

K-WANG


Emerson S Series Traditional I/O Modules
Module Category Core Usage Typical Model Example Key Features
The digital input (DI) module collects discrete signals from industrial sites (such as sensor and limit switch status), converts them into system recognizable digital signals SDI810 and SDI820, supports dry/wet contact input, has photoelectric isolation function, strong anti-interference ability, and some models support "event capture" (such as edge detection)
Emerson S Series Traditional I/O Modules
Overview of S Series I/O Module Core
Product series classification
The S series I/O modules are divided into four categories based on "signal type" and "functional characteristics". The core uses and typical models of each module are shown in the table below:
Module Category Core Usage Typical Model Example Key Features
The digital input (DI) module collects discrete signals from industrial sites (such as sensor and limit switch status), converts them into system recognizable digital signals SDI810 and SDI820, supports dry/wet contact input, has photoelectric isolation function, strong anti-interference ability, and some models support "event capture" (such as edge detection)
The digital output (DO) module receives control instructions from the system output and drives actuators (such as solenoid valves and indicator lights) to operate. SDO810 and SDO820 provide two types of outputs: transistor output and relay output. The transistor output has a fast response (microsecond level) and the relay output is resistant to high voltage (suitable for high-power loads)
The Analog Input (AI) module collects continuously changing analog signals (such as 4-20mA/0-10V signals output by temperature, pressure, and flow sensors), performs signal conditioning and AD conversion. SAI810 and SAI830 support single ended/differential input, with a maximum resolution of 16 bits, and have cold end compensation (thermocouple input model) and signal filtering functions to reduce on-site noise interference
The Analog Output (AO) module converts the digital control signals output by the system into analog signals (4-20mA/0-10V), and controls analog actuators such as regulating valves and frequency converters. SAO810 and SAO820 have high output accuracy (error ≤± 0.1% of full scale), support "manual output" function (fixed values can be output without system instructions during debugging), and have short-circuit protection
Common technical characteristics
High reliability design: All modules use "industrial grade components" with a working temperature range covering -40 ℃~70 ℃ and a humidity tolerance range of 0~95% (non condensing). Some modules have an IP20 protection level (suitable for installation in control cabinets) and are suitable for harsh industrial environments.
Isolation and anti-interference: The module adopts "photoelectric isolation" or "magnetic isolation" technology internally, and the input/output circuit is isolated from the system power circuit (isolation voltage ≥ 2500V DC), effectively suppressing on-site common mode interference and series mode interference, and ensuring signal transmission stability.
Hot swappable function: Supports "online hot swappable". When replacing modules, the system power does not need to be cut off, only the connection between the module and the base needs to be disconnected, reducing system downtime and improving operation and maintenance convenience (some early models need to confirm whether this function is supported, please refer to the specific model manual).
Diagnosis and status indication: Each module is equipped with LED status indicator lights (such as "power normal", "signal normal", "fault alarm"), which can intuitively judge the operating status of the module; Simultaneously supporting "remote diagnosis", monitoring the real-time status of modules (such as channel faults and overloads) through the DeltaV/Ovation system, and generating diagnostic reports.

Key module technical specifications
Core parameters of digital I/O module
Digital Input (DI) Module:
Input signal type: dry contact (no power supply), wet contact (external power supply, such as 24V DC).
Input voltage range: 18~30V DC (wet contact), dry contact supports "contact closing resistance ≤ 10 Ω, open circuit resistance ≥ 1M Ω".
Response time: fastest 1ms (high-speed DI models, such as SDI820), regular models ≤ 10ms.
Number of channels: A single module supports 8/16 inputs, with channels isolated from each other (some models use group isolation, such as every 4 channels).
Digital Output (DO) Module:
Output types: transistor output (24V DC, maximum load current 0.5A/channel), relay output (250V AC/30V DC, maximum load current 2A/channel).
Output protection: The transistor output has "short-circuit protection" (automatic current limiting in case of overload), and the relay output has "mechanical life ≥ 1 million times" (no load) and "electrical life ≥ 100000 times" (rated load).
