K-WANG


- Telephone:+86-15305925923
- contacts:Mr.Wang
- Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com
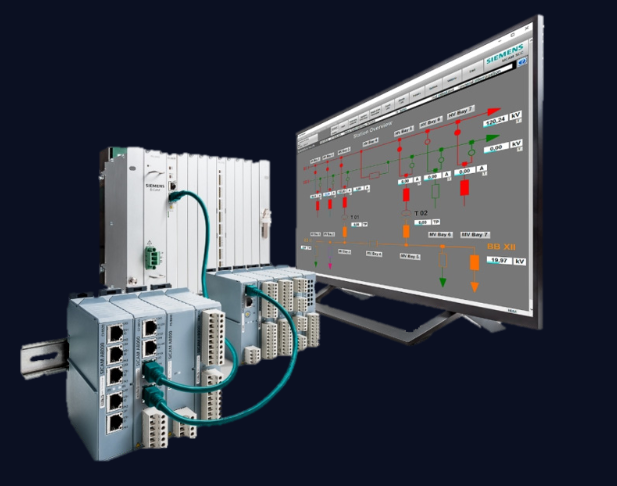
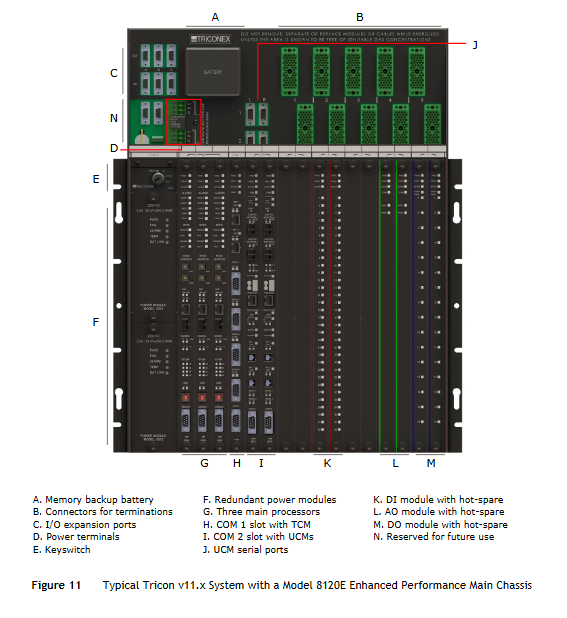
GE IC693PBS201 PLC Profibus DP network slave module
GE IC693PBS201 PLC Profibus DP network slave module
4、 GE Fanuc Profibus DP Network Product Description
The GE Fanuc series PACSystems supports Profibus DP master/slave modules 5136-PFB-VME for 90-70.
5136-PFB-VME, as a standard VME module, can be plugged into PAC70 systems and 90-70 PLCs
On the central rack and configured as "3rd PartyVME" by its programming software. This interface card uses 256K bytes
Standard memory and 1K byte short I/O storage area.
According to the working principle of Profibus DP, the DP master station should know the detailed information of all slave stations on the network
(e.g. station address and I/O quantity for each slave station). Utilizing the SST Profibus Configuration software package
These configuration information can be generated and saved as binary files (*. bss). This configuration information file can be accessed from
Download the serial port of 5136-PFB-VME to the module. This interface card can support up to 96 DP slave stations (such as stations)
If the number exceeds 32, a repeater is required.
4.1 The configuration steps for the 90-70 system using 5136-PFB-VME are as follows:
Establish a 90-70 Profibus DP network (Version 2.0)
4.1.1 Introduction
The 90-70 5136-PFB-VME interface program PB_0825 mentioned in this article can be completed in just 3ms (CPU915)
120 word slave data exchange. This program is a ladder diagram program that can be obtained through GEFanuc.
This article provides a detailed introduction on how to use the 5136-PFB-VME interface card to connect to the Profibus DP network in a 90-70 PLC.
The interface program PB_0825 mentioned in the article can support two 5136-PFB-VME interface cards. Of course, you can also
This interface program is used in PLC systems with only one interface card.
5136-PFB-VME, as a standard VME module, can be plugged into the central rack of 90-70 PLCs and can be used by 90-70
The programming software configuration is "3" PartyVME ". This interface card uses 256K bytes of standard memory and 1K bytes of short I/O
Storage area.
