K-WANG
+086-15305925923
Service expert in industrial control field!
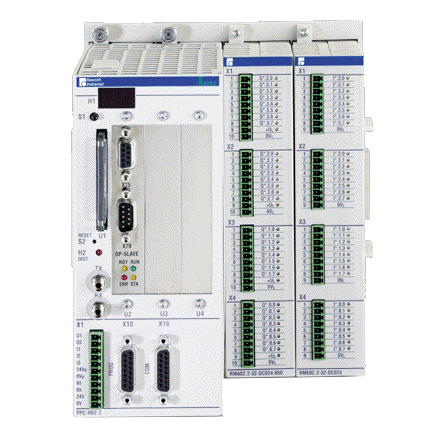
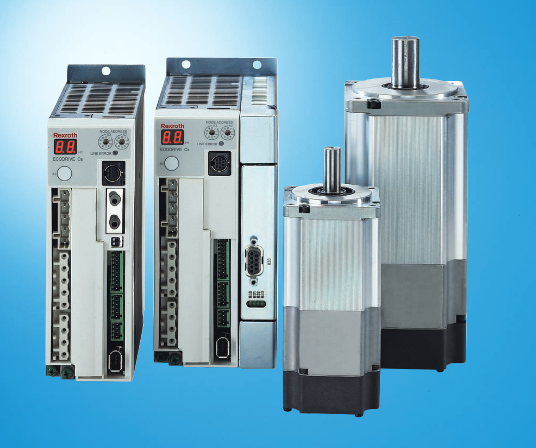
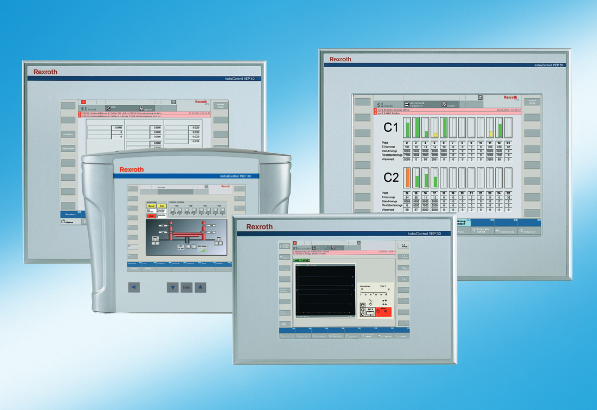
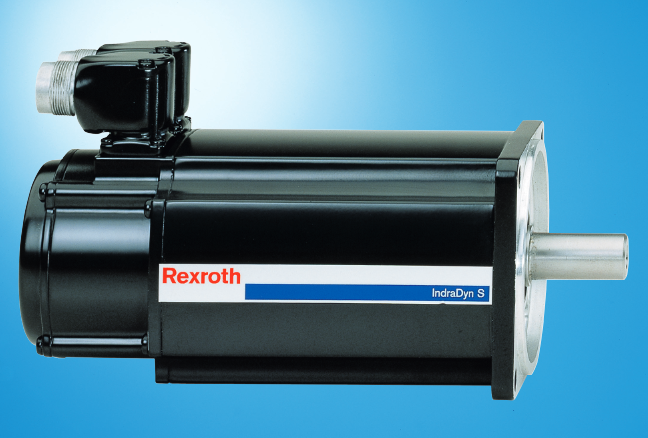
Product
Article
NameDescriptionContent
Adequate Inventory, Timely Service
pursuit of excellence


Ship control system
Equipment control system
Power monitoring system
Brand
Product parameters
- Telephone:+86-15305925923
- contacts:Mr.Wang
- Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com
Description
The Relay Output Module provides eight individually isolated, electromechanical relay outputs. Four of
the outputs are Form-C, and the other four are Form-A. A schematic showing the relationship of individual
Form-A relays and Form-C relays to external (user) connections is given in Figure 65. SIL applications
require an external series relay used to ensure outputs achieve failsafe action. See HC900 Process & Safety Controller Safety Manual for additional details.
Honeywell Analog Input (8 channel) 900TEK-0001 900TBK-0001
Relay Output Module Wiring
The Relay Output Module provides eight individually isolated, electromechanical relay outputs. Four of
the outputs are Form-C, and the other four are Form-A. A schematic showing the relationship of individual
Form-A relays and Form-C relays to external (user) connections is given in Figure 65. SIL applications
require an external series relay used to ensure outputs achieve failsafe action. See HC900 Process & Safety
Controller Safety Manual for additional details.
Examples of Relay Output wiring as they relate to connections on the Terminal Block are shown in Figure66.
Figure 65 – Schematic Example: Relay Output and External Wiring
Contact Rating
Maximum current/output: 4A at 250Vac/30Vdc with resistive load
Maximum current per module: No de-rating per module, but ensure compliance with maximum ratings
for each output.
Note: specified relay life is 1,000,000 cycles. For applications requiring constant cycling of output,
Honeywell recommends using a solid state AC or DC output module.
Required Output Fusing
Outputs are not fused in the Relay module. Install a fuse for each output at the field device that is
appropriate for the load and the wire used.
Jumper Comb
A ten-position jumper comb, available for the AC Output Module, can be cut in half and used as shown in
Figure 67 to reduce the number of wires required to connect the Relay Output Module to AC Neutral or to
DC Common.
Hazardous voltages exist at terminal blocks.
Using switches at field devices disconnect the field wiring from power sources before servicing.
Failure to comply with these instructions could result in death or serious injury.

