCP/UDP protocol IEC IP00 85g
218IF-02 RS-232C+Ethernet (10Base-T) supports Ethernet (LP) mode, with larger engineering message size IEC IP00-
217IF-01 RS-232C+RS-422/485 serial port up to 19.2kbps, half duplex/full duplex optional IEC IP00-
260IF-01 RS-232C+DeviceNet supports DeviceNet master-slave communication, explicit/implicit message IEC IP00-
261IF-01 RS-232C+PROFIBUS compatible with PROFIBUS protocol, industrial bus communication IEC IP00-
215AIF-01 RS-232C+MPLINK/CP-215 supports token passing mechanism and link communication function IEC IP00-
2. Installation and wiring requirements
Environmental conditions: working temperature ≤ 55 ℃, no corrosive gases, vibration ≤ 9.8m/s ², avoid direct sunlight and condensation
Installation specifications: The module needs to be aligned with the guide rail and inserted into the controller slot, with a bolt tightening torque of 2.94N · m. Unused slots need to be equipped with dust covers
Wiring requirements: The distance between the control signal and the power line should be ≥ 30cm, and the grounding wire should be as short as possible (single point grounding); RS-422/485 adopts a 4-wire wiring system and requires 120 Ω terminal resistors to be connected at both ends
Port protection: The FG terminal needs to be reliably grounded, and the cable shielding layer should be connected to the equipment casing to avoid electromagnetic interference
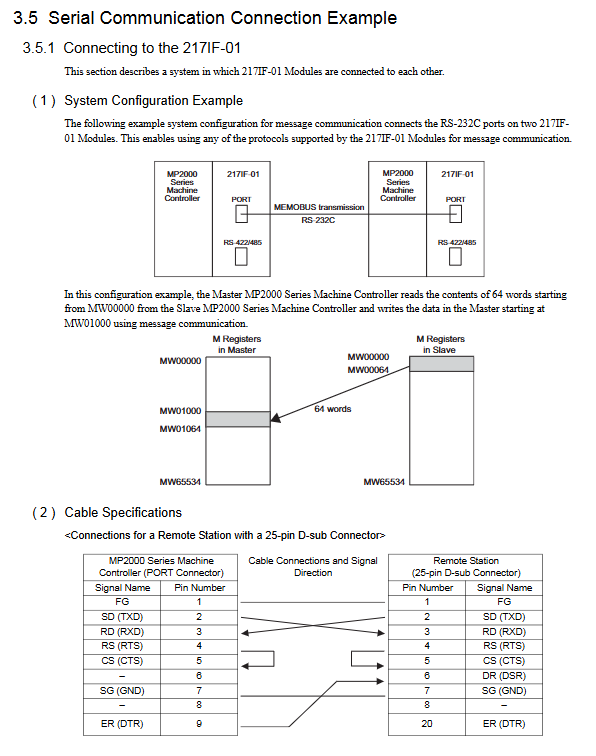
Communication mode and protocol system
1. Three major communication modes
Message communication: Triggered through MSG-SND/MSG-RCV functions, supporting master-slave data exchange and adapting to multiple protocols (MEMOBU, MELSEC, etc.)
