K-WANG


- Telephone:+86-15305925923
- contacts:Mr.Wang
- Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com
Manufacturers
ABB
Model(s)
ABB Advant Controller 31, ABB Advant OCS
Estimated Shipping Size
Dimensions: 6.0" x 4.0" x 10.0"
(15.2 cm x 10.2 cm x 25.4 cm)
Weight: 1 lbs 11.1 oz (0.8kg )
Tariff Code: 8538907080
Country of Origin: Sweden
Ships from Webster NY, USA
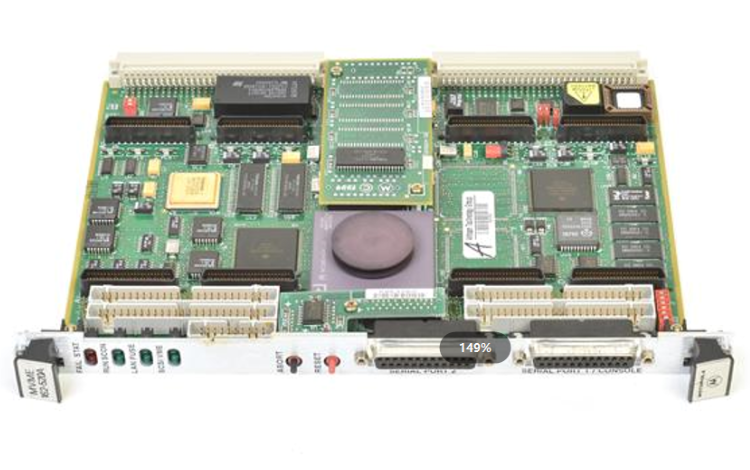
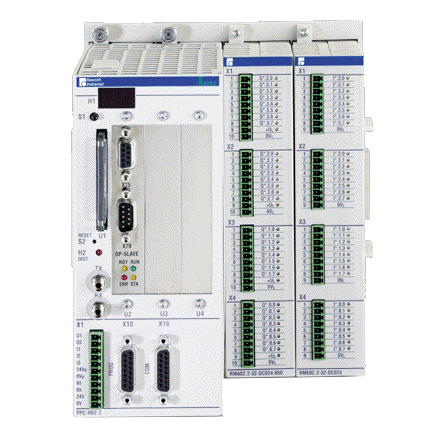
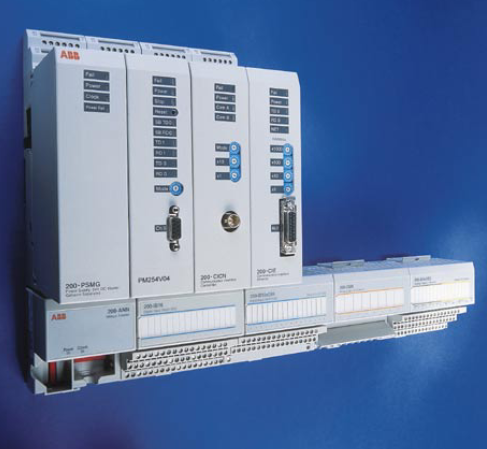
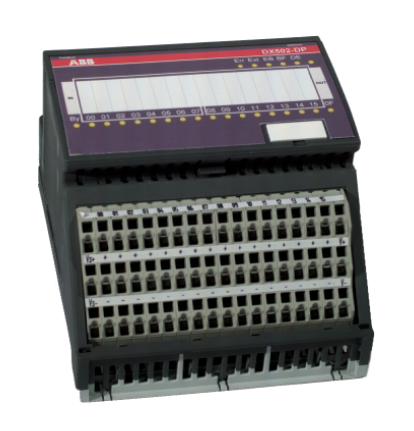
