

K-WANG


MKS Type T3B Butterfly Valve (with DeviceNet Interface)
Symbols on equipment: including power on/off (IEC 417 No.5007/5008), grounding (IEC 417 No.5017/5019/5020/5021), AC/DC (IEC 417 No.5031/5032/5033-a), Class II equipment (IEC 417 No.5172-a), three-phase AC (IEC 617-2 No.020206), hand compression risk (ISO 3864), electric shock risk (ISO 3864 No.B.3.6), etc. The manual provides detailed explanations of the meanings of each symbol in table form.
MKS Type T3B Butterfly Valve (with DeviceNet Interface)
Security Information
Symbol Definition
The symbol "Warning" in the manual indicates a potential danger of injury to personnel; CAUTION "indicates the potential danger of product damage; NOTE "indicates important information that requires special attention.
Symbols on equipment: including power on/off (IEC 417 No.5007/5008), grounding (IEC 417 No.5017/5019/5020/5021), AC/DC (IEC 417 No.5031/5032/5033-a), Class II equipment (IEC 417 No.5172-a), three-phase AC (IEC 617-2 No.020206), hand compression risk (ISO 3864), electric shock risk (ISO 3864 No.B.3.6), etc. The manual provides detailed explanations of the meanings of each symbol in table form.
Safety operation standards
Mechanical safety: Before the valve is fully integrated into the system, there is a risk of injury from moving parts. Keep away from the valve opening and do not insert objects into openings that may come into contact with moving parts; Cut off the electrical and pneumatic power supply of the valve before operation.
Component and modification restrictions: The use of substitute components or unauthorized modification of valves is prohibited. Repairs must be sent to the MKS calibration service center to ensure that safety functions are intact; Only qualified personnel are allowed to perform component replacement and internal adjustments.
Use of hazardous materials: If hazardous materials are used, safety regulations must be followed, and valves must be thoroughly purged if necessary to ensure compatibility between the materials in contact with the valves (including sealing materials); Blowing should be carried out under a fume hood and protective gloves should be worn.
Environmental and pressure requirements: Prohibited for use in explosive environments (unless specifically certified); Use connectors that meet specifications and are compatible, and assemble and tighten them according to the manufacturer's instructions; Check the sealing of vacuum component connections; The operating pressure shall not exceed the rated maximum pressure (refer to product specifications); The pressurized gas source system requires the installation of rupture discs; Prevent pollutants such as dust and metal shavings from entering the equipment; Keep away from valve openings during operation.
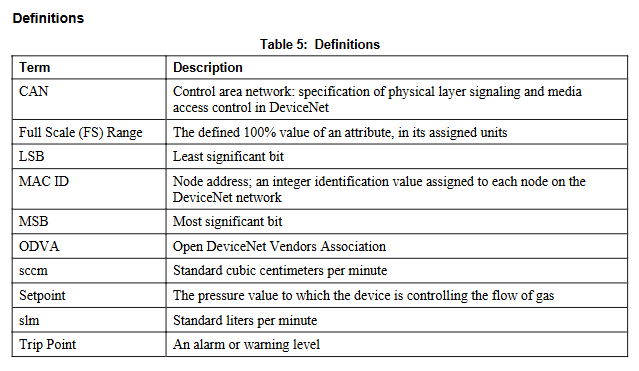
Product Overview
Core Composition and Function
Components: T3B butterfly valve consists of a throttle valve (with motor board electronic housing), microprocessor, drive circuit (no separate controller box required), DeviceNet communication interface, and analog output reflecting pressure or valve position. The valve is controlled by digital values sent through the DeviceNet network.
Control principle: Based on digital pressure/position control algorithm, guide the valve to the appropriate position for pressure or position control. The pressure or position setting value can be sent through digital DeviceNet command; Directly read the control pressure signal from the MKS Baratron pressure sensor, and all operation settings are controlled through the DeviceNet protocol.
