

K-WANG


TOSHIBA VF-S15 frequency converter
Example of input voltage level frequency converter model
Single phase 200V-240V VFS52S-2002PL__/- W1/Y-A *, VFS52S-2004PL__/- W1/Y-A*
Three phase 200V-240V VFS15-2002PM_/- W1/Y-A *, VFS15-2004PM_/- W1/Y-A*
Three phase 380V-500V VFS15-4004PL_/- W1/Y-A *, VFS15-4007PL_/- W1/Y-A*
Three phase 525V-600V VFS15-6015P_/- W1/Y-A *, VFS15-6022P_/- W1/Y-A*
TOSHIBA VF-S15 frequency converter
Basic information of the document
Scope of Application
The document specifically lists the applicable models (including multiple voltage levels) for the Toshiba VF-S15 series frequency converter, as shown in the table below. Models marked with suffixes such as "Y-A38" and "Y-A65" are not applicable.
Example of input voltage level frequency converter model
Single phase 200V-240V VFS52S-2002PL__/- W1/Y-A *, VFS52S-2004PL__/- W1/Y-A*
Three phase 200V-240V VFS15-2002PM_/- W1/Y-A *, VFS15-2004PM_/- W1/Y-A*
Three phase 380V-500V VFS15-4004PL_/- W1/Y-A *, VFS15-4007PL_/- W1/Y-A*
Three phase 525V-600V VFS15-6015P_/- W1/Y-A *, VFS15-6022P_/- W1/Y-A*
Safety warnings and personnel qualifications
1. Warning system
The document categorizes safety warnings into two types, specifying risk levels and response requirements:
Warning type meaning Typical scenarios
Warning operation errors may result in death or serious injury. Touching live cables, repairing without discharge, and short circuiting DC bus capacitors
Incorrect operation of the solution may result in minor injuries or equipment damage, voltage incompatibility, capacitor aging, and performance degradation
2. Core security taboos (Warning level)
Do not touch live cables (such as printed circuit boards) inside the frequency converter, and use insulated tools;
Before maintenance, it is necessary to follow the process of "power off → paste the prohibition closing label → lock the power-off switch → wait for 15 minutes to discharge → measure the DC bus voltage<42V";
Do not short-circuit PA/+and PC/- terminals or DC bus capacitors;
Before powering on, all cover plates must be installed and closed.
3. Personnel qualification requirements
Only qualified personnel are allowed to operate (subject to the following conditions):
Having received safety training, able to identify and mitigate risks;
Familiar with this manual and product documentation, proficient in electrical/mechanical system knowledge;
Understand international/national electrical codes and accident prevention regulations.

Detailed explanation of core security functions
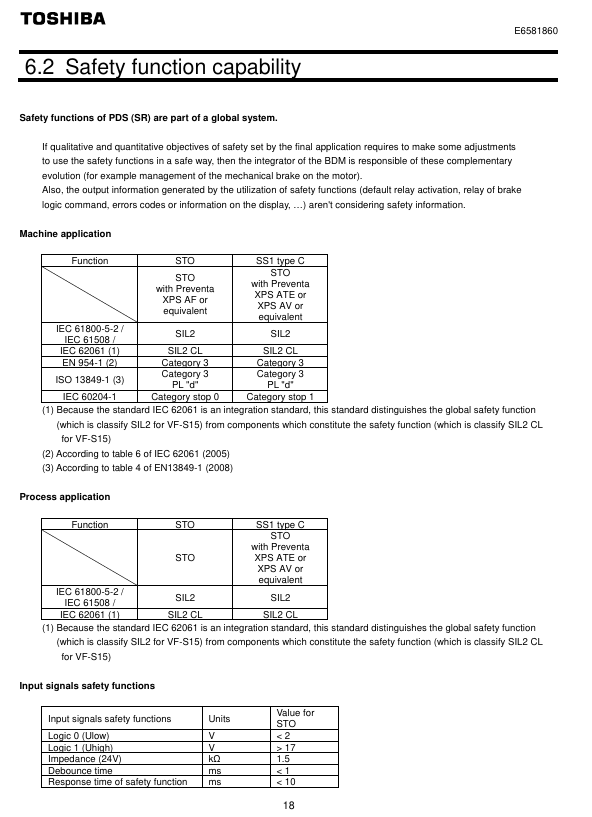
1. STO (Safe Torque Off)
Function definition: To put the motor into a torque free state (prohibiting motor start or free stop), cut off the energy supply to the motor, corresponding to IEC 60204-1 stop category 0 (uncontrolled stop).
