

K-WANG


HIMA X-CPU 01 processor module
Can handle up to 32 user programs
Perform all central functions, including communication
Use up to 3 additional processor modules to handle redundancy
Process communication through secure Ethernet.
Create and store CPU events.
Store events created by I/O modules.
HIMA X-CPU 01 processor module
Product description
The data processing within the HIMax system absolutely requires the X-CPU 01 processor module. The processor module is used for:
Can handle up to 32 user programs
Perform all central functions, including communication
Use up to 3 additional processor modules to handle redundancy
Process communication through secure Ethernet.
Create and store CPU events.
Store events created by I/O modules.
This module has obtained T Ü V's safety related application certification, with a maximum of SIL 3 (IEC 61508, IEC 61511, and IEC 62061), Cat. 4 (EN 954-1) and PL e (EN ISO 13849-1).
The security function of the module
The security features of the processor module include the following:
Processing user program. -If a malfunction occurs: Stop the user program and reset the variable to its initial value - If a malfunction occurs: Reset the processor module to a safe state and report to the CPU
status
Use safety related Ethernet protocols for secure communication between HIMA controllers (HIMax, HIMatrix, and remote I/O modules).
The data is transmitted through the Ethernet interface of the processor module itself or the Ethernet interface of the COM module.
Safety functions are executed according to SIL 3.
The following elements also contribute to achieving security features:
Hardware self-test
Secure communication with I/O modules
Reaction when a malfunction occurs
If a fault is detected in the test harness, the processor module will enter the ERROR STOP state and restart. Diagnostic information can be used to investigate the cause of the malfunction.
Start after error stop
If the cause of the malfunction still exists, the processor module will avoid restarting and repeating erroneous stops:
After the first error stop, the processor module restarts normally and switches to its system operation.
After the second error stop, the user must restart the system using PADT after resolving the issue.
Once the processor module runs for approximately one minute in system operation, the next error stop that occurs is considered the first error stop.
Type label
The type label specifies the following important details:
Product Name
Qualification mark
Barcode (QR code or one-dimensional code)
Part Number (Part Number)
Hardware Revision Index (HW Rev.)
Software Revision Index (SW Rev.)
Working voltage (power)
Explosion proof specifications (if applicable)
Production Year (Production Year:)

Security related processor system
The security related processor module is a 1oo2 processor system. Continuous self inspection ensures safety related operations.
Features:
Two synchronous microprocessors
Specific DDRAM memory for each microprocessor
Testable hardware comparator for data bus
Watchdog (WD)
Gold capacitors for buffering date/time
LED used to indicate system status
Mode switch used to configure module behavior when voltage is turned on
The processor module compares data between two processors and triggers an interrupt if the following conditions occur Fault occurred.
The monitor monitors two processors. The self check of the module will also check the watchdog.
system controller
The entire data transmission between various components of the system controller processing module:
Security related processor system
System bus A and B
Ethernet switch with connection interface
memory
This module has RAM and non-volatile memory. Non volatile memory is protected by CRC.
Non volatile memory contains the following programs and information:
operating system
User project
Enable switch, watchdog time, safety time
Online modification
Variables with RETAIN attribute
Production data, if necessary, trim data
Fault status history
event
At startup, the system transfers program code from non-volatile memory to redundant program and data storage.
Alarm and Events
The processor module records alarms and other events in its non-volatile memory.
An event is a change in the state of a variable executed by a factory or controller, with a timestamp provided.
An alert is an event that indicates an increase in potential risk.
The HIMax system records state changes as events at a specified point in time. The X-OPC server transfers events to other systems that display or evaluate events, such as control systems.
HIMax distinguishes between Boolean events and scalar events.
Boer Event:
The variation of Boolean variables, such as the variation of numerical inputs.
Alarm and normal states: They can be arbitrarily assigned to variable states.
Scalar event:
Exceeding the limit value defined for scalar variables.
Scalar variables have numerical data types, such as INT and REAL.
Two upper limits and two lower limits are possible.
For the limit value, the following conditions must be met:
Maximum limit ≥ upper limit ≥ normal area ≥ lower limit ≥ minimum limit.
