

K-WANG


YOKOGAWA ZR22G, ZR402G split zirconia oxygen/humidity analyzer
YOKOGAWA ZR22G, ZR402G split zirconia oxygen/humidity analyzer
Core parameters and components of the product
(1) Core components and functions
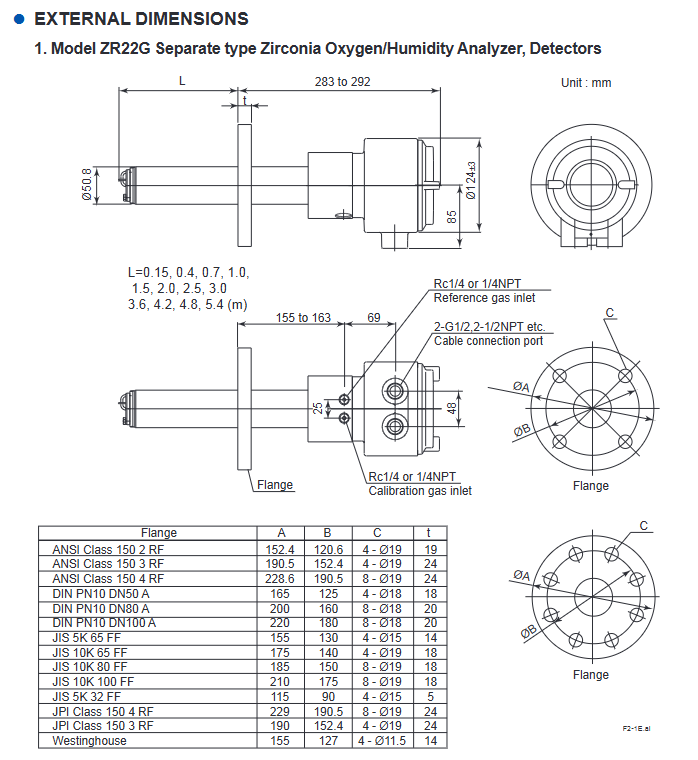
ZR22G detector:
Type: Universal type (sample temperature range 0-700 ℃), High temperature type (0.15m probe, paired with ZO21P adapter, sample temperature range 0-1400 ℃)
Probe length: 0.15-5.4m (excluding 0.15m for humidity analyzer), material: SUS316 (universal type), SiC/SUS310S (high temperature type)
Protection level: equivalent IP44D (universal type), IP66 (pressure compensation type, when cable is sealed)
ZR402G converter:
Display: 320 × 240 dot LCD touch screen, supporting numerical values, trend charts, and fault display
Power supply: 100-240V AC (50/60Hz), maximum power consumption of 300W
Communication: Supports HART protocol (refer to IM 11M12A01-51E document)
Auxiliary equipment:
ZO21R probe protector: suitable for scenarios with gas velocity ≥ 10m/s, anti dust wear
ZH21A dust protector: only for use with humidity analyzers, to prevent combustible dust from entering
ZA8F flow setting unit: for manual calibration, controlling the flow rate of calibration gas/reference gas
ZR40H automatic calibration unit: automatically switches calibration gas, supports timed calibration
(2) Key measurement parameters
Measurement type, measurement range, accuracy, related indicators, response time
Oxygen concentration 0.01-100 vol% O ₂ repeatability ± 0.5% -1% (range), linearity ± 1% -3% (range) 90% response ≤ 5 seconds
Humidity (volume fraction) 0-100 vol% H ₂ O repeatability ± 1 vol% H ₂ O (sample gas pressure ≤ 2kPa)-
Humidity (mixing ratio) 0-1.000 kg/kg --
Core operating procedures
(1) Installation and wiring
Installation requirements:
Environment: Detector ambient temperature -20-150 ℃, converter -20-55 ℃, no corrosive gases, no vibration
Probe installation: For lengths ≤ 2m, it can be installed horizontally to vertically. For lengths ≥ 2.5m, it needs to be installed vertically (± 5 °). High temperature SiC probes need to be installed vertically
Flange specifications: Supports JIS, ANSI, DIN and other standards, and needs to be matched with equipment models
Wiring specifications:
Cable: 6-core shielded cable for detector signal (two-way resistance ≤ 10 Ω), 2-core cable for heater, temperature resistance ≥ 80 ℃
Grounding: Protective grounding resistance ≤ 100 Ω, shielding layer connected to converter FG terminal
Partition wiring: separate signal cables from power/heater cables to avoid interference
(2) Calibration process
Calibration preparation:
Gas requirements: Zero gas (0.95-1.0 vol% O ₂+N ₂), span gas (dry and clean air, dew point ≤ -20 ℃)
Flow setting: Calibrate air flow rate of 600 ± 60 ml/min, reference air flow rate of 800-1000 ml/min
Calibration mode selection:
Manual calibration: Gas valve is manually controlled through ZO21S/ZA8F unit, suitable for system 1/2
Semi automatic calibration: Start with touch panel or touch input, complete calibration according to preset time
Automatic calibration: System 3 dedicated, automatically executed at set intervals (up to 255 days)
Core steps:
Span calibration: Introduce span gas and confirm calibration after the value stabilizes
Zero calibration: Introduce zero gas and complete calibration in the same way
After calibration: Close the calibration gas valve and wait for the output to stabilize (default 10 minutes)
(3) Key points for safe operation
Power safety: Confirm that the power supply voltage matches the rated value of the equipment (100-240V AC), and disconnect the power before wiring
High temperature protection: The working temperature of the detector probe reaches 750 ℃, and gloves should be worn during maintenance to avoid direct contact
Gas safety: Calibration gas/sample gas may be toxic, ventilation or protective mask should be worn during maintenance, and pipelines should be checked for leaks
