

K-WANG


Watlow EZ-ZONE ® RMA (Access) module
Watlow EZ-ZONE ® RMA (Access) module
Product basic information and positioning
1. Core positioning
As the core extension module of the RM system, it does not have independent PID control function and mainly provides auxiliary functions such as communication gateway, data log, configuration backup, real-time clock, etc. It can be networked with RM series modules such as RMC (controller), RME (extension), RML (limit), etc. It supports up to 17 modules (1 RMA+16 other RM modules) to work together.
2. Basic specifications
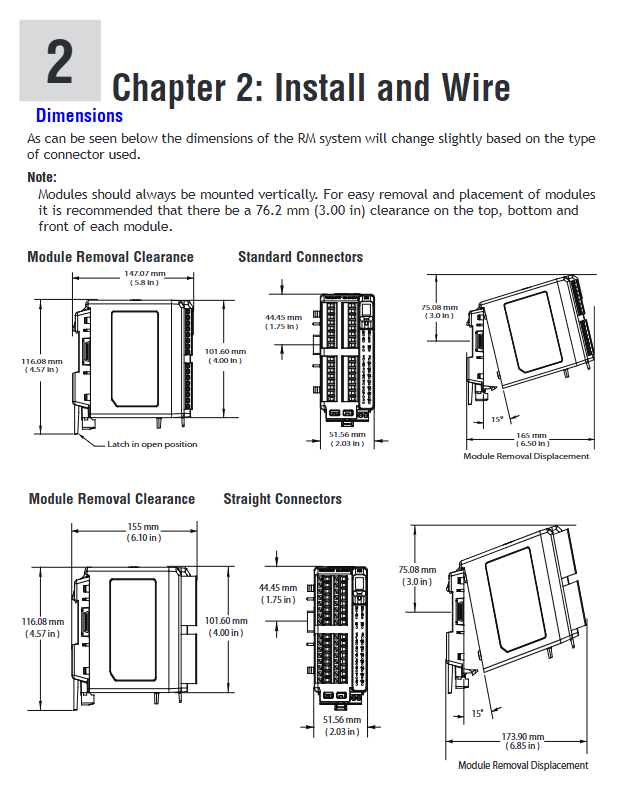
Appearance and installation: DIN rail installation (EN50022 standard), size 155mm × 116.08mm, weight 453.59g, requires vertical installation, with reserved 76.2mm maintenance space.
Power requirements: 20.4-30.8V AC/DC, Class 2 or SELV power supply, power consumption 4W/9VA, supporting Semi F47-0200 voltage drop standard.
Environmental adaptability: working temperature -18~65 ° C, storage temperature -40~85 ° C, 0-90% RH (non condensing), protection level IP20.
Certification standards: UL/EN 61010, Class 1 Div. 2 (optional), RoHS, WEEE, FM Class 3545 (limited version).
Warranty and Support: 3-year warranty (non misuse scenario), technical support can be obtained through phone, email or local representative, and RMA number needs to be applied for in advance for returns.
Core functions and technical features
1. Communication function
(1) Support agreement
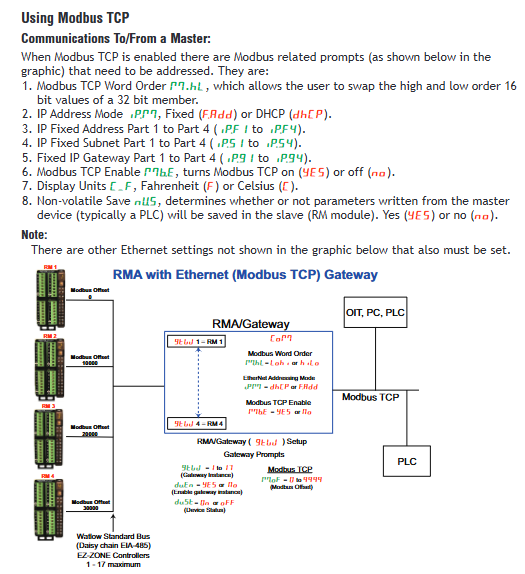
Mainstream protocol: Modbus ® RTU/TCP、EtherNet/IP ™、 DeviceNet ™、 PROFIBUS DP, Some models include USB (Mini Type B) communication.