Lag may be effective in the following situations: - if the value is below the upper limit. If the value exceeds the lower limit.
Lag is defined as avoiding unnecessary large events when the global variable oscillates strongly near the limit.
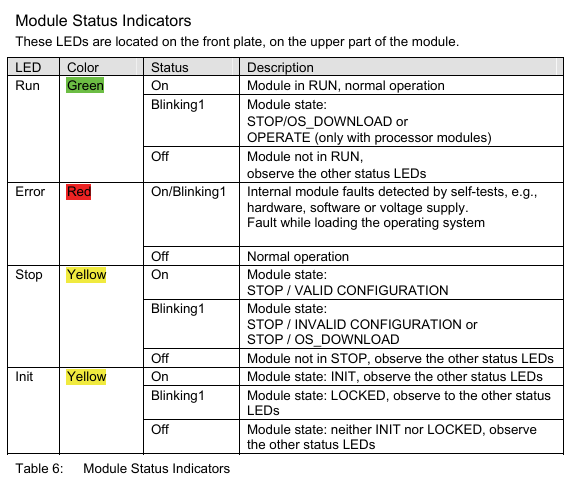
Create Event
Both processor modules and certain types of I/O modules are capable of creating events. at
In the following sections, these I/O modules are referred to as SOE modules.
Create events on the processor module
The processor module creates events using global variables and stores them in a buffer, please refer to Chapter 3.4.7. The event is created during the user program cycle.
Create events on the SOE module
The SOE module can create events using input states. The event is created within the SOE module loop.
The SOE module stores events in the intermediate buffer used by the processor module to read them. The intermediate buffer is a part of volatile memory, so if the power is turned off, events will be lost.
Every event that has been read can be overwritten by a new event.
system event
In addition to recording events related to changes in global variables or input signals, the processor and SOE module also create the following types of system events:
Overflow: Due to buffer overflow, some events were not stored. The timestamp of the overflow event corresponds to the timestamp of the event that caused the overflow.
Initialization: The event buffer has been initialized.
Operation mode stop: SOE module changes its operation mode to stop.
Operation mode 'Run': The SOE module changes its operation mode to 'Run'.
Establish communication: Communication between the processor module and SOE module has begun.
Lost Communication: Communication between Processor Module and SOE Module
Terminated.
The system event contains the SRS identifier of the module that caused the event.
state variable
State variables provide the state of scalar events for user programs. Each of the following states is connected to a state variable that can be assigned a BOOL type global variable:
Normal.
Exceeding the lower limit.
The minimum limit has been exceeded.
Exceeding the upper limit.
The maximum limit has been exceeded.
When the corresponding state is reached, the assigned state variable becomes TRUE.
Recording events
Processor module collects events:
Created by I/O module
Created by the processor module itself
The processor module stores all events in its buffer. A buffer is a part of non-volatile memory with a capacity of 5000 events.
The processor module arranges events from different sources based on their arrival time, rather than sorting them by timestamp.
If the event buffer is full, as long as no other events are read and marked as overwritten, new events cannot be stored.
OPC servers can read events and provide them to external systems for evaluation and storage.
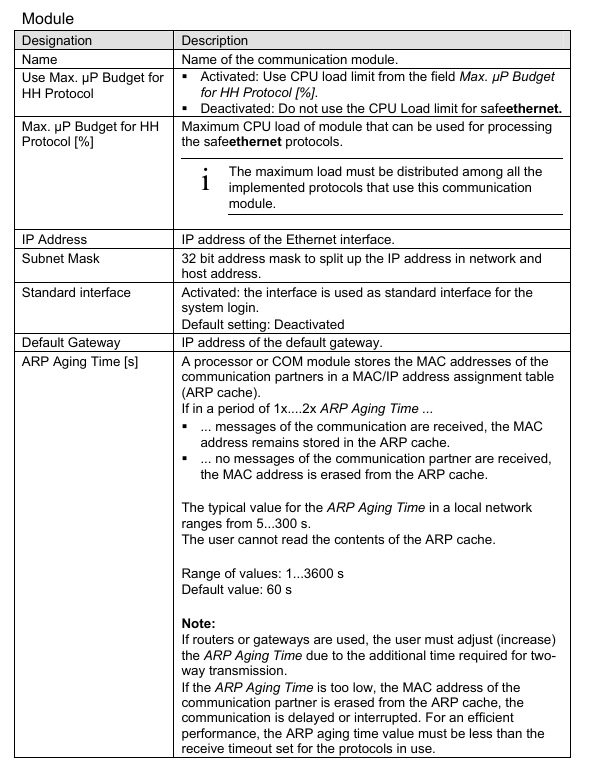
Mode Switch
The mode switch defines the behavior of the processor module when it restarts.