Number of channels: A single module supports 8/16 outputs, and some models of relay output modules support "normally open/normally closed" configurable.
Simulate the core parameters of the I/O module
Analog Input (AI) Module:
Input signal types: current signal (4-20mA, 0-20mA), voltage signal (0-5V, 0-10V), thermocouple (J/K/T/E/R/S/B type), thermistor (RTD, Pt100, Cu100).
Resolution: The current/voltage input is 16 bits, and the thermocouple/RTD input is 18 bits (some high-precision models).
Accuracy: Full scale error ≤ ± 0.1% (25 ℃ environment), temperature drift ≤ ± 0.005% full scale/℃.
Sampling rate: Single channel up to 100Hz (high-speed AI models), regular models ≤ 50Hz, supports configurable "channel scanning period" (such as 100ms/200ms).
Analog Output (AO) module:
Output signal types: current signal (4-20mA, load resistance ≤ 500 Ω), voltage signal (0-10V, load resistance ≥ 1k Ω).
Resolution: 16 bits.
Accuracy: Full scale error ≤ ± 0.1% (25 ℃ environment), output ripple ≤ 10mV (peak to peak).
Response time: From 0% to 100% full-scale output ≤ 100ms (current output), ≤ 50ms (voltage output).
Installation and Configuration Guide
Hardware installation process
Installation environment requirements: The module needs to be installed in a standard 19 inch industrial control cabinet, avoiding direct sunlight, dust, corrosive gases, and severe vibrations; The control cabinet needs to reserve a heat dissipation space (with a distance of ≥ 50mm between the top and bottom of the module). If the ambient temperature exceeds 55 ℃, a heat dissipation fan or air conditioner should be equipped.
Installation steps:
First, fix the I/O base (matching the module model) onto the DIN rail of the control cabinet, ensuring that the base is securely installed and not loose.
Connect the power cable (usually 24V DC, pay attention to positive and negative polarity) and communication cable (connected to the I/O link of the DeltaV/Ovation system, such as PROFIBUS, EtherNet/IP) to the base.
Align the module with the card slot on the base, insert it vertically and press it until it makes a "click" sound, and confirm that the module is in good contact with the base (when hot plugging, the signal circuit of the module needs to be disconnected first before plugging).
Connect on-site signal lines: Digital signals use shielded twisted pair cables (with a single end grounded on the shielding layer), while analog signals use shielded twisted pair cables (with both ends grounded on the shielding layer) to avoid parallel laying with power cables (spacing ≥ 300mm).
System configuration steps
Software tool: Use DeltaV Explorer (adapted to DeltaV system) or Ovation Configuration Studio (adapted to Ovation system) for module configuration.
Configuration process:
Add the "S series I/O module" to the software, select the corresponding module model (such as SDI810, SAI830), and assign a unique "module address" (consistent with the hardware dip switch settings to avoid address conflicts).
Configure channel parameters:
Digital input module: Set the "input type" (dry/wet contact), "edge detection" (rising/falling edge), and "filtering time" (such as 1ms/10ms to suppress noise).
Digital output module: Set the "output type" (transistor/relay) and "fault handling" (such as output hold/reset in case of fault).
Analog input module: Set the "signal type" (4-20mA/Pt100/J thermocouple), "range" (such as 4-20mA corresponding to 0-100kPa pressure), and "cold end compensation method" (internal compensation/external compensation, thermocouple input).
Analog output module: Set the "signal type" (4-20mA/0-10V), "range", and "manual output value" (for debugging purposes).
Download the configuration file to the module, and after completion, monitor the module's "online status" through software to confirm that there are no configuration errors (such as "address conflicts" or "signal mismatches").