Data storage and anti-interference: When the power is turned off, the calibration constant is saved in non-volatile memory, and it can run without recalibration after re powering on; Adopting a metal casing, optimized internal design, surge/ESD suppression network, and RFI filtering (all inputs and outputs) to enhance resistance to radio frequency interference and electromagnetic noise; When using fully metal braided shielded cables with both ends correctly grounded, they comply with the EU CE certification testing standards.
key parameters
Power Requirements: Requires 24 VDC @ 3 Amp input voltage (powered through a power connector); If a heating pressure sensor is used and powered by a valve, the sensor power demand needs to be added, and the valve can provide a maximum current of 750 mA (total of high and low sensors) for the heating pressure sensor.
Control range: The pressure control range is 0.5% -100% of the sensor range, and the position control range is 0 ° -90 °; The repeatability of the controller is ± 0.1% of full scale (FS).
control mode
Pressure control: The valve moves to maintain the target pressure (set value), supporting two algorithms: Model Based Control and PID Control.
Model based control: During the control cycle, the algorithm calculates the next valve position based on the current pressure, position, and set value, requiring knowledge of system parameters such as chamber volume and valve conductivity to optimize control; The relationship between chamber pump speed and valve position is obtained through the "LEARN function" (based on actual working conditions such as sensor type and chamber volume), which is usually executed once during initial installation. The process includes setting the chamber volume, selecting the volume estimator switch, configuring the pressure sensor range, setting the learning flow rate, and starting learning (lasting about 45 seconds, maintaining stable flow rate).
PID control: The set value optimizes the response through two parameters, Phase and Gain, and the default value can be adjusted; The response speed of phase control pressure to changes in the set value is too fast, which can lead to slow response or oscillation, and too small, which can cause overshoot and oscillation; Gain enables the controller to track the set value and minimize steady-state error. Excessive gain can cause overshoot, while insufficient gain can result in slow response.
Position control: The valve moves to the target position (set value) without feedback signal. The encoder can provide the user with the required feedback, but it is not used for closed-loop control.
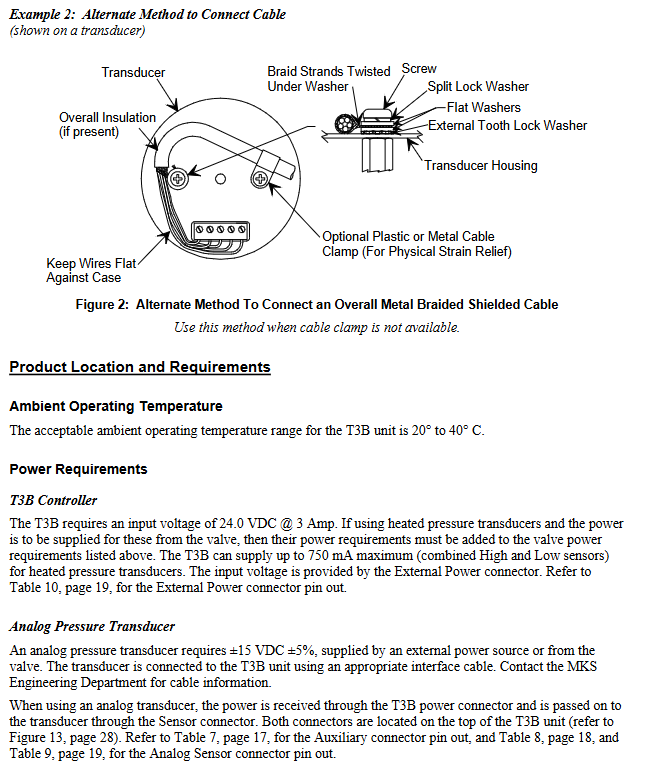
Trip Points
Basic configuration: Includes 4 software trip points that can be adjusted through digital communication commands. The status changes when the pressure is above/below the set value; The trip point can be configured to monitor pressure or valve position (any combination), two of which can be mapped to hardware relays through auxiliary connectors.
