

K-WANG


REXRTOH MDD Digital AC Servo Motors
Deep Analysis and Application Guide of Rexroth Indramat MDD Digital AC Servo Motor Technology
In the field of modern industrial automation, servo motors serve as the core power source for precise motion control, and their performance directly determines the machining accuracy and dynamic response speed of machine tools, packaging machinery, printing, and robot systems. The MDD (Mannesmann Rexroth Indramat) series digital AC servo motors have become the preferred choice for cost-effective automation systems due to their excellent power density and synchronization characteristics. This article will delve into the technical parameters of the MDD series, covering models from compact MDD 021 to high dynamic MDD 115. Combining engineering practice, it will explore their mechanical design, electrical connections, thermal management, and environmental adaptability, providing engineers with a detailed selection and application guide.
Introduction: Modular Design for Industrial Drive Solutions
The MDD series is an intelligent digital AC servo motor series launched by Mannesmann Rexroth, aimed at achieving cost-effective and fast response automation systems through modular design. This series includes nine motor models with different torques and speeds, which can meet various needs from simple feed axis motion to extreme dynamic applications. When used in conjunction with Indramat intelligent digital drive controllers, MDD servo motors can create an automated solution that is both economical and has high-speed response characteristics.
Core technology architecture and high-performance features
2.1 Permanent magnet technology: low inertia and high dynamics
The rotor of MDD servo motor is made of rare earth or ferrite magnetic materials. This material gives the motor rotor an extremely low moment of inertia. Low inertia is a key indicator of the dynamic performance of servo systems. A lower rotor inertia means that the motor can accelerate and decelerate faster, which is crucial for applications such as packaging printing and CNC machine tools that require extremely high acceleration and dynamic performance.
2.2 Brushless design and maintenance free
Brushless design: Traditional brushed DC motors require regular maintenance due to carbon brush wear, which not only increases downtime but also generates dust.
Maintenance free: The MDD series adopts a brushless design, completely eliminating the maintenance needs caused by carbon brush wear, greatly improving the reliability of the system, and suitable for long-term continuous operation without frequent maintenance.
2.3 High overload capacity and heat conduction
Wide speed regulation range: The motor can maintain high torque within a wide speed range, which is particularly important for packaging machine spindle applications that require constant torque and wide speed regulation. *Efficient heat conduction: The heat generated by the stator winding can be efficiently conducted to the motor housing and cooling air duct, which gives the motor excellent overload capacity.
Series Overview and Application Fields
The MDD series is divided into nine main model series based on torque and speed range. Each model has been optimized for specific loads and applications:
Compact (MDD 021): Designed specifically for screw drives, auxiliary shafts, and tool changers. Suitable for packaging, printing, and auxiliary applications.
High dynamic type (MDD 065, 071, 093): Due to its extremely high power density and overload capacity, it is suitable for high dynamic applications such as roller feed, stamping, punching, and tool changing devices.
High precision type (MDD 090, 112, 115): used for applications that require extremely high synchronicity, such as grinding machines.
Powerful type (MDD 112, 115): As a spindle or tool replacement device, suitable for spindle drives with high torque requirements.
Electrical Connection and Feedback System
4.1 Power Supply and Braking Control
MDD servo motors support integrated electrical connections, simplifying system wiring. The motor power cable integrates power connection, brake control, and temperature monitoring functions. This avoids the complexity of on-site wiring and ensures the reliability of the connection.
Temperature monitoring: The built-in temperature sensor continuously monitors the temperature of the stator winding to prevent overheating damage and improve the lifespan of the motor.
Brake control: Supports external brake connection for static holding of the shaft. The brake holds when the power is off and releases when the power is on. Intelligent digital drivers automatically manage opening and closing timing.
4.2 Feedback device and encoder system
The MDD series supports high-performance motor feedback systems, including parsers and digital servo feedback. This allows users to choose the most suitable technical solution based on their accuracy requirements.
Parser Feedback (RSF): Suitable for harsh environments, sturdy and durable, providing relative position detection.
Digital Servo Feedback (DSF): A high-resolution optical system that provides absolute position detection and is suitable for precise positioning.
