K-WANG


- Telephone:+86-15305925923
- contacts:Mr.Wang
- Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com
Manufacturers
ABB
Model(s)
ABB Advant Controller 31, ABB Advant OCS
Estimated Shipping Size
Dimensions: 5.0" x 4.0" x 6.0"
(12.7 cm x 10.2 cm x 15.2 cm)
Weight: 0 lbs 15.0 oz (0.4kg )
Tariff Code: 8537109060
Country of Origin: Germany
Ships from Webster NY, USA
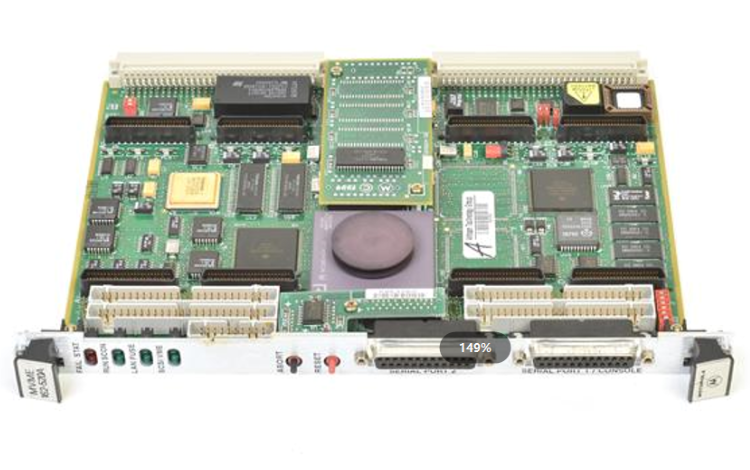
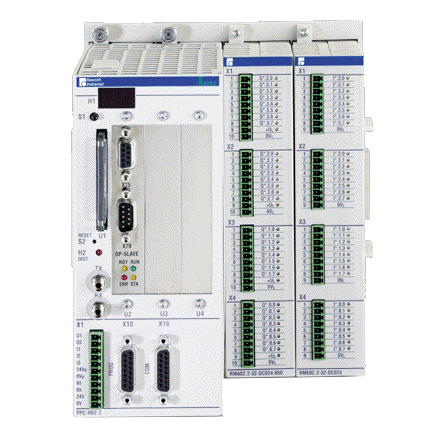
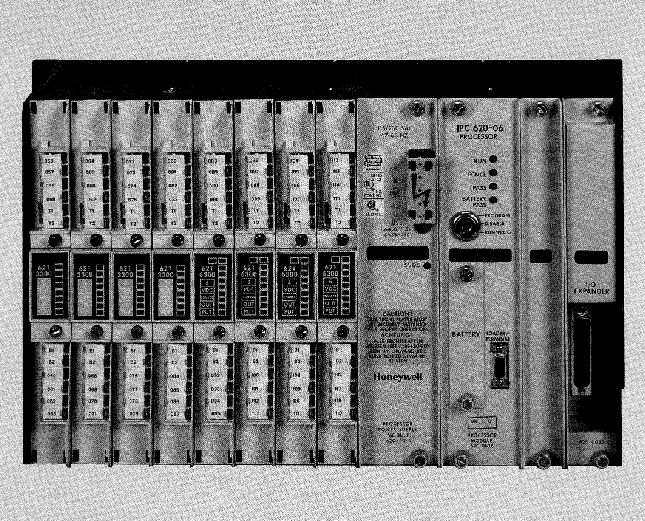
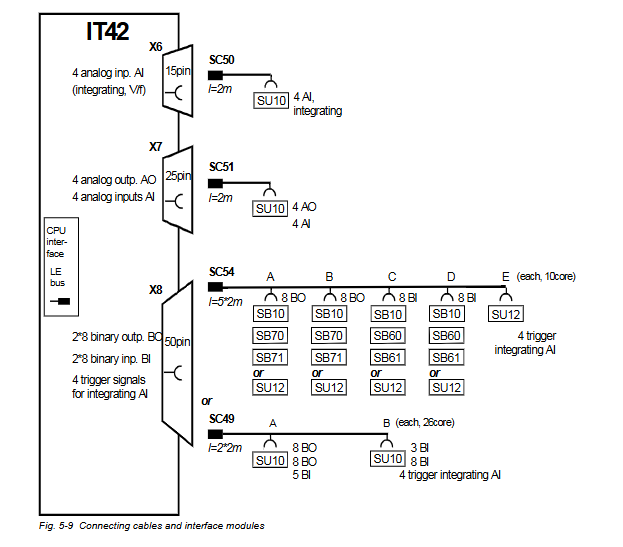
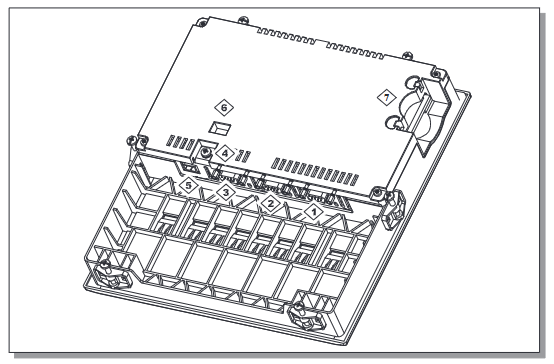
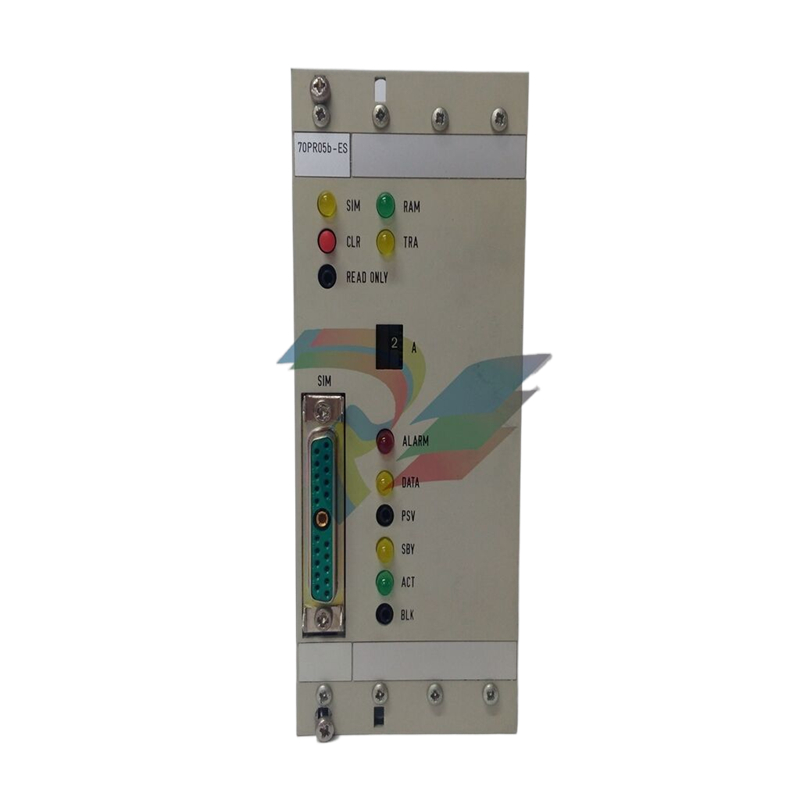
ABB GJR5252100R3161 07KT94 Advant Basic Controller Unit
Product Overview
Model number and logo meaning: ABB GJR5252100R3161 07KT94 is the basic controller unit of the Advant family. The ‘GJR5252100R’ part may represent a specific series, model number and configuration information of the product, the ‘3161’ may be a version number or a specific function code, and the ‘07KT94 ‘ is used to classify and identify the controller unit within the ABB product family.
Core function position: In an industrial automation system, this basic controller unit is at the centre. It is like a central nervous system, responsible for collecting various signals from field devices (e.g. sensors), processing them in accordance with predefined rules and algorithms, and then sending control commands to the actuators (e.g. motors, valves, etc.) in order to achieve precise control and coordination of the entire industrial process.