Figure 67 – Relay Output Module Jumpers
Pulse/Frequency/Quadrature Module Wiring (Figure 68 through Figure 74)
The 4 Channel Pulse/Frequency/Quadrature Module provides four different functionalities in the form of
Pulse Input, Frequency measurement, Quadrature encoder input and Pulse Output. Each of the 4 channels
can be configured for any one of these four functionalities; with the exception that quadrature encoder input
(A and B pulses) can be applied to only Channels 1 and 2 respectively. When configured for quadrature,
Channels 3 and 4 will still be available for use.
The Pulse Output functionality uses the digital output available on the module for outputting pulses.
Before installing be sure to set the module DIP switches for differential or single ended. See page 88.
Communications Installation
Overview
This section contains descriptions, procedures and recommendations for installing communications systems
and components.
Wiring and cabling
Table 16 – Connect Communications Wiring and Cabling
Step Procedure Comments/Reference
1 Determine requirements
for communications links.
See:
Ethernet
Devices/Considerations
on page 33
For legacy system,
serial Ports (RS-232
and RS-485) on page
42. For new system,
two RS-485 serial ports
on page 42
Cabling/Wiring Distance
Planning on page 54.
2 Refer to the diagram at
right, and to Table 17
Links to Controller
Communication Ports for
connection details.
All ports are shown.
(Availability depends on
controller model, see
Figure 12 page 29.)
Connect communications
cabling.
For Modbus connections,
see page 152.
Step Procedure Comments/Reference
Set IP addresses and
subnet masks.
Default IP addresses:
C30/C50: 192.168.1.254 and Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0.
C70/C75: E1: 192.168.1.254, E2: 192.168.2.254. Must be on
different subnets.
Links to controller communication ports
Refer to Table 17 and the figure in Step 2 above. Port availability depends on Controller model.
Table 17 – Links to Controller Communication Ports
Controller
Port
/Connector Type
Link Type:
Controller to
Cable Type To Device/Port Details
Legacy controller
only RS-232
3-plug connector
Desktop or Laptop
PC
RS-232 Null Modem
cable, up to 50’
Or
RS-232 PC modem
cable, up to 50’
Serial port of PC (w/ Null
Modem cable)
or
Modem. Refer to RS-
232 Remote Connection
to PC Configuration Tool
on page 135.
For Wiring details of
Null Modem cable see
Table 19.
Legacy controller
only RS-232
3-plug connector
Modbus master
(controller is single
slave)
RS-232 Null Modem
cable, up to 50’
Or
RS-232 PC modem
cable, up to 50’
RS-232 to RS-485
converter
Refer to device’s port
instructions
Legacy controller
only RS-232
3-plug connector
Modbus master
(controller is one of
multiple slaves)
RS-232 to RS-485
converter
Refer to device’s port
instructions
Legacy controller
only RS-232
3-plug connector
Modbus slave
network (controller
is master)
RS-232 to RS-485
converter
Refer to device’s port
instructions
RS-485
3-Plug connector
Operator interface Belden #9271 (or
equivalent)
Terminal connector of
operator interface. (Refer
to Table 18.)
Connect from each CPU
(A and B) to the OI.
SIL applications require
shield drain wire to be
connected to grounding
bar.
RS-485
3-Plug connector
Modbus master
(controller is slave)
Belden #9271 (or
equivalent)
Refer to device’s port
instructions
SIL applications require
shield drain wire to be
connected to grounding
bar.
RS-485
3-Plug connector
Modbus slave
network (controller
is master)
Belden #9271 (or
equivalent)
Refer to device’s port
instructions
SIL applications require
shield drain wire to be
connected to grounding
bar.
Purchase history
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|
Total 0 Record
Related products
Customer Reviews
Satisfaction :
5 Stars
No evaluation information



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923