K-WANG


- Telephone:+86-15305925923
- contacts:Mr.Wang
- Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com
Manufacturers
ABB
Model(s)
ABB Advant Controller 31, ABB Advant OCS
Estimated Shipping Size
Dimensions: 5.0" x 3.8" x 3.5"
(12.7 cm x 9.5 cm x 8.9 cm)
Weight: 0 lbs 12.0 oz (0.3kg )
Tariff Code: 8537109060
Country of Origin: France
Ships from Webster NY, USA
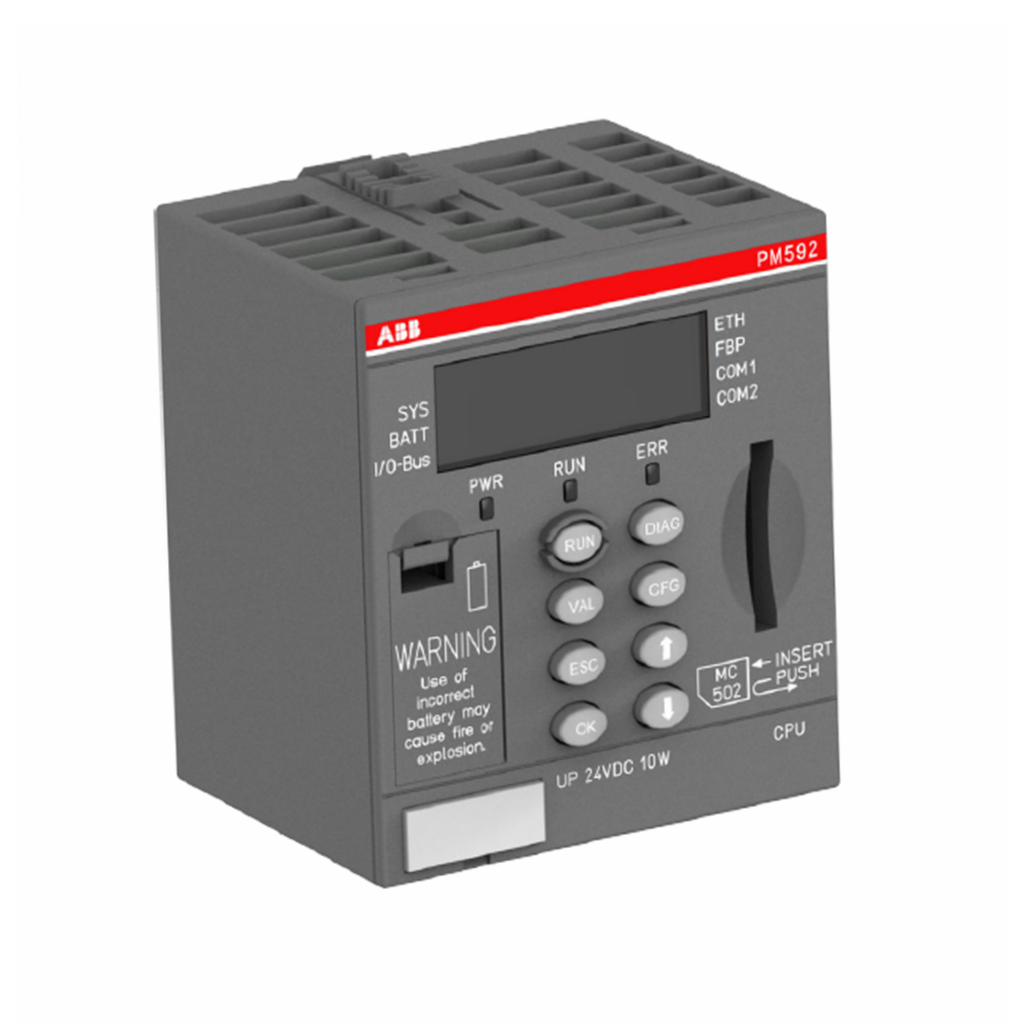
ABB 1SBP260025R1001 07CT42 Programmable Logic Controller
Basic introduction
Product Overview: ABB 1SBP260025R1001 07CT42 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a key device in the field of industrial automation control. It is programmed to achieve automated control of a variety of industrial processes and equipment, and is capable of receiving input signals, processing them according to pre-written logic programs, and then outputting control signals to drive external devices, such as motors, valves, indicator lights, and so on.