Performance Characteristics
Processing Power and Computing Speed
Highly efficient data processing: The controller unit is equipped with a high-performance processor that is capable of quickly processing large amounts of input data. For example, in a complex chemical production process, it can receive data from multiple temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and flow sensors at the same time and be able to analyse and process the data in a very short time. This is crucial for real-time monitoring and control of various parameters in the industrial process, and can ensure that the system responds to changes in a timely manner.
Support for complex algorithms: Support for a variety of complex control algorithms, such as PID (proportional-integral-derivative) control, fuzzy control, adaptive control and so on. Taking PID control as an example, it can accurately adjust the control signal according to the deviation between the set value and the actual measured value, so that the output of the system can quickly and stably reach the expected target value. This precise control algorithm has a wide range of applications in the field of industrial process control, such as temperature control, pressure control, flow control and so on.
Input and output interface characteristics
Rich interface types: with a variety of types of input and output interfaces to meet the needs of different equipment connection. Including digital input (DI) interface, used to receive digital signals sent by devices such as limit switches, buttons, proximity switches, etc.; digital output (DO) interface, which can be used to drive relays, indicators, solenoid valves and other devices; analogue input (AI) interface, which can be connected to analogue sensors, such as temperature sensors (the output of which is a voltage or current signal), pressure sensors, etc., and convert the analogue signals into digital signals for processing; analogue output (AI) interface, which can connect to analogue sensors, such as temperature sensors (output of which is a voltage or current signal), pressure sensors, etc., and convert analogue signals into Analogue output (AO) interface, used to control devices that require continuous adjustment, such as control valves, inverters, etc.
Interface expandability: Provides good interface expandability, users can add expansion modules to increase the number of input and output points according to the actual needs. For example, when the factory needs to expand the production scale, add new equipment or monitoring points, just add the corresponding I/O expansion module, you can easily access these new devices to the control system without replacing the entire controller unit, which greatly reduces the cost and complexity of the system upgrade.
Communication Functions
Diversity of communication interfaces: There are a variety of communication interfaces, such as Ethernet interface, RS-485 interface, RS-232 interface, etc. The Ethernet interface supports high-speed data transmission. The Ethernet interface supports high-speed data transmission and can be used to connect the controller unit to the plant's LAN or Internet for remote monitoring and management. Through Ethernet, the operator can check the operation status and data of the equipment in the central control room or through remote terminal devices (such as notebook computers, smart phones, etc.) anytime, anywhere, and carry out remote control.RS-485 and RS-232 interfaces are commonly used communication interfaces in industrial field, which can be used for connecting a variety of field devices, such as smart meters, human-machine interfaces (HMI), other controllers, etc., to build a fieldbus network and realise the communication between devices. fieldbus network to achieve interconnection between devices.
Communication protocol compatibility: It supports a variety of industrial communication protocols, such as Modbus, Profibus - DP, Ethernet/IP and so on. This makes it possible to communicate seamlessly with devices produced by different manufacturers, enhancing the compatibility and openness of the system. For example, in an automation system containing multiple brands of equipment, it can use Modbus protocol to communicate with sensors of one brand, Profibus - DP protocol to communicate with inverters of another brand, and Ethernet/IP protocol to communicate with the upper computer monitoring system, thus realising the integration and collaborative work of the whole system.
Reliability and Stability
Hardware Reliability Guarantee: The use of high-quality electronic components and advanced manufacturing process ensures the high reliability of the equipment. For example, the circuit board adopts multi-layer design with good anti-interference performance, which can effectively prevent the influence of external electromagnetic interference on the internal circuitry; the key components (such as processor, chip, etc.) have been strictly screened and tested, with high resistance to temperature change, vibration, static, etc., which can run stably for a long time in the harsh industrial environment.
Software stability measures: A perfect software system is built-in with error detection and recovery functions. In the process of software operation, if there is an abnormal situation (such as program runaway, data conflict, etc.), the system can automatically detect and try to recover, for example, by restarting some of the function modules or reloading the program, etc., to minimise the impact on the industrial production process. At the same time, the software system also supports regular data backup and system update to ensure the security and stability of the system.
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923