Sensor protection: The sensor is made of ceramic material to avoid impact and pressure, and direct contact with water droplets is prohibited
Maintenance and troubleshooting
(1) Regular maintenance
Daily maintenance: Clean and calibrate the gas pipeline (anti clogging), check the filter (K9471UA dust filter)
Regular replacement: Sensor components (according to the calibration coefficient, zero gas calibration proportional to 100 ± 30% and span gas calibration proportional to 0 ± 18% are normal), metal O-rings (must be replaced when replacing sensors), heater units (when resistance is abnormal)
Cycle: It is recommended to conduct regular inspections at intervals not exceeding those specified in the equipment manual, and the calibration cycle should be adjusted according to the usage scenario
(2) Common faults and their solutions
Key points for troubleshooting fault types, fault codes/phenomena
Cell voltage fault Error 1: Check the CELL ± wiring, whether the sensor is damaged, and the internal wiring of the detector
Heater temperature fault Error 2: Check the heater resistance (≤ 90 Ω), thermocouple wiring, and cold end temperature (-25-155 ℃)
Zero calibration coefficient alarm Alarm 6 confirms that the zero gas concentration is consistent with the set value, the gas flow rate is normal, and the sensor is not contaminated
High measurement value (oxygen analyzer) - check whether the reference gas humidity is stable, whether the calibration gas leaks, and whether the sample gas pressure is abnormal
Other key information
Product disposal: Local/national environmental regulations must be followed, and batteries must be classified and recycled (EU/UK region)
Spare parts list: Key spare parts include sensor components (E7042UD/ZR01A01), fuses (A1113EF, 3.15A), and metal O-rings (K9470BJ)
Key issues
Question 1: What are the core differences between the three system configurations of ZR22G and ZR402G analyzers? What scenarios are they applicable to?
Answer: The core difference lies in the calibration method and auxiliary equipment configuration, which are applicable in the following scenarios:
System 1: Only includes detector+converter+ZO21S standard gas unit, without fixed calibration gas pipeline, requiring manual connection of calibration gas, suitable for simple humidity monitoring scenarios such as small boiler oxygen concentration monitoring and food production;
System 2: Add ZA8F flow setting unit, zero gas cylinder, pressure reducing valve, reference gas is instrument air, support manual precise calibration, suitable for scenarios such as large boilers and heating furnaces that require regular manual calibration;
System 3: Replace with ZR40H automatic calibration unit, support timed automatic calibration, including combustible gas detection contact input (cutting off heater power), suitable for scenarios such as large industrial furnaces that require long-term stable operation and reduce manual intervention.
Question 2: How to determine if the sensor (zirconia cell) needs to be replaced? What are the key points to pay attention to when replacing?
answer:
Replacement criteria: ① The calibrated zero gas calibration ratio exceeds 100 ± 30% or the span gas calibration ratio exceeds 0 ± 18%; ② In the detailed data display, the cell internal resistance significantly increased (new sensor ≤ 200 Ω, reaching 3-10k Ω after aging); ③ Cell robustness shows' life<1 month '; ④ The sensor has cracks, corrosion, or impact damage.
Replacement precautions: ① Operate after the detector has completely cooled down to avoid high-temperature burns; ② The metal O-ring (K9470BJ) and contact (E7042BS) must be replaced and old parts cannot be reused; ③ When installing the sensor, the four fixing bolts should be tightened evenly (with a torque of about 5.9 N · m) to avoid uneven force damage; ④ After replacement, the calibration process needs to be re executed to ensure measurement accuracy.