Hardware structure: usually with a rugged shell to adapt to the industrial environment of dust, moisture, vibration and other unfavourable factors. Its internal includes processor, memory, input/output (I/O) interface and other major components. The processor is responsible for executing programme instructions, the memory is used for storing programme codes and data, and the I/O interface is used for connecting external devices and realising the input and output of signals.
Functional Features
Programming Flexibility
Programming language support: Supports various programming languages, such as Ladder Diagram (LAD), Instruction Table (STL), Function Block Diagram (FBD), etc. Ladder diagram language is similar to relay control circuit, intuitive and easy to understand, suitable for users with basic electrical control; instruction table language is closer to machine language, more convenient for users familiar with assembly language; function block diagram language builds the program through graphical function blocks, which is conducive to modular programming of complex functions.
Programme capacity and complexity handling: with sufficient programme storage capacity, it can handle complex control logic. Users can write programs containing multiple logic blocks, timers, counters, arithmetic operations and comparison instructions, etc. to achieve precise control of industrial processes. For example, in an automated packaging line, programs can be written to control multiple steps of the packaging machine, such as feeding, wrapping, and sealing, as well as to handle complex logic such as fault detection and alarms.
Input/Output Functions
Number and type of I/O points: Equipped with abundant I/O interfaces, including digital input (DI), digital output (DO), analogue input (AI) and analogue output (AO) interfaces. The digital interface is used to process switching signals, such as input signals of buttons, limit switches, etc., as well as output signals of control relays, indicators, etc.; the analogue interface can receive and process continuously changing signals, such as input signals of temperature sensors (4-20mA), pressure sensors (0-10V), as well as outputting control signals to regulate inverters, regulating valves and other devices.
I/O Expansion Capability: Support I/O expansion module, when the number of basic I/O points can not meet the application requirements, you can increase the number of input and output points by adding expansion modules. This enables the PLC to flexibly adapt to industrial automation systems of different scales, from small single machine equipment control to large-scale production line control.
Communication Function
Communication interfaces and protocols: There are various communication interfaces, such as Ethernet interface (RJ45), serial interface (RS-232, RS-485) and so on. Through these interfaces, the PLC can communicate with the host computer monitoring system, other PLCs, human-machine interface (HMI) devices, and intelligent meters. Supported communication protocols include, but are not limited to, Modbus, Profibus, TCP/IP, etc., thus realising data sharing and system integration.
Remote monitoring and control: Using the communication function, remote monitoring and control can be realised. In large-scale factories or distributed control systems, operators can remotely access the PLC through the upper computer software in the central control room to view the status of the equipment in real time, modify the parameters, download the programme and other operations, which greatly improves the maintainability of the system and management efficiency.
Technical Parameters
Electrical parameters
Operating voltage range: usually has a wide operating voltage range, such as 18 - 30V DC or 85 - 264V AC, to adapt to different power supply conditions, and in a certain voltage fluctuation range can still work normally.
Input/Output Electrical Characteristics: The input voltage range of digital input interfaces depends on the specific channel type, e.g., a 24V DC input channel may have an input voltage range of 18 - 30V DC, and the input current is typically between a few milliamps and tens of milliamps; the output current rating of digital output channels is typically between 0.5 - 2A, and the output voltage can be of various levels depending on the load and configuration; The analogue input interfaces are capable of handling common analogue signal ranges such as 0 - 10V DC, 4 - 20mA, with signal resolutions of 12 - 16 bits possible; the analogue output channels have similar output signal ranges and resolutions to ensure accurate analogue signal output.
Performance Parameters
Processor performance: the processor's operating speed and processing power determines the efficiency of the PLC to execute the programme. Generally has a high clock frequency and instruction execution speed, can quickly respond to changes in the input signal and output control signals. For example, the instruction execution time may be in the range of microseconds or milliseconds, which is very important for real-time requirements of industrial control applications.
Programme storage capacity: The size of the storage capacity varies depending on the model and is generally measured in bytes (B), kilobytes (KB) or megabytes (MB). Sufficient storage capacity can store complex control programmes and a large amount of data, such as system configuration parameters and historical data records.

| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923