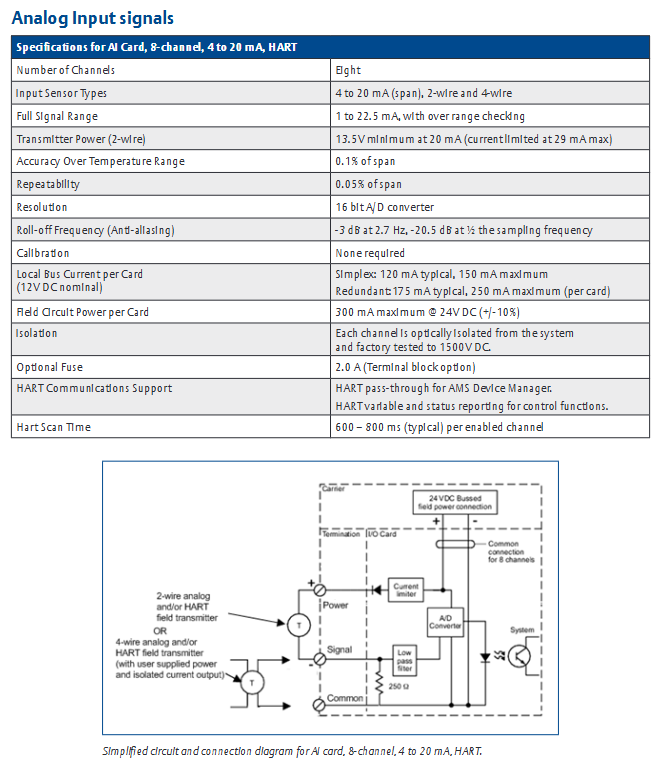
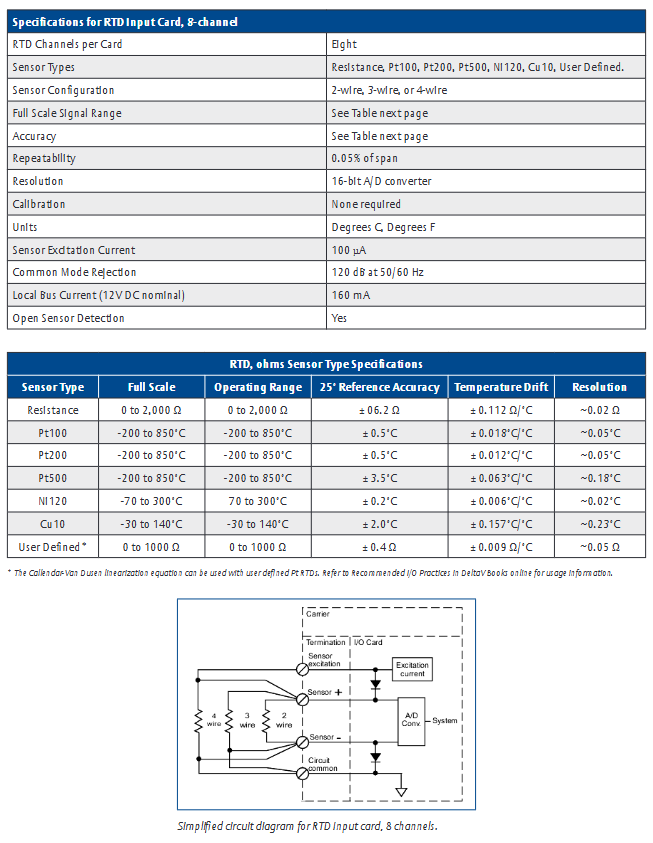
Functional characteristics and application scenarios
Core functional highlights
Signal conditioning function: The analog I/O module has a built-in "signal conditioning circuit" that can amplify and filter weak signals collected on site (such as mV level signals from thermocouples) to reduce noise interference; Simultaneously supporting "disconnection detection" (such as triggering a fault alarm when the RTD is open or the current signal is disconnected).
Redundancy configuration support: Some key modules (such as analog input and digital output modules) support "1:1 redundancy", which means that the main module and backup module run simultaneously. When the main module fails, the backup module automatically switches (switching time ≤ 100ms) to ensure that the control circuit is not interrupted. This is suitable for safety critical scenarios (such as emergency shutdown systems in petrochemicals).