**According to * *: IEC 61800-5-2 § 4.2.2.2, it should be noted that additional mechanical brakes are required for suspended load scenarios, and electronic components cannot replace anti electric shock isolation measures.
Security level:
Configuration method SIL (IEC 61508) PL (ISO 13849-1) EN 954-1 category
With/without Preventa module SIL 2 PL d 3
Key parameters: response time<10ms, logic input 0<2V, 1>17V, impedance 1.5k Ω.
Module requirements: Mechanical applications (compliant with IEC 60204-1) require mandatory use of Preventa modules (such as XPS AF) to prevent accidental restarts; Use as needed in other scenarios.
2. SS1 (Safe Stop 1, Safety Stop Class 1, Type C)
Function definition: First, slow down the motor according to the specified time delay. After the delay ends, trigger the STO function, corresponding to IEC 60204-1 stop category 1 (control stop).
Normative basis: IEC 61800-5-2 § 4.2.2.2, requires the use of specific safety relays to implement delay logic.
Security level:
Configuration method SIL (IEC 61508) PL (ISO 13849-1) EN 954-1 category
STO+Previnta module (such as XPS AV) SIL 2 PL d 3
Application logic: The deceleration delay time needs to be set according to the actual scenario, and the motor will enter a torque free state after the delay ends.
Compliance standards and safety performance
1. Follow the standards
Specific core requirements for standard categories
IEC 61800 series variable speed electric drive system safety requirements for drive systems
Functional Safety IEC 61508 Ed.2 Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Systems Functional Safety, Defining SIL Levels
Mechanical safety ISO 13849-1/2, EN 954-1 Safety components of mechanical control systems, defining PL levels and categories
Process Safety IEC 62061 Process Industry Safety Instrumented Systems, Distinguishing Global/Component SIL
2. Safety performance indicators
Taking the STO function as an example, the key performance parameters are shown in the following table:
Explanation of Indicator Values
SFF (Safety Failure Score) 96.7% represents the proportion of safety failures to total failures, reflecting the safety of the system
MTTFd (Mean Time to Failure) is the average interval between system failures in the year 16200
PFHequ_1y (annual hazard failure probability) 7.04 FIT 1FIT=10 ⁻⁹ times/hour, which means the annual failure probability is extremely low
HFT (Hardware Fault Tolerance) 1 allows one hardware fault to maintain safety functionality
Equipment type B complies with the definition of Class B subsystems in IEC 61508
System architecture and application limitations
1. Authentication architecture (3 types)
The document provides three certified security system architectures, adapted to different application scenarios:
Architecture Type Applicable Scenarios Core Configuration Compliance Standards
Case 1 Mechanical Applications - STO VF-S15+Preventa XPS AF Module EN 954-1, ISO 13849-1, IEC 60204-1
Case 2 Mechanical Applications - SS1 VF-S15+Preventa XPS AV Module EN 954-1, ISO 13849-1, IEC 60204-1
Case 3 Process Application - STO VF-S15 (without additional modules) IEC 61508 (SIL 2/SIL 1)
2. Application restrictions
Prohibited scenarios: Applications where the load may accelerate after shutdown (such as vertical conveyors, elevators, and winches) pose safety hazards;
Function priority: STO has the highest priority. If STO is triggered, no torque operation will be executed first regardless of whether other functions are activated or not;
Prerequisite: The motor/frequency converter needs to be matched with the application capacity, and the speed loop and torque characteristics should be correctly configured. If necessary, dynamic braking resistors and other options should be provided.
Maintenance and compliance documents
1. Maintenance requirements
Preventive maintenance: It is recommended to check the safety function once a year (such as opening the protective door to verify whether the frequency converter stops according to the set safety function);
Component replacement: After replacing non VF-S15 components such as motors and emergency stop switches, acceptance testing must be performed again;
Capacitor maintenance: For products stored for more than 2 years, the capacitor needs to be gradually boosted and activated through a variable power supply (25% → 50% → 75% → 100% rated voltage, each for 30 minutes) before use.
2. Compliance documents
EU Declaration of Conformity: covering ATEX Directive, Machinery Directive, EMC Directive, to be executed in conjunction with the ATEX Guidelines and Safety Guidelines accompanying the product;
Declaration signing: Signed by both Technical Document Manager (Fredric Roussel, France) and Marketing Manager (Shin Okada, Japan), released in 2019;
Option compliance: Communication options (such as CANopen, PROFINET) and power options (such as EMC filters) require the use of original factory certified accessories (refer to the appendix options list).
Key issues
Question 1: Why is it necessary to use Preventa module for the STO function of VF-S15 frequency converter in mechanical applications? What is its core function?
