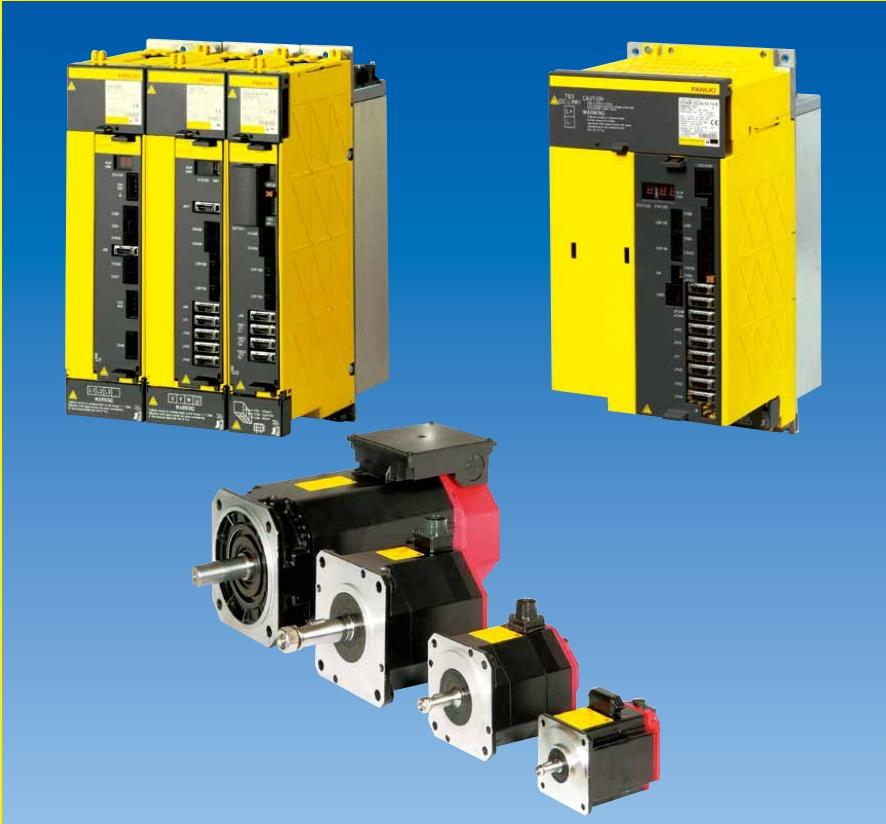
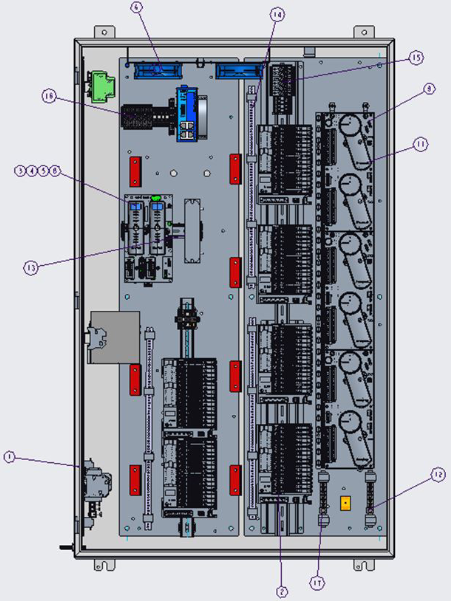
K-WANG
+086-15305925923
Service expert in industrial control field!
Product
Article
NameDescriptionContent
Adequate Inventory, Timely Service
pursuit of excellence


