K-WANG


- Telephone:+86-15305925923
- contacts:Mr.Wang
- Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com
Manufacturers
ABB
Model(s)
ABB Advant Controller 31, ABB Advant OCS
Additional Information
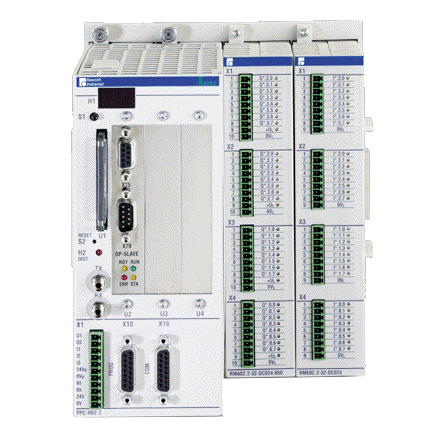
The basic unit 07KT94 with order number GJR5252100R0101 is 24 Vdc input power.
Estimated Shipping Size
Dimensions: 10.0" x 4.0" x 6.0"
(25.4 cm x 10.2 cm x 15.2 cm)
Weight: 1 lbs 10.1 oz (0.7kg )
Tariff Code: 8537109060
Country of Origin: Germany
Ships from Webster NY, USA
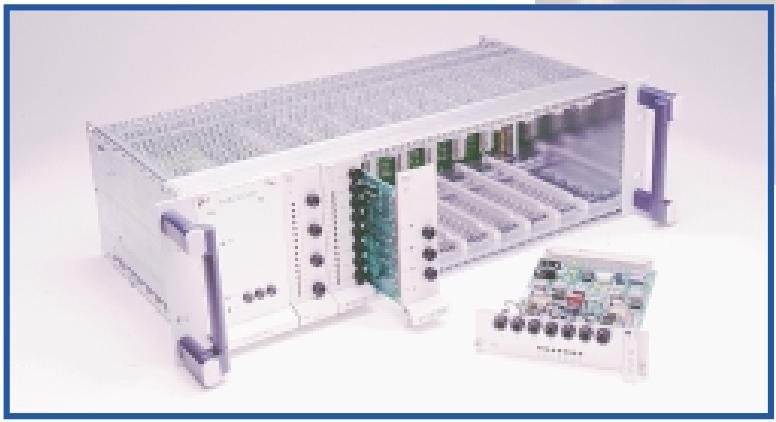
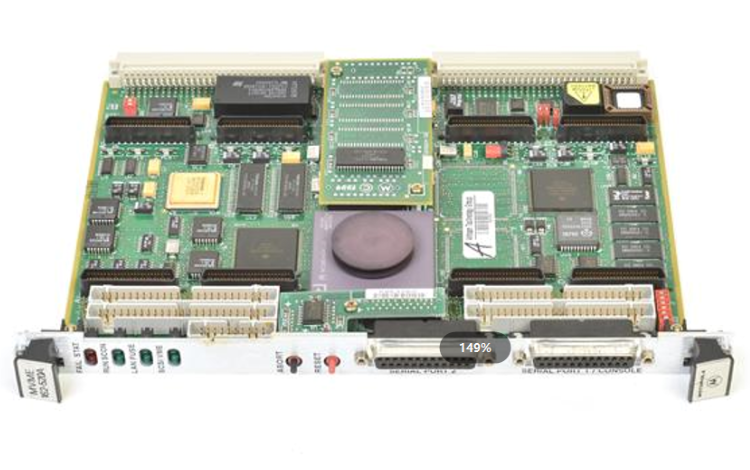
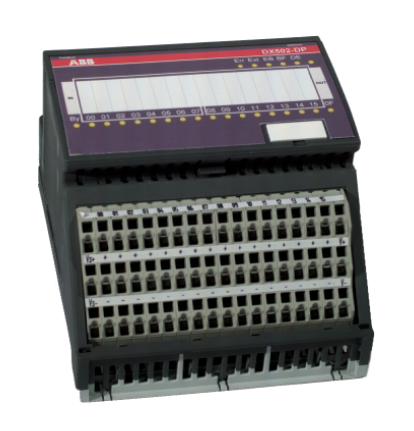
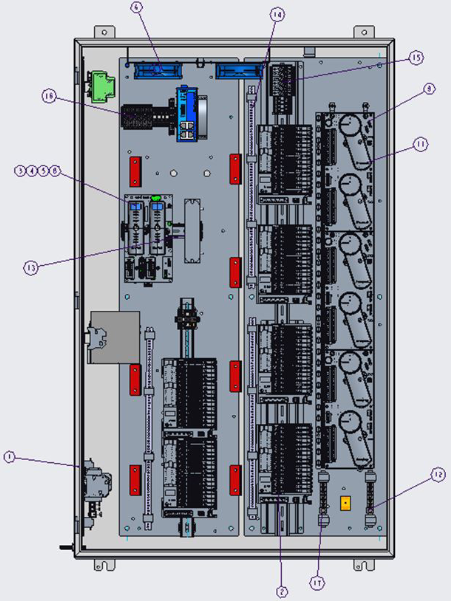
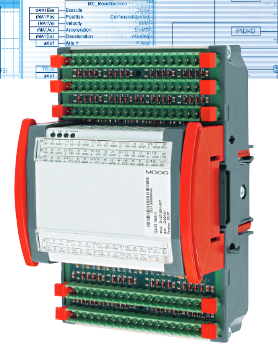
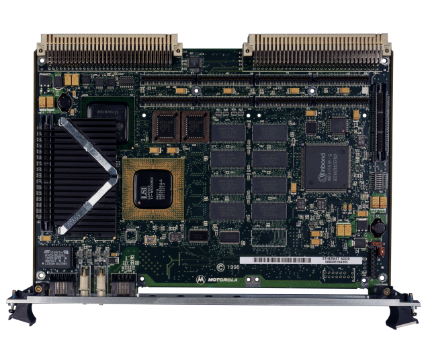
ABB GJR5252100R0101 Advant Controller 31 Basic Unit
Product Overview: ABB GJR5252100R0101 belongs to Advant Controller 31 series.