Key parameters:
Hysteresis: default 10%, adjustable through digital commands, used to compensate for system noise and avoid "relay jitter", ideal value close to but not less than peak to peak noise.
Delay: The alarm status of the trip point needs to be continuously set for a set time (0-10000 ms, default 0) before reporting "ON". Different delay values can be set for different trip points (monitoring controller object pressure properties, trip point object valve position properties).
Direction: default "low" (when the pressure is lower than the set value, the trip point is activated, the LED lights up, and the pressure needs to be higher than the hysteresis value to release), can be changed to "high" through digital commands (when the pressure is higher than the set value, it is activated, and the pressure needs to be lower than the hysteresis value to release).
Top panel component
Connectors: Includes 5-pin miniature digital communication connector (DeviceNet communication interface), 25 pin D-type female auxiliary connector (sensor power supply, alarm relay output, RS-232 communication), 9-pin D-type male external power connector (valve power supply), and 2 15 pin D-type female analog sensor connectors (high/low sensor power supply and pressure input).
Indicator lights and switches:
Valve position indicator light: "OPEN" (red) lights up to indicate that the valve is fully open, and "CLOSE" (red) lights up to indicate that it is fully closed.
Manual valve switch: a button type switch that can manually drive the valve to the open/close position.
Trip point indicator light: It lights up green when the trip point is activated.
DeviceNet status light: including module status light (green/red dual color) and network status light (green/red dual color), the power startup sequence complies with the ODVA DeviceNet specification, the module status light is always green to indicate normal, and the red to indicate unrecoverable fault; The green constant light of the network status indicates that the communication link is normal and a connection has been established, the green flashing indicates online but no connection, and the red constant light indicates a serious link failure.
Configure switch:
Baud rate switch: 4-bit rotary switch, optional PGM (read from non-volatile memory), 125 Kb, 250 Kb, 500 Kbps.
MAC ID (Node Address) Switch: Two 10 bit rotary switches, set the node address (0-63), with ten bits on the left (MSD) and one bit on the right (LSD); When the address is greater than 63, it is equivalent to the "PGM" position.
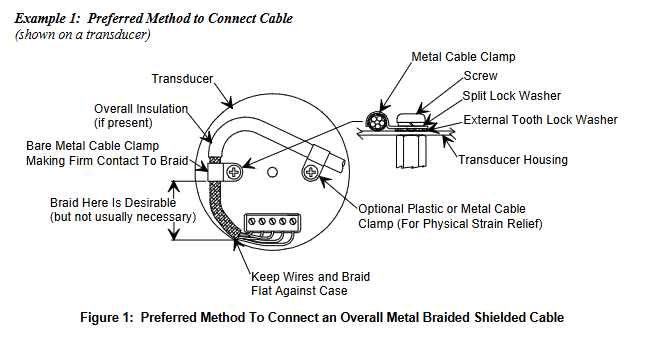
Installation Guide
Unpacking and Inspection
Unboxing process: MKS uses professional packaging to ensure that the equipment is in good condition. After receiving it, it is necessary to check whether the valve is damaged, the connector is damaged, and other transportation damages are present. Do not discard the packaging materials until safety is confirmed.
Problem handling: If damage is found, immediately notify the carrier and MKS; If you need to return the device, you need to first obtain the ERA number (device return authorization number) from the MKS service center. The MKS calibration service center list is listed on the inside of the back cover of the manual; Only qualified personnel are allowed to install and debug, and ESD protection and operating procedures must be followed.
Standard accessories: including T3B unit, T3B with DeviceNet interface user manual, MKS T3B/T3P with DeviceNet interface supplementary manual (No. 138993-P1, installation needs to refer to this supplementary manual).