Answer: Mechanical applications (compliant with IEC 60204-1 and the Machinery Directive) mandate the use of Preventa modules (such as XPS AF), with the following core reasons and functions:
Prevent accidental restart: If there is a power outage after the STO is activated, and the STO is mistakenly released during the power outage, the motor may automatically restart after the Preventa module is restored, posing a safety risk; The Preventa module can intercept this false trigger and ensure that manual operation is required to restart after power restoration, meeting the mechanical safety requirements of "reset does not trigger automatic start";
Multi device emergency stop coordination: If the system contains multiple BDMs (background debugging modules), the Preventa module provides multiple safety output interfaces, which can achieve synchronous emergency stop control of multiple devices and meet the safety linkage requirements of complex mechanical systems;
Compliance guarantee: Only with the Preventa module can the STO function fully comply with the requirements of EN 954-1 category 3 and ISO 13849-1 PL d, ensuring that mechanical applications pass safety certification.
(Note: For non mechanical scenarios such as process applications, if there is no need to prevent accidental restarts or multi device collaboration, the Preventa module is not necessary.). )
Question 2: What is the core difference between the SS1 function (Safety Stop Class 1 Type C) of VF-S15 and the STO function? How to choose which function to use in practical applications?
Answer: The core differences and application selection logic between the two are as follows:
1、 Core difference
Comparison Dimension STO (Safe Torque Off) SS1 (Safe Stop Class 1, Type C)
The functional logic directly cuts off the motor torque, and the motor stops freely. First, it decelerates according to the set time, and then triggers STO after a delay
Stop category (IEC 60204-1) Category 0 (uncontrolled stop, fast but no deceleration) Category 1 (controlled stop, with deceleration process)
Applicable scenarios require emergency torque cut-off (such as personnel entering a dangerous area by mistake) and require smooth deceleration to avoid load impact (such as transporting fragile items)
Module dependent mechanical applications require Preventa modules, while other scenarios require the use of Preventa modules (such as XPS AV) to implement delay logic as needed
2、 Application selection principle
Select STO: When the scenario requires "immediately cutting off torque to avoid emergency risks" (such as operators accidentally touching dangerous areas or equipment operating abnormally), prioritize using STO to ensure that the motor quickly enters a torque free state;
Select SS1: When the scenario requires "smooth shutdown to protect the load or equipment" (such as conveying glass, precision parts, or avoiding mechanical impact during shutdown), use SS1 to achieve controlled shutdown through delayed deceleration and reduce the risk of load damage.
Question 3: According to the IEC 61508 standard, what does SIL 2 level mean for the STO function of VF-S15 frequency converters? How do its key performance indicators support the requirements of this level?
Answer: The meaning of SIL 2 level and the performance support of VF-S15 are as follows:
1、 The meaning of SIL 2 level (IEC 61508 Ed.2)
SIL (Safety Integrity Level) is an indicator that measures the ability of safety functions to resist dangerous failures. SIL 2 represents:
In high demand or continuous operation mode, the annual probability of failure (PFH) of safety functions must meet the requirement of 10 ⁻⁷ ≤ PFH<10 ⁻⁶;
Suitable for scenarios where dangerous events may cause serious injuries but have a low probability of occurrence, such as personnel protection for industrial machinery and overload protection for process equipment.
2、 Performance support for VF-S15 STO function
The STO function meets SIL 2 requirements through the following key indicators:
PFH index: The measured PFHequ_1y (annual equivalent hazard failure probability) is 7.04 FIT (1 FIT=10 ⁻⁹ times/hour), which is equivalent to an annual PFH of approximately 7.04 × 8760 × 10 ⁻⁹ ≈ 6.17 × 10 ⁻⁵? No, the document clearly states "PFHequ_1y=7.04 FIT", combined with SFF=96.7% (high proportion of safety failures), the actual probability of dangerous failure is in the range of 10 ⁻⁷~10 ⁻⁶, which complies with SIL 2;
Hardware Fault Tolerance (HFT): HFT=1, which allows the STO function to still execute normally in the event of one hardware fault (such as a single input signal failure), meeting the hardware fault tolerance requirements of SIL 2;
Safety Failure Factor (SFF): SFF=96.7%, much higher than the minimum SFF requirement of IEC 61508 for SIL 2 (60%), indicating that most system failures are safety failures and the proportion of hazardous failures is extremely low;
Mean Time to Failure (MTTFd): MTTFd=16200 years, reflecting the extremely long interval of hazardous failures during long-term system operation, further verifying the stability of SIL 2.

- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