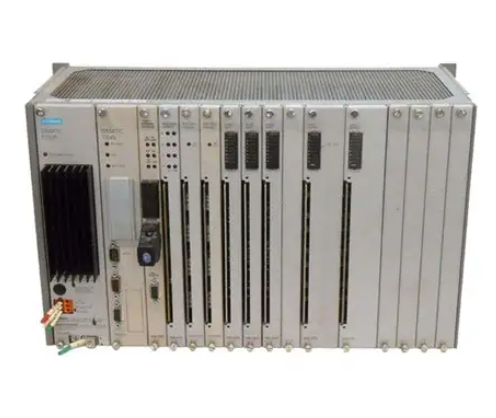
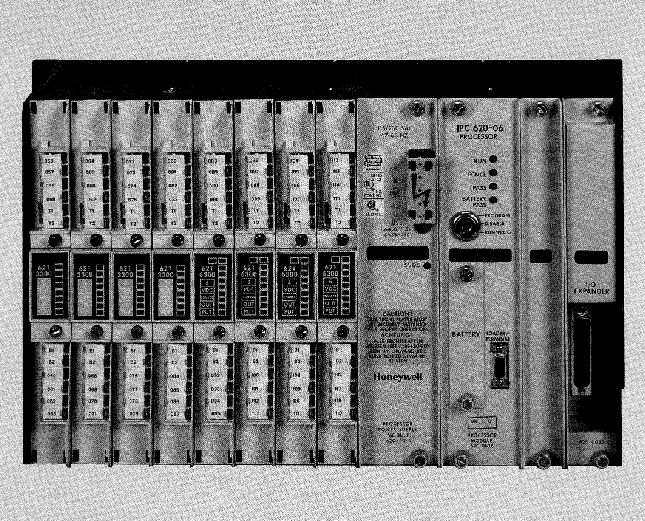
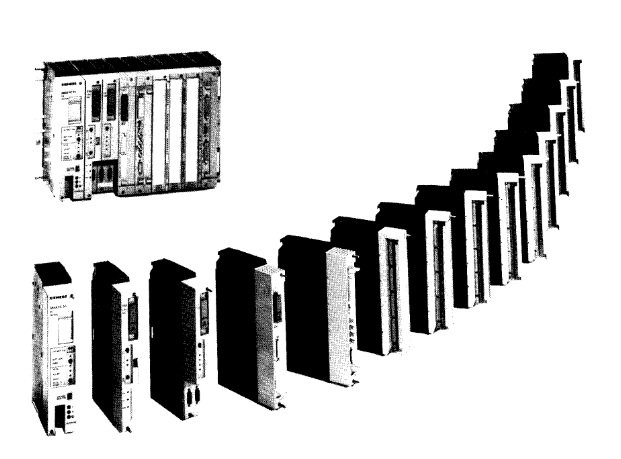
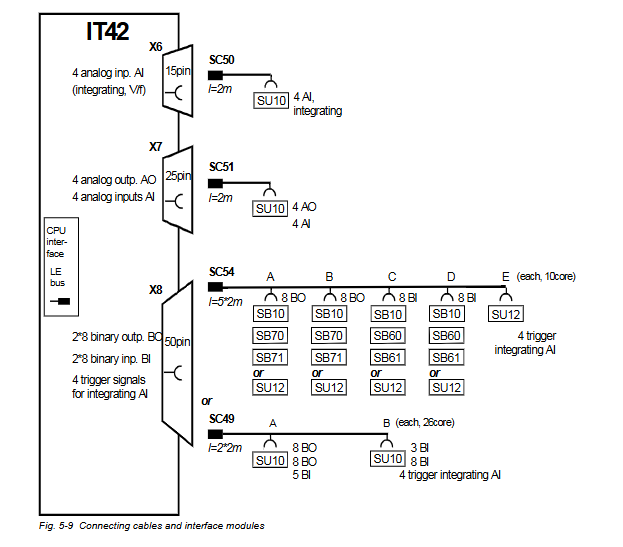
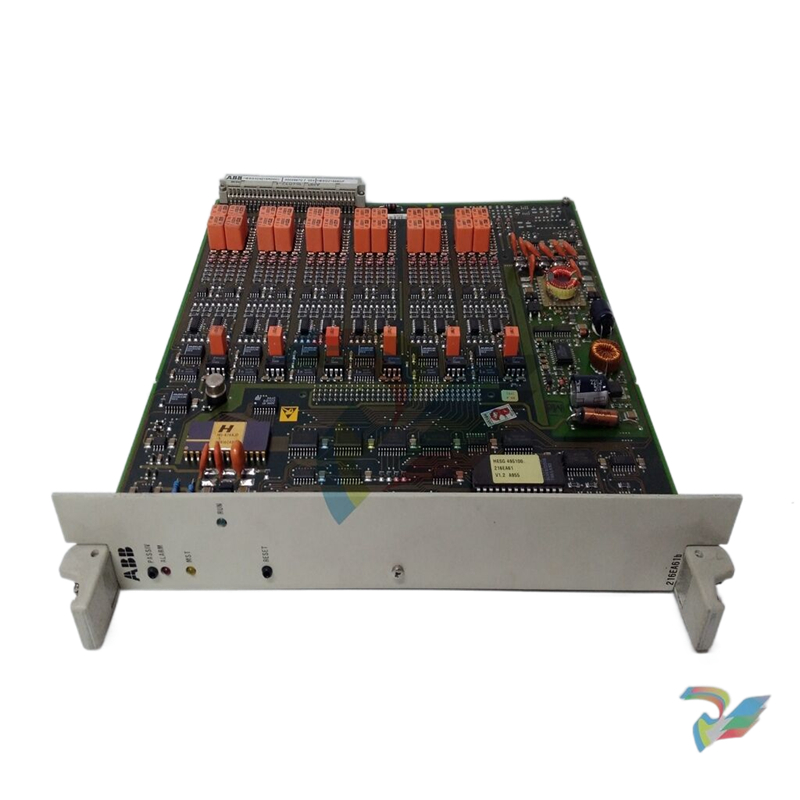
ABB GJR5253000R0100 07KT97 Advant Controller 31 Basic Unit
Product Overview
Model and Series: ABB GJR5253000R0100 07KT97 belongs to the Advant Controller 31 series of basic units. This indicates that it is the basic component of the control system of the series, providing core functional support for the operation of the entire system.