4.1.2 Hardware Installation
4.1.2.1 Setting Short I/O Address
The 5136-PFB-VME interface card occupies a short address interval of 1K bytes on the VME bus, and this memory interval can be occupied by 90-
Use the VME-Read/Write instruction (AM=29H) in CPU 70 to access. The starting address of this memory area is dialed
Set the 1st to 6th positions of code switch S1, and the switch settings in the following figure will connect the ground of two 5136-PFB-VME modules
The addresses are set to 8000H and 7000H respectively. Here, the interface card with address 8000H is referred to as the first card,
7000H is called the second card.
Short I/O Base Address
Base Address
position 1
Position 2
Position 3
position 4
position 5
position 6
8000H
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
7000H
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
The first card is set to 8000H, and the second card is set to 7000H
These two interface cards can be inserted into any slot on the mainframe, but there must be no empty slots between these two modules and the CPU.

GEFanuc Automation Network and Communication
Profibus DP network
The interface program consists of three basic subroutine blocks: Init_0, Init_1, and Assign. Init_0 is used to initialize the first block
Port card (with an I/O address of 8000H). Init_1 is used to initialize the interface card with an I/O address of 7000H. Assign subroutine
Used to exchange slave data between CPU and interface card.
Due to the internal use of the% L variable in the Init_0, Init_1, and Assign blocks, these three blocks must
Called in PB0 and PB1.
Note: After successfully initializing the first interface card with Init_0, the variable "Init_0_oK" (% T00217) will be set to
1. After successfully initializing the second interface card (with an I/O address of 7000H), the variable 'Init_1_SK'
(% T00233) will be set to 1. Variables% T00209 to% T00256 are reserved for initialization program use, user
Please do not use these variables in the program The variables% L00001 to% L01320 of subroutines PB-0 and PB_1 are assigned
When using program blocks, user programs should use variables with addresses of% L01320 or higher.
Steps:
4.1.3.1 Call the Init_0 and Init_1 subroutine blocks
Wg: Set whether the watchdog of the interface card is working. Fill in 1 to allow the watchdog to work, and fill in 0 to prohibit it from working.
Tx: The data sent from the master station to the slave station (i.e., the output of the slave station) is temporarily stored at the starting address in the% L variable. length
512 words. Its meaning is consistent with the BT parameters. Note that all output data from the slave station is in ascending order of the slave station address
The sequence is arranged in blocks, and the word length of each output data block from the slave station must be a multiple of 4 (for example, on the bus)
There are 4 slave stations with addresses 3, 4, 6, and 8 respectively. If the Tx parameter is% L01750, slave station 3 has 5 bytes
The output data from station 4 has 10 bytes and station 6 has 1 byte. Then the output data block from station 3
%Starting from L01750, the output data from station 4 starts from% L01754, and the output data from station 6 starts from
%Starting from L01762, the output data from station 8 starts from% L01766. Users can calculate each slave station themselves
The offset address of the output data in% L, and then use the MOV instruction to move the actual output data (% Q) to this address
Some% L. However, after the Assign program block is called for the first time, it will automatically calculate the output data of each slave station
%The offsets in L are stored in the TF parameters.
TF: The offset address of the output data block of each slave station calculated after the first call of the Assign program block. long
120 words. If TF=% L01501, calculated according to the above example, then after the first call of the Assign program block,
%L01501=1750,% L01502=1754,% L01503=1762,% L01504=1766. The user program should be in
After assigning the program, use indirect addressing to move the actual output data from the slave station to% L01750,% L01754
%L01762,% L01766. As shown below:
Mov
%O001
@L01501
RF: The offset address of each slave input data block calculated by the Assign program block, which has the same meaning as the TF parameter
Like. Length of 120 words.
Rx: The starting address of the data received by the master station from the slave station (i.e., the input from the slave station) is temporarily stored in the% L variable. long
The degree is 512 words, and its meaning is similar to the TX parameter.
St: Slave station status word, with a length of 120 words. Each status word represents the status of a slave station, with the first word representing the station's location
The status of the slave station with address 0, and the second status word represents the status of the slave station with address 1. The height of the status word
The byte stores the sequence number of the slave station (for example, if there are 4 slave stations on the bus with addresses 3, 4, 6, and 8, then this
The sequence numbers of the slave stations are 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The low byte of the status word contains the current status information of the slave station
If it is 80H, it means that the slave station is working normally; If it is 00H, it means that the slave station has a fault, which may
It is a cable or connector malfunction or configuration error. If the entire status word is FFO0H, it means that the slave is not present
It is configured in the SST Profibus configuration software.
be careful:
If you only have one 5136-PFB-VME interface card in your system, you only need to use the program blocks PB-0 or PB_1
One of them.
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923