Mechanical design, installation, and thermal management
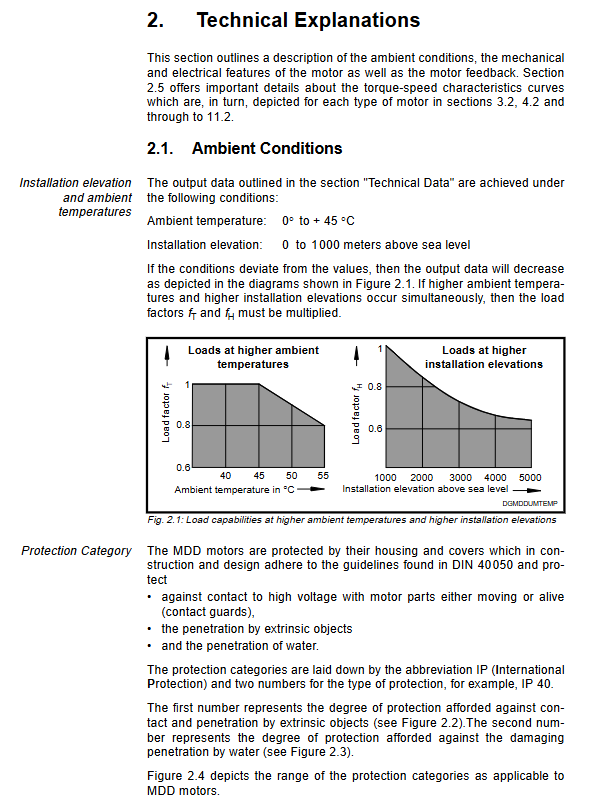
5.1 Installation direction and load bearing capacity
Standard flange installation: All motors support IM B5 flange installation (through-hole).
Threaded flange (IM B14): Some models support IM B14 flange installation (with threaded holes).
Shaft seal: For applications that require dust and water resistance (IP 65), an option with shaft seal is available.
5.2 Bearing Capacity Calculation and Life
Engineers must correctly calculate the radial and axial forces borne by the shaft to avoid shortening the bearing life.
Radial force F_radial: The radial force depends on the average velocity and the distance from the point of action. The document provides detailed calculation charts. For high loads, the bearing life will sharply decrease in a cubic relationship.
Axial force: Axial force is usually less than radial force. The axial force calculation formula is Faxian=0.34 * Fradial (where Fradial is the allowable radial force). Excessive axial force can cause damage to the B-side bearing.
5.3 Surface Cooling and Options
For extreme load conditions, natural cooling may not be sufficient for heat dissipation. Larger models in the MDD series (such as MDD 065 and above) support surface cooling options (fans). *Axial cooling: suitable for scenarios that require a compact structure.
Radial cooling: suitable for scenarios that require short structures.
Cooling system and option expansion
In order to cope with high-frequency start stop and high load, the MDD series provides modular cooling solutions.
Fan model: Provides 1xAC 230V and AC 115V power supply, operates independently.
Options: Includes thermal protection switch and installation components to ensure safety.
Selection and Order Information
Selection is a crucial step in system integration. The correct selection code determines the function, interface type, and accessories of the motor.
7.1 Analysis of Model Code Structure
The model codes of the MDD series strictly follow specific logic.
Structure: For example, in MDD 090 B-N-020, 90 represents the serial number (90), 020 represents the length code, and B represents the standard design.
Feedback options: G represents parser feedback, K represents integrated pulse absolute encoder.
Braking options: 0 represents no braking, 1 represents braking.
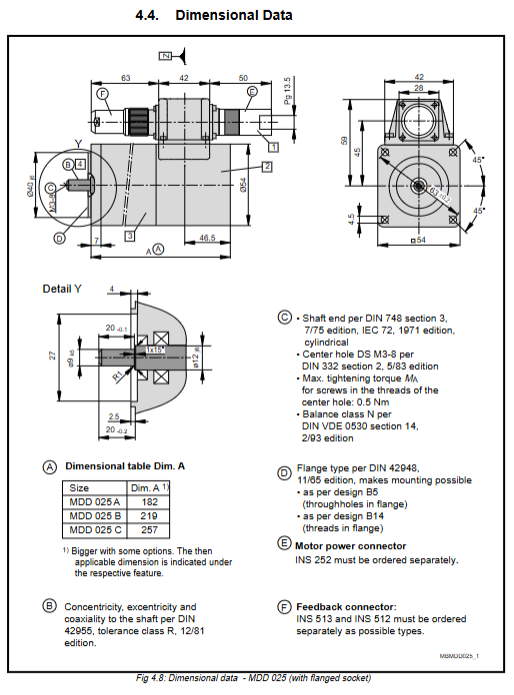
7.2 Dimensional Data and Interface Configuration
The technical documentation contains detailed data for all models and is the final step in mechanical integration.