Role in the system: As the basic unit, it is similar to a ‘brain centre’, responsible for receiving, processing and sending various control signals. It connects different input devices (e.g. sensors) and output devices (e.g. actuators) and coordinates their work to achieve effective control of industrial processes or equipment.
Performance Characteristics
Processing power and speed
Efficient data processing: powerful computing power to quickly process signals from multiple input channels. For example, in an automated factory environment, it can simultaneously process data from multiple sensors such as temperature sensors, pressure sensors, flow sensors, etc., analyse this data in real time and respond quickly according to a preset control strategy.
Multi-tasking capability: It can run multiple tasks at the same time, such as executing control algorithms, performing data logging, and processing communication protocols. This makes it capable of meeting multiple needs in complex industrial scenarios, such as controlling production equipment while also communicating and transmitting data to a host computer system.
Input and output interface functions
Rich interface types: Equipped with various types of input and output interfaces. These include digital input interfaces, which are used to receive switching signals, such as the start/stop button signals of equipment; digital output interfaces, which can be used to control relays, indicators and other equipment; analogue input interfaces, which can be used to connect to analogue sensors, such as temperature sensors (the output of which is continuous voltage or current signals), pressure sensors, etc., and to convert the analogue signals into digital signals for processing; and analogue output interfaces, which can be used to Analogue output interfaces can be used to control control valves, inverters and other devices that require continuous control signals.
Interface expandability: These interfaces have a certain degree of expandability, which may allow users to increase the number of interfaces by adding expansion modules to adapt to application scenarios of different scales and complexity. For example, when more sensors need to be accessed or more actuators need to be controlled, the interface can be easily expanded.
Communication Functions
Multiple communication interfaces: It may be equipped with multiple communication interfaces, such as Ethernet interface, RS-232 interface, RS-485 interface and so on. Ethernet interface can be used to achieve high-speed, long-distance data transmission, which is convenient to connect the equipment to the internal LAN or Internet, so as to realise remote monitoring and management.RS-232 and RS-485 interfaces are commonly used in the industrial field, which can be used to connect with other devices, such as human-machine interface (HMI), other controllers or intelligent meters, etc., to build a fieldbus network.
Communication protocol support: It supports a variety of industrial communication protocols, such as Modbus, Profibus and other common protocols. This makes it possible to communicate with devices produced by different manufacturers, enhancing the compatibility and openness of the system. For example, in an automation system with mixed brands of equipment, it can use the Modbus protocol to communicate with sensors of one brand, and at the same time use the Profibus protocol to communicate with inverters of another brand.
Reliability and Stability
Hardware Reliability Design: High-quality electronic components are used, which are rigorously screened and tested to ensure stable operation in harsh industrial environments. For example, its circuit boards may be made of high-quality PCB (Printed Circuit Board) materials with good anti-interference performance and mechanical stability; key components such as chips also have high resistance to electromagnetic interference and temperature tolerance.
Fault tolerance and redundancy mechanism (possible): In order to ensure uninterrupted operation of the system, there may be some fault tolerance and redundancy design. For example, there may be redundancy design in the power input section so that when one power supply fails, another backup power supply can continue to supply power to the equipment; in the data storage and processing section, there may be a data backup and recovery mechanism to prevent the loss of data or errors leading to system failure.
Software Features and Flexibility
Programming Flexibility: Supports a variety of programming languages, such as ladder diagram, instruction table, structured text, etc.. Users can choose the appropriate programming language according to their programming habits and specific control tasks. For example, for simple logic control, ladder diagram programming is intuitive and easy to understand for beginners, while for complex data processing and algorithm implementation, structured text programming is more advantageous.
Customisable control strategies: Users can customise various control strategies to suit different industrial processes through software programming. For example, in the temperature control process, PID (Proportional-Integral-Differential) control algorithms can be programmed to dynamically adjust the output power of the heating or cooling equipment according to the deviation of the actual temperature from the set temperature, achieving precise temperature control.
Technical specifications (presumed)
Power supply specifications
Input Voltage Range: May support a wide input voltage range, such as AC 85 - 264V or DC 24 - 48V, to suit different industrial power supply environments. This allows it to work properly in different factories and under different power supply conditions.
Power Consumption: Power consumption may vary depending on specific configurations and load conditions, the approximate range may be between 30 - 300 watts. This depends on factors such as the number of devices connected, the use of interfaces and the complexity of the tasks being run.
Processing Performance
Processor Type and Frequency: An industrial grade processor such as the ARM-Cortex family or similar may be used, and the frequency may range from a few hundred megahertz to several gigahertz. Such processors can provide enough computing power to handle large amounts of real-time data and complex control algorithms.
Memory capacity: Contains flash memory (for storing program and configuration data) and random access memory (RAM, for running programs and temporary data storage). Flash memory capacity may range from a few megabytes to tens of megabytes for storing the operating system, applications, and user configuration files; RAM capacity may range from a few megabytes to tens of megabytes to ensure that the system is able to run various applications and process real-time data smoothly.

| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923