Interface cable requirements
Cable specification: Full metal braided shielded cable (correctly grounded at both ends) is required to comply with CE certification; MKS provides a full range of cables, and if self-produced, they must meet the following requirements: shielding layer covering all wires (insufficient aluminum foil or spiral shielding effect may affect compliance); The metal shell of the connector is in direct contact with the entire circumference of the cable shielding layer (to avoid reduced shielding effect caused by flying wires); Good contact between the connector and the controller housing (approximately 0.01 ohms, with grounding surrounding all wires); Consider voltage level, wire I ² R heating, IR voltage drop, capacitance and inductance of fast signal cables, and internal wire shielding requirements.
Connection method: Two shielding cable connection methods are provided (priority is to use cable clamps to fix the shielding layer, and if there is no cable clamp, the shielding layer can be twisted and fixed with washers), ensuring that the shielding layer is grounded and the wire is in contact with the shell.
Installation environment and location
Environmental requirements: The working temperature range is 20 ° C-40 ° C, the working humidity is 0% -95% (non condensing), and the storage temperature range is -20 ° C-80 ° C.
Installation position: It can be installed on the vacuum exhaust pipeline (with suitable joints). To achieve optimal pressure control, the pressure sensor and T3B should be as close to the process chamber as possible to reduce the time constant; The connecting pipe between the sensor and the chamber should be less than 6 inches and have a diameter of not less than 1/4 inch. If it exceeds 6 inches, a larger diameter pipe should be used to compensate for the conductivity loss.
System configuration and electrical connections
Typical configuration: The system includes a DeviceNet network host (sending set values, receiving pressure/position/diagnostic data), a 24 VDC valve power supply, a sensor power supply (optional ± 15 VDC), a T3B unit, an analog Baratron sensor, and an alarm relay output that can be connected to external alarm devices.
Grounding requirements: If power is taken from the DeviceNet network, it must comply with the grounding requirements of the ODVA DeviceNet specification (Volume I).
Definition of connector pins:
Digital communication connector (5-pin): 1-pin (Drain), 2-pin (V+), 3-pin (V -), 4-pin (CAN_S), 5-pin (CAN_L).
Auxiliary connector (25 pins): includes receive data (RX), send data (TX), pressure output (A Out), position output (A Out), 2 sets of relays (normally open/normally closed/common terminal), valve open/closed status (digital output), interlock (digital input), analog ground, digital ground, chassis ground, etc. Pins 11-13 are related to analog signals, pins 14-19 are relays, pins 20-22 are digital status and input, and pins 24-25 are ground.
Analog sensor connector (15 pins, with the same high and low sensor pins): 2-pin (pressure input+), 5-pin (sensor power return), 6-pin (-15 V), 7-pin (+15 V), 12 pin (pressure input -), 14 pin (+24 V power output), 15 pin (chassis ground), with no other pins connected.
External power connector (9-pin): 1-2 pins (+24 V input), 3-4 pins (24 V return), 5-pin (+15 V auxiliary input, for instruments), 6-pin (15 V return), 7-pin (-15 V auxiliary input, for instruments), 8-pin (reserved), 9-pin (chassis ground).
startup process
Power on sequence: First supply power to the DeviceNet network, then supply power to T3B; When powered on, the device checks the communication link, EEPROM, and RAM internal diagnostics, and the results are indicated by the top status LED (color and flashing status).
LED startup sequence: The module status LED flashes alternately green and red for about 0.25 seconds each before turning green; The network status LED flashes alternately in green and red for about 0.25 seconds each before turning off; After initialization is completed, the module status LED remains constantly green; When there are no other network devices, the network status LED remains off; When there are other devices, the network LED flashes green during repeated MAC checks and before establishing a connection.
Preheating time: After installation and power on, the preheating time of the controller is less than 1 minute.
Operation Guide
Operation Mode
User mode: default power on mode, which is the normal operation mode.
Calibration mode: used to access specific calibration and operating parameters. The device functions are the same in both modes, but network access to certain attributes may be restricted (refer to the object attribute table in the supplementary manual for specific permissions).