- YOKOGAWA
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Energy and Gender
- Covid-19
- man-machine
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- Industrial information
- xYCOM
- Motorola
- architecture
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
-
ABB UFC092BE01 Universal Field Controller Module
-
ABB UNS2980c-ZV4 Advanced Industrial Control Module
-
ABB UNS0874A Industrial Energy Management Module
-
ABB 5SHY3545L0003 Advanced Industrial Power Protection Module
-
ABB 5SHY35L4510 High-Speed Circuit Breaker Module
-
ABB DSDP140B Distributed Control System Module
-
ABB DAPC100 High-Performance Automation Control Module
-
ABB DSQC545A Servo Drive Module
-
ABB PM861AK01 Programmable Logic Controller Module
-
ABB 57160001-KX Communication Interface Module
-
ABB EI813F Intelligent Energy Interface Module
-
ABB IEPAS01 Power and Signal Interface Module
-
ABB AI845 Analog Input Module
-
ABB PM803F Safety CPU Module
-
ABB 3HAC4776-1/1 Industrial Control Module
-
ABB IMASI23 Analog Signal Interface Module
-
ABB YB560100-EA S3 Power Interface Module
-
ABB XO16N1 Digital Output Module
-
ABB XM06B5 Analog Input Module
-
ABB XI16E1 Digital Input Module
-
ABB V4550220-0100 Industrial Automation Module
-
ABB TU804-1 Terminal Unit Module
-
ABB TK516 Industrial Control Module
-
ABB TC625 Communication Interface Module
-
WATLOW LLS200212 E257034 Accessory Line - CLS208 Compatible
-
WATLOW ANAFAZE 997D-11CC-JURG Controller - Industrial Temperature Regulation
-
WATLOW CLS2163C1 Temperature Controller - High-Precision Industrial Control
-
WATLOW PPC-TB50 30280-00 Temperature Controller - Industrial Process Control
-
WATLOW NLS300-CIM316 Temperature Controller - Industrial Precision Control
-
WATLOW MLS300 Temperature Controller - High-Performance Thermal Management
-
WATLOW CAS16CLS/CAS Temperature Controller - Advanced Industrial Control
-
WATLOW CAS200 CLS216 Temperature Controller - Industrial PID Solution
-
WATLOW CLS208 Temperature Controller - Precision Industrial Control
-
HIMA K9212 Fan Assembly
-
ABB 500TRM02 Termination Module | 1MRB150011R1
-
ABB 500AIM02 Analog Input Module | 1MRB150022 R0002Y | 1HDF 930412 X010
-
ABB 500MTM02 Interface Module | 1MRK001967-AA | 1HDF 930512 X010
-
ABB 500CSP04 Power Supply Module | HE401314/0002 | 1MRB150051R2
-
ABB 500CIM05 Communication Interface Module | 1MRB150077R1/B
-
ABB 500PSM03 Power Supply Module
-
ABB 500MBA02 Memory Backup Module
-
ABB 500AIM02 Analog Input Module
-
ABB 500CPU05 Central Processing Unit Module
-
ABB 500TTM02 Temperature Transmitter Module
-
ABB 500BIM01 Binary Input Module (1MRB150024R0002)
-
ABB 500MBA01 Memory Backup Module (1MRB150003R0002)
-
ABB 500BIO01 Binary Input/Output Module 1MRB150005R1
-
ABB 500BOM01 Binary Output Module 1MRB150023R0002
-
ABB 500CIM05 Communication Interface Module 1MRB150077R1/B
-
ABB 500CMP04 Control Module HE401314/0001 1MRB150051R1
-
ABB 500CSP04 Control System Processor Module
-
ABB 500MBA02 Memory Backup Module
-
ABB 500MTM02 Measurement Module
-
ABB 500PB101 Processor Bus Module
-
ABB 500PSM03 Power Supply Module
-
ABB 500SCM01 System Communication Module
-
ABB 500TTM02 Temperature Transmitter Module
-
ABB TA524 Temperature Monitoring Module – Industrial Thermal Safety
-
ABB SR511 Signal Relay – Industrial Signal Control
-
ABB SPCJ4D34-AA Programmable Controller – Advanced Industrial Control
-
ABB SPAD346C Digital Automation Controller – Industrial Process Control
-
ABB SE96920414 YPK112A Motor Protection Relay – Reliable Motor Control
-
ABB SC513 Control Relay – Industrial Automation Control
