

K-WANG


SIEMIENS S7-1200/1500 Controller TIA Portal Programming Guide
SIEMIENS S7-1200/1500 Controller TIA Portal Programming Guide
Overview
The Siemens S7-1200/1500 Controller TIA Portal Programming Guide (V1.6 version) focuses on optimizing programming and covers the core innovations of the S7-1200/1500, such as optimization blocks, new data types VNet, direct machine code compilation, general programming specifications (block structure, symbol addressing, memory management), hardware independent programming methods, STEP 7 Safety programming points, and visual automatic generation solutions. It explicitly recommends using optimization blocks instead of non optimization blocks, symbol addressing instead of absolute addressing, and global data blocks instead of bit memory. At the same time, it provides a large number of performance optimization techniques (such as avoiding deep call hierarchy and using loop instructions reasonably), aiming to help users achieve standardized, efficient, and reusable automation program development.
S7-1200/1500 Core Innovation
1. Programming languages and compilation optimization
Language support differences:
Programming language S7-1200 S7-1500
Ladder diagram (LAD) ✅ ✅
Function Block Diagram (FBD) ✅ ✅
Structured Control Language (SCL) ✅ ✅
Statement Table (STL) ❌ ✅
Sequential Function Graph ❌ ✅
Compilation method: S7-1200/1500 generates machine code directly for all languages, without the intermediate step of "LAD/FBD → STL → machine code" for S7-300/400, ensuring consistent performance for all languages.
2. Optimize block technology (core innovation)
Optimized block vs non optimized block:
Feature optimization block (recommended) Non optimization block (only compatible)
Data storage is automatically sorted by data type, stored in declared order without gaps, and may have gaps
The addressing method can be either symbolic addressing or absolute addressing
Retention settings: A single label can be set to maintain the entire block or not to maintain it
Download feature supports uninitialized download (RUN mode update) not supported
Fast access speed (processor optimized storage) slow
Setting method: By default, "Optimize Block Access" is enabled for new blocks, which can be batch modified in the "Program Block" list; The optimization properties of instance DB inherit from the associated FB.
3. New data types
Core new type:
Data Type Applicable Controller Purpose Key Features
VARIANT S7-1500; S7-1200 (FW4.1+) dynamic pointer with type detection, replacing the ANY pointer, supporting symbol access
Date_Time_Long (DTL) both support timestamp storage containing year/month/day/nanosecond, with symbol accessible sub fields (such as DTL. Hour)
Both LReal and LReal support high-precision floating-point numbers of 64 bits and 15 decimal places, making them suitable for precise calculations
LTime only has a long-term storage range of ± 106751 days for S7-1500 and supports nanosecond level accuracy
WSRING only supports S7-1500 Unicode strings for multiple languages (such as Chinese and Latin), with a maximum of 16382 characters
4. Key instruction upgrade
MOVE series instructions:
Advantages of Instruction Usage
MOVE supports single value copying and complete copying of structures/arrays
MOVE_SLK array partial copy specifies the starting index and quantity, efficiently processing the array
MOVE_SLK_VARIANT Dynamic Type Copy Run Time Detect Data Types, Supports PLC Data Types/Arrays
The serialize/deserialize structure and byte array conversion are used for communication frame packaging/unpacking, supporting VNet input
Other instructions:
TypeOf(): detects the data type pointed to by VNet on the label (SCL only);
RUNTIME: measures program/block running time, supports performance optimization;
Multi assignment (V14+): such as # a:=# b:=# c:=0; Simplify initialization.