Communication Configuration
Baud rate and MAC ID settings: can be set through software (DeviceNet protocol network command) or manually (top rotary switch). When powered on, if the switch is in the "PGM" position, the baud rate/address can be read from non-volatile memory, and the network can modify parameters. Changes in the switch position require a power outage and restart to take effect; If the switch is not in the "PGM" position and the switch value is directly read, the network modification request is rejected and an error code of "Attribute_Cot_Settable" is returned.
Communication specifications: Supports 125/250/500 Kbps baud rates; The network topology is linear (trunk/branch), with power and signals sharing the same cable; Supports up to 64 nodes; Explicit message communication delay<50 milliseconds (average<25 milliseconds), I/O polling message delay<4.5 milliseconds (average<1.5 milliseconds); Equipped with module status (green/red) and network status (green/red) LED indicators.
Core operational functions
Parameter setting and monitoring: Through the DeviceNet network, set values (pressure/position), valve direction (forward/reverse), pressure values and units, valve position, trip point values/hysteresis/delay/status can be set and reported, monitoring system status, reporting operating time, and setting valve soft start; Storage device identification information (manufacturer information, model serial number, factory calibration data, software and hardware version number).
Maintenance and troubleshooting
routine maintenance
Routine inspection: No special maintenance requirements, only correct installation and operation are required; Regularly check for cable wear and signs of shell damage; Regularly wipe the surface of the equipment with a damp cloth.
Equipment return: If you need to return the MKS for repair, you need to obtain the ERA number first; The returned equipment must be free of harmful, corrosive, radioactive, or toxic substances.
troubleshooting
General faults:
When the valve is closed, the conductivity does not meet the standard: it may be due to wear or damage of the baffle seal, and the factory needs to be contacted to obtain a seal replacement kit.
25 pin I/O connector interlock missing (22-24 pins): Connect pin 22 to pin 24 or verify external interlock wiring.
Valve not open/closed: Check if the 24V power supply is properly connected to the valve terminal or if the valve is faulty (need to be sent to MKS for repair); Simultaneously confirm the interlocking wiring.
Pressure control failure (report full range/low/zero): Sensor disconnected (reconnect) or pressure gauge not powered (check power supply).
Pressure control oscillation/poor effect: PID mode needs to optimize gain and phase, and the model base mode needs to relearn the pump speed curve; The control offset may be due to high grounding impedance (judged by MKS valve GUI as a debugging or grounding issue); The control difference within a specific pressure range may be due to incorrect intersection point settings (configuring and installing pressure gauges for intersection pressure).
Unable to achieve target pressure: The baffle seal is worn or damaged (replace seal).
Report negative/abnormal pressure: pressure gauge not zeroed (zeroing), no power supply (checking power supply); Pressure gauge full range setting error (configured with correct range), voltage range error.
Pump speed learning failed: The pressure gauge is not connected to the high range (retry after connecting to the high range).
Communication malfunction:
RS-232 communication failure: Check baud rate, data bits, checksum, CR-LF settings, or cable wiring issues.
DeviceNet communication failure: Check MAC address and baud rate settings, or network power supply for normal operation.
Meaning of fault indicator light:
Module status LED: evergreen (normal), flashing green (visual indication), constantly red (non recoverable fault), flashing red (minor fault, such as interlock not enabled), off (no power supply), alternating red and green (self check).
Network status LED: evergreen (communication link normal, online and connection established), flashing green (online but no connection established), constantly red (severe link failure, such as repeated MAC address or bus shutdown), flashing red (connection timeout), alternating red and green (initialization), off (not online, such as incomplete repeated MAC check or no power supply); When using a single device network, it is normal to keep it off until there is no connection.
Fault type:
Minor faults: MAC ID or baud rate switch changed during operation, safety interlock opened (only T3P gas interlock), controller error reported through abnormal status bit (refer to supplementary manual), equipment remains in operation.
Serious malfunction: During self inspection, EEPROM hardware or RAM memory issues were detected, the module status LED is constantly red, and the device has entered a serious malfunction state, unable to respond to network services. MKS needs to be contacted.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