The processor module will restart in the following situations:
Automatic: - When connected to working voltage - After severe malfunction - After loading the operating system
During the operation, use the corresponding commands on PADT.
The mode switch has three different switch positions:
initialization
stop
run
The switch position during normal operation is in operation.
Switch position: initialization
The Init switch position is used to set the processor module to LOCKED state. In this state, the settings previously configured for the module cannot be accessed anymore. For example, if the administrator password is unknown, this operation may need to be performed.
In the locked state, the module is reset to factory settings:
Default SRS, slot number depends on the slot used
Default IP address and IP settings
Only administrator user accounts with empty passwords can access
Enable the switch set to default value
The modified settings in this state will overwrite the factory settings and all previously used settings!
If the settings remain unchanged, the previously saved settings (switch not set to Init) will be used when restarting the module.
start
To start the processor module, insert it into the allowed motherboard slot. If the substrate is already running, the processor module will start and adopt the operating state set through its configuration and mode switch position. If the substrate is not working, please connect the power supply voltage.
install
When installing the processor module, please pay attention to the following points:
This module is designed for use with HIMax substrates. For more information about the bottom plate structure, please refer to the corresponding system documentation.
Operate the processor module only in the expected slot
Only the forced cooling (X-FAN) operation module can be used.
Only use appropriate connector boards to operate the module.
The effect of removing and inserting modules:
When disassembling the module, the connector board remains in the HIMax substrate.
Since all external interfaces are connected through the module's connector board, the module can be replaced without affecting the external interfaces
The SRS of the module is stored on the connector board and becomes SRS after the module is inserted.
The effect of removing the plug
Pulling out the plug will interrupt external communication.
Take appropriate grounding measures.
User Program
The application program functions that PES should execute are specified in the user program. PADT is used to create and compile project configurations using user programs, and load them into processor modules.
Start processor module
The processor module can be started as follows:
Insert it into the substrate that provides working voltage
Open the working voltage of the substrate for inserting the module.
The behavior at module startup depends on:
Position of mode switch
There are additional redundant processor modules present
There are valid project configurations (including user programs) in non-volatile memory
When the switch is set to stop or run, the processor module will check if there are any other processor modules present
If there are no other processor modules, the module will start running separately.
If there is at least one additional processor module, the module attempts to automatically start operating using the configuration of the existing processor module. Maintain a safety rope.

- YOKOGAWA
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- man-machine
- Covid-19
- Energy and Gender
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- architecture
- Industrial information
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- xYCOM
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
KEBA C10-1aa-abb - Control Terminal
-
KEBA T50-T41-CPU - CPU Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 - IRC5 Sx TPU 2 Teach Pendant Controller
-
KEBA D3-DA 330/A-1211-00 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA K2-200 250/X (71580) - Processor Module
-
KEBA O70-bra-A0a-F - Operator Panel
-
Creative Duster Vinyl Brush - Record Stylus Cleaner Brush
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1/04 - Touch Panel Touchscreen Glass Replacement
-
KEBA OP350/Y-1016 - Keyboard Membrane Protective Film K2-200
-
KEBA DO 321/B - Digital Output Card
-
KEBA DI 325/B - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA E-16-DIGOUT-PLUS (D1456E-2) - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA AI 240/A (068370) - Kemro K2-200 Analog Input Module
-
KEBA TM 220/A (066676) - Kemro K2-200 Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