Question 3: What is the highest priority troubleshooting step when the device displays Error 2 (heater temperature fault)? What are the corresponding criteria for judgment?
Answer: The steps and criteria for priority screening are as follows:
Firstly, check the polarity of the thermocouple wiring: confirm that the detector TC+is connected to the converter TC+, and TC - is connected to TC -. If connected incorrectly, it will directly cause abnormal temperature detection, which is the most common cause;
Measure heater resistance: Disconnect the HTR terminal of the detector and measure the resistance value. The normal value should be ≤ 90 Ω. If the resistance value is too high, the heater will be disconnected and the heater unit needs to be replaced;
Check thermocouple resistance: After the detector cools down to a temperature difference of ≤ 50 ℃ from the environment, measure the TC ± terminal resistance. Normally, it should be ≤ 5 Ω. If it is>5 Ω, the thermocouple will break and the heater unit needs to be replaced;
Check the cold end temperature: Check the C.J. temperature through detailed data display. The normal temperature should be between -25-155 ℃. If it exceeds, check the cold end sensor or wiring.
- YOKOGAWA
- Energy Access
- Renewable Integration
- Energy Subsidies
- Energy and Water
- Net zero emission
- Energy Security
- Critical Minerals
- A-B
- petroleum
- Mine scale
- Energy and Gender
- Covid-19
- man-machine
- Reliance
- ADVANCED
- SEW
- ProSoft
- WATLOW
- Kongsberg
- FANUC
- VSD
- DCS
- PLC
- Sewage treatment
- cement
- Yaskawa
- Woodward
- BOSCH Rexroth
- MOOG
- General Electric
- American NI
- Rolls-Royce
- CTI
- Honeywell
- EMERSON
- Industrial information
- xYCOM
- Motorola
- architecture
- New energy
- Automobile market
- electricity
- Construction site
- HIMA
- ABB
- Rockwell
- Schneider Modicon
- Siemens
- MAN
- GE
- TRICONEX
- Control Wave
- ALSTOM
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bentley
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- schneider
- Foxboro
- KB
- REXROTH
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- XP POWER
- Baldor
- Meggitt
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
-
ABB 216AB61 Industrial Control Module for Automation Systems
-
ABB 5SHX1060H0003 High Power Thyristor Module for Industrial Power Control
-
ABB 07KT97H3 PLC Central Processing Unit for Industrial Automation
-
ABB 3BHB005171R0101 Power Semiconductor Module for Industrial Power Systems
-
KEBA E-SP-CCEC/A/22 - Keyboard Panel
-
KEBA ERHL33 - Module
-
KEBA K-FTC-AN/B - Control Panel Board
-
KEBA DO321 1914D-0 - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA T70Q - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA BL272/A / BL272/B - Bus Coupling Module
-
KEBA T70R - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PRONET-E-20A-K - Servo Drive
-
KEBA T55-RA0-AU0-LK - Mobile HMI KeTop
-
KEBA DO-272/A - Digital Output Module
-
KEBA PS240/A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA 2134-00393 - Module Code
-
KEBA E-10-ANALOG-SU - Analog Card
-
KEBA 1904D-0 / D1458E - E-10 Analog Card
-
KEBA FM265A - Function Module
-
KEBA CR17910086 - Controller Board
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC2 - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PD242A - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA DI-325 - Digital Input Card
-
KEBA C2-TM-240/A - Digital Input Module
-
KEBA D1547C - I/O Bus Coupling Board
-
KEBA CR-092 - Interface Module
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-003 - IRC5 Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA KETOP-T150-MA0 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA KC-P30-EC24011 - Control Module
-
KEBA 1770B-1 - E-8-THERMO Card
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-CE6 - KeTop Terminal
-
KEBA D1633C-1 - CPU Card
-
KEBA HT401-232-8/0 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA AO-570 - Analog Output Module
-
KEBA T10-mAb-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA C70-rqa-AK0-Le - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA 1918F-0 - Digital Output Board
-
KEBA T10-mAa-DMV - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT2-SCHLUSSELS - Key Switch for HT2
-