Engineering Communication: Used for debugging communication between MPE720 programming software and controller, supporting interfaces such as serial port and Ethernet
Link communication: only applicable to 215AIF-01 module, automatically timed transmission of preset I/O data, based on token passing mechanism
2. Core Communication Protocol
Protocol Name Applicable Interface Core Features Application Scenarios
MEMOBU serial/Ethernet YASKAWA standard protocol, master-slave communication, supports coil/register read/write data transmission between devices of the same brand
Extended MEMOBU Ethernet/MPLINK Extended MEMOBU, supporting up to 508 words of data transmission for large data volume industrial communication
MELSEC serial/Ethernet compatible with Mitsubishi MELSEC PLC, supporting communication between CPUs, buffering communication, and cross brand PLC interconnection
MODBUS/TCP Ethernet Industrial General Protocol, client/server mode, cross vendor device compatible communication
OMRON serial port compatible with Omron SYSMAC PLC, Host Link mode Omron device integration
Non protocol full interface without preset protocol, directly transmitting continuous register data custom protocol scenario
DeviceNet 260IF-01 module device network protocol, supports explicit/implicit message industrial bus device interconnection
Software Configuration and Programming Implementation
1. Basic configuration process
Communication Manager Settings: Configure logical ports (up to 16), select port types such as serial/Ethernet/CP-215, and set parameters such as baud rate and IP address
Self configured execution: triggered by the DIP switch or MPE720 software of the controller, automatically identifies the module and generates a configuration file
MPE720 parameter settings: Start programming software and configure project communication parameters (logical port, IP address, protocol type)
Transmission definition configuration: Set transmission protocol, master-slave mode, data address, timeout time, etc. for different modules
2. Core programming functions
MSG-SND (Message Sending Function): sends data to remote devices, supports multi protocol selection, core parameters include execution bit, device type, protocol type, circuit number, parameter list address
Input parameters: Execute (start send), Abort (interrupt send), Dev Typ (device type), Pro Typ (protocol type), etc
Output parameters: Busy (processing), Complete (sending completed), Error (sending error)
MSG-RCV (Message Reception Function): Receive remote device data, support automatic/manual reception switching, core parameters correspond to the sending function
Support data offset storage, receive range limitation, and can monitor communication status and error messages
3. Programming Example Scenarios
218IF-01 Ethernet Communication: Master (IP 192.168.1.2) and Slave (IP 192.168.1.3) transmit 100 word data via UDP using Extended MEMOBU protocol
MELSEC PLC connection: Read the D0000-D0063 register data of Mitsubishi PLC, store it in controller MW10000-MW10063, and automatically convert it through MELSEC protocol
Non process protocol communication: Unidirectional transmission of 254 word continuous register data, no response mechanism, suitable for custom protocol interaction
Detailed operation of each module (taking 218IF-01/02 as an example)
Module 218IF-01
Interface specifications: RS-232C (9-pin D-sub)+Ethernet (RJ-45), supporting TCP/UDP protocols
Key settings:
Ethernet parameters: IP address (default 192.168.1.1), subnet mask 255.255.255.0, port numbers 256-65535
Serial port parameters: data bits 7/8, parity bits (odd/even/none), stop bits 1/2, baud rate 9600/19200bps
Communication example: Ethernet connection between modules, Master reads Slave's MW00000-MW00063 data through MSG-SND and stores it locally in MW01000-MW01063
Module 218IF-02
Core advantages: Supports Ethernet (LP) mode, larger engineering message size, faster communication speed
Unique settings: Ethernet (LP) is selected as the logical port, 9999 is set as the engineering port, and the IP address is compatible with 218IF-01
Connection example: Ethernet connection with a personal computer, engineering debugging through MPE720 software, supporting high-speed data transmission
Maintenance and troubleshooting
1. Key points for regular maintenance
Daily inspection: Terminal fastening, cleaning of heat sink (compressed air blowing), no damage to cables
Component replacement cycle: cooling fan 2-3 years, smoothing capacitor 5 years, motor bearing 2 years/12000 hours, fuse 10 years
Safe operation: Before maintenance, the power must be cut off and wait for the capacitor to discharge (CHARGE LED to turn off); Use insulated tools and do not touch CMOS components
2. Common troubleshooting
Common causes and solutions for fault phenomena
Communication timeout (ERROR light on) IP address conflict, port number error, transmission parameter mismatch check network configuration, unified baud rate/checksum and other parameters
Data transmission error: loose wiring, ungrounded shielding layer, electromagnetic interference: re tighten terminals, optimize wiring (away from power lines), and rectify grounding
Hardware malfunction (ERR light flashing) ROM/RAM error, module not recognized, perform self diagnostic test, replace control board, reinstall module
Ethernet connection failure, network cable damage, switch failure, IP configuration error. Replace the network cable, check the switch status, and confirm that the IP is in the same network segment
3. Fault reset method
Trigger reset input signal, press the [RESET] button on the operator, turn off the main circuit power and restart
Reset premise: eliminate the cause of the fault and turn off the external operation command (FWD/REV/ORT)
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