Universal Programming Specification
1. Program block structure
Core block type:
Key features of block type functionality
Organizational block (OB) operating system call, management program execution including loop OB (OB1), interrupt OB (OB40 hardware interrupt), etc; S7-1200 up to 100 cycles/start OB, S7-1500 supports clock interrupt OB
Function (FC) has no state block and no independent storage temporary label. Only the current call is valid, and data needs to be passed through parameters; Support direct participation of return values in SCL formulas
Function block (FB) has a status block that requires the instance DB static label to maintain its value; The instance DB structure is defined by FB and cannot be modified separately
Data Block (DB) stores data in a global DB for all blocks to access; Instance DB is only associated with FB usage
Block Reuse Techniques:
Multiple instances: FB calls other FBs to store data in their own instance DB, reducing the number of instance DBs;
Typeization block: Store FB/FC/PLC data types in the global library, supporting cross project reuse and batch updates.
2. Memory management
Memory type and access speed (from fast to slow):
Optimize the temporary labels, FC/FB parameters, and non persistent static labels of the block;
Optimize the retention labels of blocks and optimize the global database;
Non optimized blocks;
Array access for runtime calculation index (such as # Array [# i]);
Indirect memory access (such as pointer operations);
Data replication between optimized and non optimized blocks.
Key recommendations:
Replace bit memory with global DB (M-zone): The size of M-zone varies depending on the controller, while global DB is more flexible and supports optimized storage;
Use temporary tag caching for frequently accessed I/O tags to reduce the number of I/O accesses;
Retention setting: Only the necessary labels need to be set to hold (such as process parameters) to reduce the cost of saving power-off data.
3. Addressing method
Symbol addressing (mandatory recommendation):
Advantages: The tag name is descriptive (such as # Motor1_Run) and automatically updates when the address changes, reducing errors;
Operation: Simply enter the symbol name in the instruction input box, right-click on "Define Label" to quickly create it.
Indirect access scheme:
Indirect array access: Replace pointers with # Array [# Index], such as # Temp:=# MotorSpeed [# i];;
Slice access: Directly access the bits/bytes of Byte/Word/DWord, such as # WordVar.% X0 (bits), # DWordVar.% W1 (words).
4. Performance optimization techniques
Disable the ENO evaluation (LAD/FBD) of blocks to reduce runtime detection;
Avoid deep level calling (≤ 8 layers), otherwise TIA Portal will compile alarms and increase protection code overhead;
FOR loop: Do not manipulate the loop counter (compiler optimized times), use EXIT to interrupt the loop;
Reduce unnecessary IF instructions, such as # Motor:=# On1 AND # On2; Replace IF # On1 AND # On2 THEN # Motor:=TRUE; ELSE #Motor:=FALSE; END_IF;。
Hardware independent programming
1. Data type compatibility
Only use EN 61131-3 standard data types (such as INT/DINT/REAL/BOOL), avoiding S7-300/400 specific types (such as S5TIME);
The timer/counter of S7-1200/1500 uses IEC standard blocks (such as TON/CUTU) and is integrated through multiple instances to avoid absolute addresses (such as T37).
2. Clock signal replacement
Do not use hardware clock memory (such as M0.5), use programming clock generation block instead:
Example: SCL writes FB, sets the frequency through the # Frequency parameter, # Q outputs pulses, and # Countdown outputs the remaining time;
Advantage: The clock frequency can be flexibly adjusted without relying on hardware configuration.
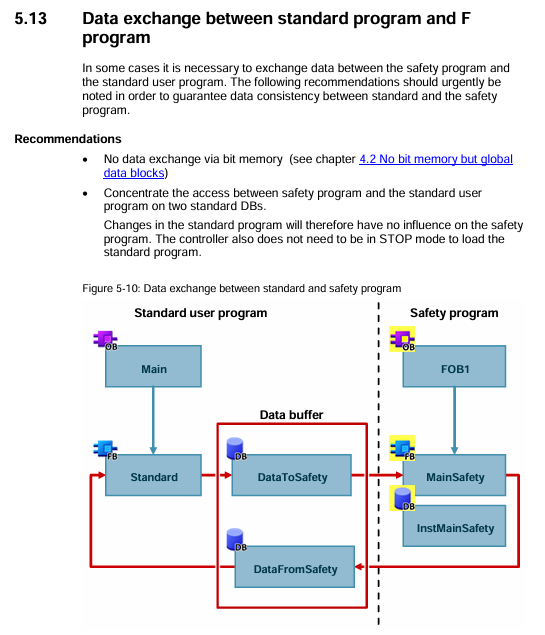
STEP 7 Safety Programming
1. Core components
F operation group: the execution unit of safety programs, including 1 fault safety OB and 1 main safety block, with a maximum of 2 created;
F-signature: a unique identifier for each F-component (F-I/O, F-block) used to detect configuration/programming changes;
Security Management Editor: Manage F run groups, F signatures, access permissions, and set security program passwords.
2. Key specifications
Data exchange: Standard programs and security programs only interact through two standard DBs, avoiding direct access to the security DB;
Performance optimization:
Avoid using TP/TON/TOF instructions (add protection code);
Disable the JMP/Label structure (resulting in additional system protection blocks);
Loop call hierarchy ≤ 8 layers;
Test restriction: The security program can only force testing when the security mode is disabled, with a maximum of 5 F-I/O forced at a time.
Visual automatic generation (SiVArc)
1. Basic requirements
Tools: TIA Portal V14++SiVArc Options Package;
Prerequisite: The program is modularized (such as motor control FB, conveyor belt FB), and the visualization library includes standard image templates.
2. Control mode
Network comment: Add a tag (such as "SiVArc: Generate=True") when calling the network on FB. The SiVArc rule triggers generation through Contains (Block. NetworkComment, "Generate=True");
SiVArc variable: Define a variable in the "Plugin" label of the block (such as Location="Bottling_Test"), and the rule filters the generated range based on the variable value.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