KEBA T100-003-CES - HMI Terminal
-
KEBA GVME610IO - I/O Module
-
KEBA HT501-231 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA E-CG-CONTROL - Graphic Control Card
-
KEBA D1420F - F-SIC-1 Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-ANA-SUB2 - Analog Sub-module
-
KEBA HT401-222-4 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA II030 - Input Module
-
KEBA T155-M10-AN0-W - KeTop Mobile HMI
-
KEBA CP088-B - Processor Module
-
KEBA HT40123280 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT4222 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA H24025369 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA H24024891 - Replacement Part
-
KEBA SR161 - Analog Input Card
-
KEBA 1762A - E-CRT/EL Circuit Board
-
KEBA T50-011-CES-CE5 - Operator Terminal
-
KEBA E-CON-ELD/B/15 - Control Panel
-
KEBA E-8-THERMO - Thermocouple Card
-
KEBA 330/A-1211-20 - Axis Module
-
KEBA T55-maw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA C150-110-AK0-N - KeTop HMI
-
KEBA HT4-20656 / HT4-221 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 18658-1 - Analog Board
-
KEBA LM64P89 - LCD Display Screen
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-A - CPU Board
-
KEBA D-CE/59718/15 - Control Board
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400E2-E00 - Control Module
-
KEBA 3HAC12929-1 - Teach Pendant SX TPU
-
KEBA E-CON-CC100/A - Control Panel Engel
-
KEBA T200-M01-P20-WES7 - Panel PC Windows Embedded
-
KEBA KC-P30-ES2400B2-M0R - KeControl C3 Module
-
KEBA E8ANALOGC - Analog Card
-
KEBA E-CPU-88-B - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-raw-AU0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA D1633C - CPU Board
-
KEBA T55-MAW-Au0-CE6 - Mobile HMI
-
KEBA 3HAC11266-4 - Teach Pendant Cable
-
KEBA T20e-m00-Br0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA E-3-ACU-INC - Controller Board
-
KEBA E-PS-24V - Power Supply Module 24V
-
KEBA C55-2aw-1U0-R - Control Unit
-
KEBA T70-qqu-Aa0-LK - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA PS244 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA ECPU186B - CPU Circuit Board
-
KEBA E-8-ANALOG/C - Analog Input Card Engel
-
KEBA AT-4041 - KeControl C3 Controller
-
KEBA T50-ADP - Adapter Module
-
KEBA CP088/D - Control Processor Module
-
KEBA CU312 - Central Unit Module
-
KEBA K2-400 SC440/A - Communication Module
-
KEBA CU212 - Power Supply Module
-
KEBA T20T-T00-AR0-C - KeTop Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA HT4014X20B21572 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA HT4010V4X201K4 - Operating Terminal
-
KEBA HT401/NC-4X20/20844 - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA RS-091 / RS091A - Remote Station Module
-
KEBA E8THERMOA - Thermocouple Input Card
-
KEBA TI-570 - Temperature Input Module
-
KEBA C35E 10m/79421/02 - KeTop Teach Pendant
-
KEBA T40-001/58599/06 - Teach Pendant
-
KEBA CR17910087 C5G-GTP5 - Controller Board
-
KEBA T20E-R00-AR0-C - Handheld Terminal
-
KEBA 3HAC023195-001 /02 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA AR281 - Analog Input Module Engel
-
KEBA D3-DA330/A-0611-20 - D3 Axis Module
-
KEBA CU313 / C-SICU313KEB - Control Unit
-
KEBA k2-700 - Kemro Control System
-
KEBA CU211 - Central Unit Power Supply Module
-
KEBA C5G-TP5WC - Robot Teach Pendant
-
KEBA C100D-CE - Control Panel
-
KEBA D3-DR361/D-6341-30 - D3 Drive Module
-
KEBA D3-DP/A-1000-0 - D3 Supply Module
-
KEBA SXTPU-21664 - Teach Pendant Unit
-
KEBA T70-rqa-AK0-LK - KeTop Touch Screen Glass Panel
-
ABB REF610 Protection and Control Relay
-
ABB DSQC633 Robot Control Interface Module
-
ABB DSQC332A Robot Control Module
-
ABB F362 Industrial Interface Module
-
ABB SK616001-A Industrial Control Module
-
ABB 3HAC0977-1 Robot Control Interface Module
-
ABB S503X Industrial Protection and Switching Device
-
ABB BC25 Industrial Automation Communication Interface
-
ABB DSQC504 Robot Servo and Control Module
-
ABB DSQC509 Robot I/O and Control Interface Module
-
ABB DSQC346B Robot Motion Control Board
-
ABB 3HAB8859-1/03A Industrial Robot Control Interface Board
-
ABB 3HAB9271-1/01B Robot Controller Communication Module
-
ABB 3HAC5497-1 Robot Control Processing Module

KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923