Ship control system
Equipment control system
Power monitoring system
Brand
Product parameters
- Telephone:+86-15305925923
- contacts:Mr.Wang
- Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com
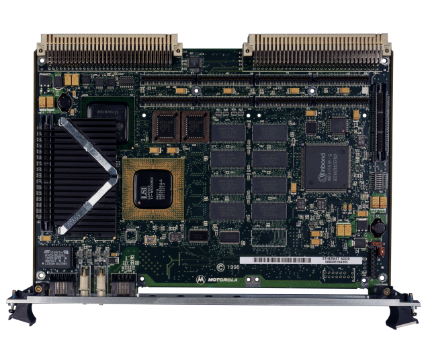
Description
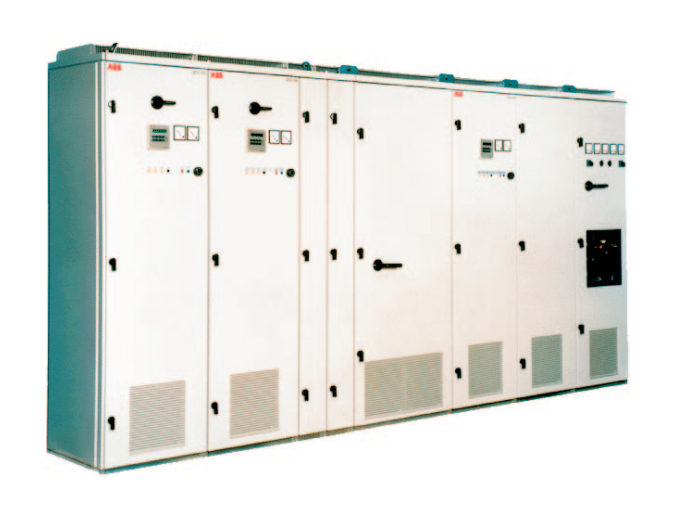
for 6-/ and 12-pulse DC drive systems
in Drive-MNS-cabinets
22 to 5150/10300 A
10 to 4900/9400 kW
ABB DCV700 thyristor panels
Latest Technology, High Performance, and a User
Friendly Concept – the New DCV 700 Series
The DCV 700 series is a complete range of DC converters intended for the
supply and control of DC machines, in stand-alone or multi-drive systems
with high performance and reliability specifications.
Wide Variety of Industrial
Applications
The DCV 700 series can handle the most demand ing applications in:
• rolling mills
• pulp and paper
• metals (casters, processing lines etc.)
• material handling (cranes, hoists etc.)
Digital Control
To meet the most stringent control requirements,
the DCV 700 features speed control, which re duces the effects from gear backlash and torsional
vibration arising in mechanical systems.
High-performance speed and torque control will
fulfill all requirements for rapid response and
control accuracy. Autotuning for armature cur rent control will simplify the commissioning
procedure.
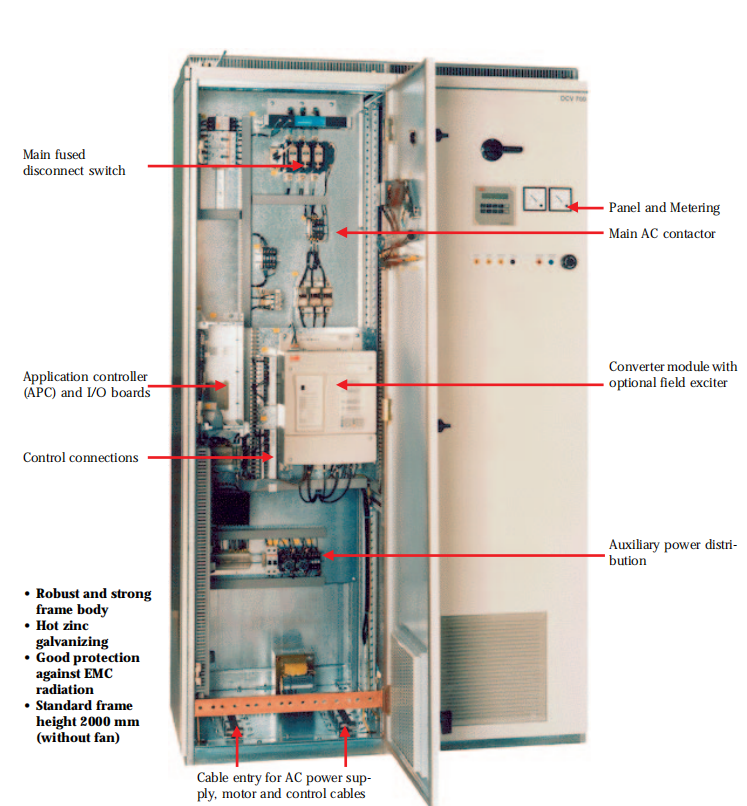
DCV 700 converters are fully digital and mounted
in an enclosure complete with all necessary
equipment, meeting the most stringent safety
standards. The converter can be used for stand ard applications but has the flexibility to be
customized for the most demanding applica tions.
Comprehensive Product Range
DCV 700 converters are available as 6-/ and 12-
pulse 2- or 4-quadrant, in a current range 22 to
5150/10300 A and supply voltages of 200 to 1000
VAC. A selection of options is available to provide
the user with a system meeting the most demand ing technical requirements and performance ex pectations.
Common control electronics throughout the range
reduces spare parts inventory and training re quirements.

Diagnostics
Commonality with AC Drives -
Digital control allows comprehensive diagnos-
Flexible System Configurations
tics, including for example detection of
Some of the most important features and benefits
.overcurrent
common to both the DC and AC drives are:
.overvoltage
application controlsystem (APC)-fewer spare
.earth faults
parts
Troubleshooting is easily undertaken via the
.link to automation systems
Control Panel and the Commissioning and Main-
·commissioning,maintenance and program-
tenance Tools.
ming tools - less training
control panel - quick information
. drive-MNScabinets - standardization ben-
efits; possibility to build mixed systems
·EMC design available

Basic Functionality
Figure 2. Drive and Torque Control, block diagram
The thyristor bridge can be 2-quadrant (6 thyristors)
or 4-quadrant (12 thyristors). For current ratings
up to 700 A the thyristor bridge consists of
integrated thyristor modules – more compact,
cost effective, less components – so the fuses are
installed outside the module, in the supply line.
For higher current ratings, disc thyristors are
used, so there is a branch fuse for each thyristor.
Each thyristor is protected by a snubber circuit.
AC voltage, AC current and DC voltage are
monitored. These measurements are utilized by
the converter software for supervision and protection. Overvoltage protection by means of
varistors is also provided.
Converters are always equipped with a cooling
fan integrated in the converter module.
The monitor and protective features, provided as
standard and listed below, have been designed,
keeping in mind, personnel safety, equipment
integrity and continuity of the process.
Motor: Loss of speed feedback
Overtemperature
Overload
Overspeed
Stall
Armature overcurrent
Armature current ripple
Armature overvoltage
Minimum field current
Field overcurrent
Converter: Thyristor temperature
Supply: Main supply undervoltage
Auxiliary supply undervoltage
Wrong phase sequence
The converter includes emergency stop and prevention of unexpected start-up as standard protective functions. The software also includes a
fault logger storing up to 100 faults in real time.
Information on internal signals is stored in the
data logger and it can be displayed by the
Commissioning and Maintenance Tool for easy
fault finding.
Converter software for application,
drive, and torque control
Drive Control receives either speed or torque
reference and gives a torque reference to the
Torque Control.
Torque Control is controlling the armature current, the field current and the EMF. It receives the
torque reference from the Drive Control or from
the Application Controller (APC). Auto/manual
tuning for armature current simplifies the commissioning and makes the tuning procedure
flexible.
Purchase history
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|
Total 0 Record
Related products
Customer Reviews
Satisfaction :
5 Stars
No evaluation information



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923