Basic communication: EIA-485/232 interface, Standard Bus (default), supports up to 247 Modbus nodes, maximum communication distance of 1200 meters.
(2) Communication parameters
Modbus: Address 1-247, baud rate 9600/19200/38400bps, supports Non/Even/Odd parity, configurable high and low byte order.
Ethernet: Supports DHCP/fixed IP, EtherNet/IP and Modbus TCP dual protocol enabled, with a maximum of 100 implicit communication members.
DeviceNet: Node address 0-63, baud rate 125/250/500kbps, supports Quick Connect for fast communication.
PROFIBUS DP: Address 0-126, supports DP-V0 (cyclic communication)/DP-V1 (non cyclic communication), maximum distance of 1200 meters.
2. Core extension functions
(1) Data Logging
Storage medium: Micro SD card (standard 2GB, supports larger capacity), CSV file format (can be opened directly with Excel).
Recording capability: up to 200 log points, with a recording period of 1-3600 seconds, supporting two full storage strategies: "stop" or "overwrite".
Trigger method: Recording can be started/stopped through signals such as digital input, alarm, timer, etc. The log contains a timestamp (dependent on real-time clock).
(2) Configure backup and recovery
Backup capacity: The basic version supports backup of 4 modules, while the enhanced version (SD card storage) supports full configuration backup of 16 modules.
Recovery mode: Manual recovery (Now), automatic recovery after module replacement (Change), supports cross module cloning configuration, reduces downtime.
Backup content: Module parameters (excluding User Set 1/2), excluding communication protocol assembly configuration.
(3) Real time clock (RTC)
Function: Provides date and time stamps (log/program linkage), supports program continuation after power interruption (Power Off Time parameter configuration).
Accuracy: ± 30ppm (25 ° C), battery backup (BR1225 lithium battery), typical battery life of 3 years after power failure.
(4) Security and Permissions
Password protection: Supports user/administrator two-level passwords, and can enable rolling passwords (automatically changed after power failure) to prevent unauthorized operations.
Hazardous area adaptation: Some models support Class 1 Div. 2 (Groups A-D), temperature code T4, and require the use of certified components.
Installation and Wiring Guide
1. Installation process
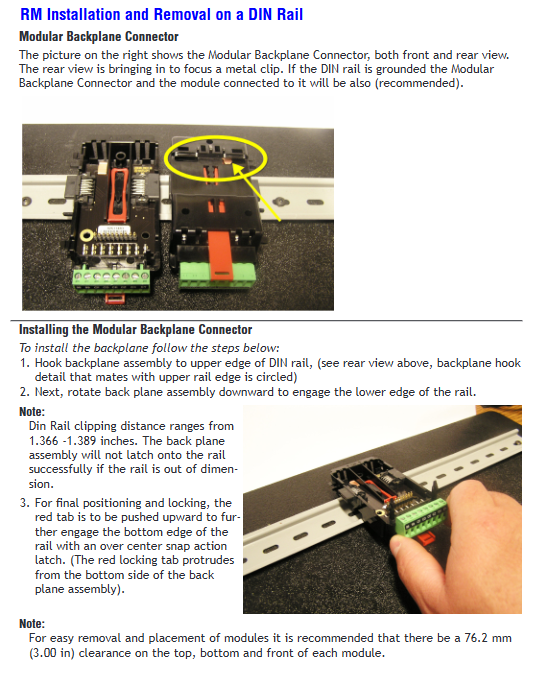
Rail installation: The hook is fixed to the 35mm rail and the rotating buckle is locked; Optional panel installation (customers need to provide their own fasteners).