Series and basic functions: ABB GJR5252100R0101 belongs to the Advant Controller 31 series of basic units. In the industrial automation system, it is the core control component, mainly responsible for the control and management of various industrial equipment and processes. Its function is similar to a ‘brain’ that receives input signals from sensors, processes them according to preset procedures and logic, and then outputs control signals to actuators to realise automation operations.
Performance Characteristics
Processing power and arithmetic performance
Highly efficient data processing capability: Equipped with a powerful processor, it is capable of quickly processing large amounts of input and output data. In complex industrial environments, such as automated production lines with multiple devices running at the same time, massive amounts of data are generated, such as temperature, pressure, position, and other sensor data. The controller can quickly collect, analyse and process this data to ensure that the system can respond in real time.
Multi-tasking function: It supports multi-tasking at the same time, and is able to perform operations such as data logging, communication, and troubleshooting while executing control tasks. For example, while controlling the motor speed, it can also record and upload the equipment operation data to the upper computer system, and monitor itself and the external equipment in real time to see if there is any fault.
Input and output interface characteristics
Abundant interface types: There are various input and output interfaces, including digital input (DI), digital output (DO), analogue input (AI) and analogue output (AO) interfaces. The digital inputs can receive signals such as switching signals (e.g. start/stop button signals for devices), and the digital outputs can control devices such as relays and indicator lights. The analogue input interfaces can be connected to analogue sensors, such as temperature sensors (output voltage or current signal proportional to temperature), pressure sensors, etc. The analogue output interfaces are used for controlling devices that require continuous regulation, such as control valves, frequency converters, etc.
Good interface expandability: Expansion interfaces are provided to facilitate users to increase the number of input and output points according to the actual demand. For example, when the enterprise needs to expand the production line and add new equipments and monitoring points, the number of interfaces can be easily expanded by adding expansion modules without replacing the whole controller, which effectively reduces the cost of system upgrading.
Communication function
Multiple communication interface support: Equipped with a variety of communication interfaces, such as Ethernet interface, RS-485 interface, RS-232 interface and so on. Ethernet interface is used to achieve high-speed, long-distance data transmission, which can easily connect the controller to the internal LAN or the Internet to achieve remote monitoring and management.RS-485 and RS-232 interfaces are commonly used in the industrial field, which can be used to connect the human-machine interface (HMI), other controllers or intelligent meters and other devices to build a fieldbus network.
Strong communication protocol compatibility: It supports a variety of industrial communication protocols, such as Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP and so on. This makes it possible to communicate with devices produced by different manufacturers, and in an automation system containing multiple brands of devices, interconnection between devices can be well realised. For example, it communicates with sensors to obtain data via Modbus protocol, and then sends control commands to actuators via Profibus protocol.
Reliability and Stability
Hardware Reliability Measures: High-quality electronic components are used and undergo strict screening and testing processes to ensure stable operation even in harsh industrial environments. For example, the circuit board adopts high-quality printed circuit board (PCB) materials with good anti-interference performance, which can effectively prevent the influence of electromagnetic interference on the internal circuit. Chips and other key components have high resistance to temperature changes, vibration and static electricity.
Fault Diagnosis and Recovery Function: Built-in fault diagnosis system can monitor its own hardware and software status in real time. When a fault occurs, such as an input/output interface failure, a communication failure, or an abnormal programme operation, it will send out an alarm signal in a timely manner and recover itself as much as possible. For example, if the communication is temporarily interrupted, it will try to re-establish the connection; for some repairable hardware failures, it will continue to run by adjusting the working mode or enabling the spare module.
Software Features and Flexibility
Programming Language Diversity Support: Supports a variety of programming languages, such as ladder diagram, instruction table, structured text, etc.. Ladder diagram programming is intuitive and easy to understand, suitable for beginners and simple logic control scenarios, such as controlling a simple motor start/stop and forward/reverse logic. Instruction list programming is more compact and efficient, suitable for occasions with requirements on programme size and execution speed. Structured text programming is more suitable for complex algorithms and data processing, such as in the implementation of complex PID control algorithms is very advantageous.
Customisable control strategies: Users can customise a variety of complex control strategies to suit different industrial processes through the programming software. For example, in chemical production, control strategies for parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, etc. are customised according to the different stages of the chemical reaction. PID (Proportional-Integral-Differential) control algorithms can be programmed to dynamically adjust valve openings or stirrer speeds, etc., based on the deviation of the actual value from the set value, to achieve precise process control.
Technical specifications (presumed)
Power supply specifications
Input Voltage Range: A wide range of input voltages such as AC 85 - 264V or DC 24 - 48V may be supported to suit different industrial power supply environments. This ensures that the controller will function properly under different plant power conditions, including fluctuations in utility power or the use of backup power.
Power Consumption: Power consumption will vary depending on the specific configuration and load conditions. Under normal operating conditions, the approximate range may be between a few tens of watts and a few hundred watts. For example, when there are more connected devices, complex control tasks and frequent communication, the power consumption will be relatively high; while in standby or light load state, the power consumption will be low.

| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923