-
ABB SB512 Safety Relay – Industrial Safety Control
-
ABB SAFT103 Battery Monitoring Module – Reliable Power Management
-
ABB SA801F Safety Automation Module – Industrial Machine Protection
-
ABB RF615 Feeder Protection Relay – Reliable Industrial Power Safety
-
ABB REF542PLUS Protection Relay – Advanced Power System Protection
-
ABB RB520 Remote I/O Module – Reliable Industrial Connectivity
-
ABB R1.CAIR Air Circuit Breaker – Industrial Power Protection
-
ABB PU515A Processor Unit – Advanced Automation Control
-
ABB PS130/6-75-P Power Supply – Reliable Industrial Power
-
ABB PM630 Protection Relay – Advanced Industrial Protection
-
ABB NAIO-03 Analog I/O Module – Industrial Signal Control
-
ABB MSR04XI Safety Relay Module – Industrial Safety Control
-
ABB M2004HW Motor Module – Precision Industrial Motion
-
ABB L110-24-1 DC Power Supply – Reliable Industrial Power
-
ABB IMMPI01 Motor Interface Module – Robust Industrial Control
-
ABB IMMFP12 Motion Feedback Processor – Accurate Motion Control
-
ABB IMFEC12 Fieldbus Encoder Module – Precision Industrial Feedback
-
ABB IMDSI14 Digital Signal Interface – Robust Industrial Connectivity
-
ABB EI803F Encoder Interface – Accurate Position Feedback
-
ABB EHDB280 Digital Output Module – Industrial Control Interface
-
ABB EHDB130 Digital Input Module – Reliable Industrial Sensing
-
ABB DSQC627 Robot Controller – Advanced Automation Control
-
ABB DSQC608 Robot Controller Interface – High-Reliability Control
-
ABB DSQC346U Servo Drive Module – Advanced Robot Control
-
ABB DSQC327A Robot Servo Drive – High-Performance Motion Control
-
ABB DSPC406 Robot Interface & Power Module – Industrial Automation
-
ABB 07KT97B Control Logic Module – Efficient Industrial Automation
-
ABB PU516 Processor Board – High-Performance Industrial Control
-
ABB DSIH72VP ENOK Interface Unit – Reliable Industrial Connectivity
-
ABB DSBB175 System Board Module – Central Control Backbone
-
ABB DSAO110 Analog Output Module – Precision Industrial Control
-
ABB DRA02 Card Rack Module – Modular Automation Framework
-
ABB DPW01 Power Supply Module for ABB Control Systems
-
ABB DLM01 Load Management and Distribution Module
-
ABB DAO01 Analog Output Module
-
ABB D-20-0-1102 Digital Input Module
-
ABB CP450-T-ETH Touch Panel Operator Interface
-
ABB CI520V1 Communication Interface Module
-
ABB BRC300 Controller
-
ABB BB510 (DC5256) Control System Module
-
ABB AX411/50001 Communication Interface Module
-
ABB AO610 Analog Output Module
-
ABB AI835 Analog Input Module
-
ABB AI625 Analog Input Module
-
ABB AI610 Analog Input Module
-
ABB 3HNA000512-001 Robot Automation System Component
-
ABB 3HAC17326-1/02 Robot Controller Component
-
ABB 3HAC14550-2/09A Industrial Robot Control Component
-
ABB 3HAC031683-001 Robot Control System Component
-
ABB 3HAC025466-001 Robot Automation Component
-
ABB 3HAB8101-8/08Y and Related Robot Control Components
-
ABB 3HAB3700-1 Automation Module
-
ABB 3BHB003689 Control Board
-
ABB 3ASC25H204 Control Board
-
ABB 3ASC25H203 Control Board
-
ABB 35AE92 Control Module
-
ABB CP800 Control Panel
-
KEBA JB241 22336 - HT Junction Box
-
KEBA EC100A03/C0L/C AN/4MB/53890 - PLC Chassis 16-Slot Rack Motherboard
-
KEBA GVME-610-I/O - VME I/O Module
-
KEBA SX TPU 2 16/64 3HAC023195-001 - Teach Pendent Connector Cable 10M
-
KEBA HT4 / HT.4 - Hand Terminal Keypad
-
KEBA KEMRObus-8 22393 - Rack Bus System
-
KEBA FM 265/A 067215 - Kemro K2-200 Module
-
KEBA II030 / II 030 A 22360 - Engel Interface Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