Module networking: Multiple modules are horizontally spliced, sharing power and communication through the backplane bus, and supporting remote networking (up to 200 feet) using the "_stplit rail".
2. Wiring specifications
Terminal specifications: Supports 12-30 AWG wires, with a torque of 0.56 Nm (right angle terminal)/0.5 Nm (front terminal), and a stripping length of 7.6mm.
Core wiring:
Power supply: Slot C terminals 98 (+), 99 (-), need to distinguish AC/DC polarity.
Communication: Slot E (protocol terminal), Slot C (standard bus terminal CF/CD/CE), EIA-485 needs to distinguish T+/R+/T -/R -.
Bus wiring: Adopting a daisy chain topology, the first and last modules need to be connected to 120 Ω terminal resistors to avoid parallel wiring with power lines.
3. Typical networking methods
Single rail networking: RMA is directly connected to other RM modules through a backplane bus, sharing power and communication.
Track based networking: Connect two rails through Inter module Bus, provide single power supply across rails, and support remote module deployment.
Operation and Configuration Guide
1. Menu and Operation
Operation level: divided into three menus: Operations, Setup, and Factory, which can be configured through RUI (Remote User Interface) or software.
Core operation:
Address setting: Long press the panel button for 2 seconds to modify the Zone address (1-17), ensuring that the module address is unique.
Configuration method: Supports RUI local operation, EZ-ZONE Configurator/Composer software configuration (free download), Bluetooth (some models) remote configuration.
2. Key configuration items
(1) Communication configuration
Modbus: Set address, baud rate, parity, TCP mode requires configuring IP address (DHCP/fixed).
EtherNet/IP: Enable implicit/explicit communication and configure the number of assembly members (0-40).
DeviceNet: Set node address, baud rate, and enable Quick Connect.
(2) Data recording configuration
Log parameters: Set the recording period, full storage strategy, select up to 200 log points, support data sources such as analog inputs, alarms, process values, etc.
Format settings: Time format (HH: MM/HH: MM: SS), date format (MM/DD/YYYY/DD/MM/YYYY), configurable log precision (integer/decimal).
(3) Backup and Recovery Configuration
Backup operation: Setup → Backup → Save, select the backup range (single/multiple modules), and store the enhanced version to the SD card.
Recovery operation: Setup → Backup → Restore, supports manual triggering or module replacement for automatic recovery.
Maintenance and troubleshooting
1. Daily maintenance
Regular inspection: fastening of wiring terminals, SD card status, power stability, annual verification of communication links and log storage.
Cleaning and maintenance: Wipe the shell with a dry cloth to avoid corrosive cleaning agents, and regularly backup data for the SD card.
Battery replacement: After the real-time clock battery is depleted, the BR1225 model needs to be replaced by disconnecting the power supply.
2. Common faults and solutions
Possible causes and solutions for the fault phenomenon
Communication failure address/baud rate mismatch, wiring error, terminal resistance not connected. Check communication parameters, check EIA-485 polarity, and connect 120 Ω resistors at the beginning and end of the bus
Data recording failure: SD card not inserted/damaged, log points not configured. Replace SD card, reconfigure log point data source and cycle
Backup failed due to insufficient memory/SD card space, incompatible module model, cleaning storage media, confirming that the module belongs to the RM series and the address is unique
Power failure: voltage exceeds the range, power ripple is too large. Replace the compliant Class 2/SELV power supply and check the power supply circuit
Typical application scenarios
Multi protocol gateway: enables cross protocol communication between PLC and RM modules (such as EtherNet/IP to Modbus RTU).
Data collection and traceability: Record process parameters such as temperature and pressure, generate CSV logs for quality traceability.
System configuration backup: Batch backup of multiple module configurations for quick replacement of faulty modules and system recovery.
Distributed control networking: Through the track based networking function, remote module deployment and centralized monitoring can be achieved.
- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