System Integration: The module seamlessly integrates with the DeltaV/Ovation system, supporting "global database" sharing. The signals collected by the module can be directly used for the system's control algorithms, alarm logic, and historical data storage; Simultaneously supporting the OPC protocol, it can communicate with third-party systems (such as MES production execution systems) to achieve data exchange.
Safety certification: Some modules have passed "ATEX certification" and "IECEx certification" and are suitable for explosive hazardous environments (such as Zone 2, Class I Division 2); Simultaneously complying with the "EN 61000" electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standard, it has strong resistance to electromagnetic radiation and electrostatic discharge.
Typical application scenarios
Petrochemical industry: used to collect temperature (thermocouple/RTD input) and pressure (4-20mA input) signals of reaction vessels, drive the action of feed valves and discharge valves through digital output modules, and control the opening of regulating valves through analog output modules to achieve precise control of the reaction process.
Power industry: Suitable for Ovation control system in thermal power plants, collecting steam pressure and water level of boilers (4-20mA signal from differential pressure transmitter), controlling the speed of feed pumps through analog output module, and monitoring the operating status of fans and pumps through digital input module (such as overload alarm).
Water treatment industry: The digital input module collects the status of liquid level switches and flow switches, the analog input module collects signals from water quality sensors (such as pH and turbidity), and the digital output module drives solenoid valves and water pumps to achieve automated start stop and regulation of the water treatment process.
Fault diagnosis and maintenance
Common faults and troubleshooting methods
The document provides a "fault diagnosis flowchart" and provides troubleshooting steps for typical module faults. The core fault types and solutions are as follows:
Possible causes and solutions for fault phenomena
Module "power light not on" 1. The base power cable is not properly connected or disconnected; 2. Abnormal power supply voltage (such as below 18V DC); 3. Internal power failure of the module: 1. Check the connection of the power cable (whether the positive and negative poles are reversed); 2. Measure the power supply voltage with a multimeter to ensure it is within the range of 18-30V DC; 3. Replace the module and test if it returns to normal
Digital input module "no signal input" 1. On site signal line breakage or poor contact; 2. Input type configuration error (such as configuring dry contacts as wet contacts); 3. The filtering time is set too long. 1. Check the continuity of the on-site signal line (measure the contact resistance with a multimeter); 2. Verify that the "input type" configured in the software matches the actual wiring; 3. Reduce filtering time (such as changing from 10ms to 1ms)
Analog output module "no output signal" 1. Output channel fault; 2. Range configuration error (such as 4-20mA configured as 0-10V); 3. Load resistance exceeds the rated range. 1. Switch to "manual output" mode and observe if there is any output; 2. Verify the range configuration and re download the configuration file; 3. Measure the load resistance to ensure that the current output load is ≤ 500 Ω and the voltage output load is ≥ 1k Ω
Module "Fault light always on" 1. Channel short circuit (such as load short circuit in analog output module); 2. Module address conflict; 3. Configuration file error: 1. Disconnect the on-site signal line and check if the fault still reports (eliminate the short circuit problem); 2. Verify that the hardware dialing address of the module matches the software configuration address; 3. Download the correct configuration file again
Daily maintenance suggestions
Regular inspection: Check the LED status indicator lights of the module every 3 months to confirm that there are no abnormal alarms; At the same time, check whether the connection between the module and the base is firm, and whether the wiring terminals of the on-site signal line are loose (to avoid poor contact caused by vibration).
Cleaning and maintenance: Clean the surface of the module with dry compressed air (pressure ≤ 0.3MPa) every 6 months to avoid dust accumulation and affect heat dissipation; If there is oil contamination inside the control cabinet, a soft cloth dipped in isopropanol can be used to wipe the module housing (be careful to avoid liquid entering the interior of the module).
Spare parts management: For critical modules (such as redundant analog input modules), it is recommended to reserve 1-2 spare modules, which need to be regularly powered on for testing (every 12 months) to ensure normal performance.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


