K-WANG
+086-15305925923
Service expert in industrial control field!
Product
Article
NameDescriptionContent
Adequate Inventory, Timely Service
pursuit of excellence


Ship control system
Equipment control system
Power monitoring system
Brand
Description
The main circuit breaker (MCB) is a major protection device of the drive. If a serious fault
occurs in the drive, the MCB must disconnect the main power supply to the drive
immediately. The main power supply must be disconnected without delay on an open or trip
command from the drive to prevent hazard to the personnel and further damage to the
equipment. The MCB is located on the primary side of the converter transformer
ABB ACS5000 water-cooled SYSTEM DRIVES
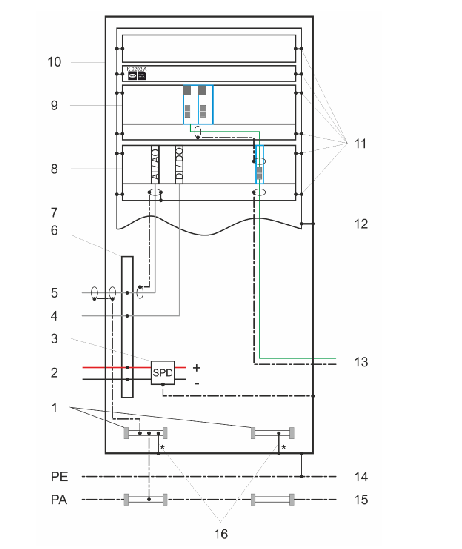
1.9. Items covered by delivery
The delivery includes the following items, whereas items 3 – 5 are shipped in a separate
container.
Figure 1–1 Typical delivery
1.9.1. Identifying the delivery
The drive and accessories are identified by the type code printed on the rating label.
The rating label is located on the back of the control compartment door.
The label provides information on the type of drive, the rated voltage, the frequency and the
current of the main and the auxiliary power supply.
1.10. Tools
ABB offers various tool sets containing all necessary tools and equipment for installation,
commissioning and maintenance of the drive. The content of the tool sets is described in
the manual Service equipment.
1) Drive (frame size 1 shown): shipped in
transport units.
Shipping splits are defined in the customer specific layout drawing.
2) Rating plate: on the first door from the left.
3) Roof joints
4) Roof attachments (only for marine drives)
5) Door keys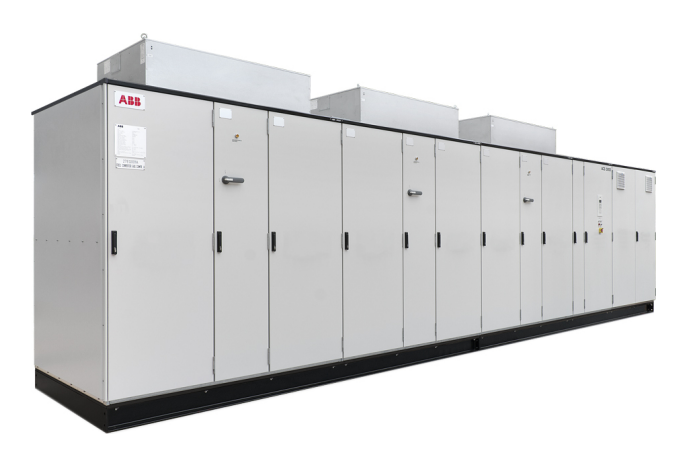
2.4. General safety instructions
1) Minimize hazards
2) Before energizing the drive:
• Remove all foreign objects are from the drive
• Fasten all internal and external covers securely
• Close, lock, and/or bolt all doors
• Move the release dial of the door safety switches into the locked position
3) Before working on the drive:
• Turn off, lock out, and tag out the main and auxiliary power supplies to the
drive
• De-energize the drive
• Ensure that the safety ground connections are in place
• Ensure that the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is
available and used when required
• Inform the involved personnel about the potential safety hazards
• Wear hearing protection when a drive is running.
4) Before working simultaneously on the drive and on other drive
system equipment:
• Observe the relevant safety codes and standards
• Turn off all energy sources for the equipment
• Ensure that all lockout and tagout devices are in place
• Install barriers around and use appropriate covers on the equipment that is
still energized
• Inform the involved personnel about the potential safety hazards
5) In case of fire in the drive room:
• Observe the established rules and regulations for fire safety
• Only allow firefighters with the appropriate PPE to enter the drive room
2.5. The 7 steps that save lives
ABB’s 7 steps that save lives concept is a series of actions that must take place prior to
commencing work on or near electrical installations.
1) Prepare for the work: do an on-site risk assessment or job hazard analysis
that considers the limits of approach for shock and arc-flash.
• Be in possession of a clear work order to execute the work.
• When required, the access or work permit is to be obtained by a person who
is authorized for the specific electrical system.
• Engage the person responsible for electrical equipment or system to review
single-line diagrams, schematics, switching plans, etc.
• Ensure the competence of workers.
• Check for proper tools for the job.
• Determine and select the proper arc-rated Personal Protective Equipment
(PPE).
• Decide of the appropriate work methods and initiate the Permit To Work
(PTW) process.
2) Clearly identify the work location and equipment.
• Use your senses (sight, hearing and smell) to identify problem areas.
• Define the work area via barriers and barricading and label equipment.
• Avoid distractions such as talking or texting on the phone.
3) Disconnect all sources of supply and secure against reconnection by
applying Lockout/Tagout..
• If ABB is responsible for switching and it cannot be done remotely, then the
person performing the switching must be properly trained and wearing the
proper PPE identified in step 1.
• The Person in Charge of Work (PICW) must ensure that switching is
performed in the proper manner by witnessing it from a safe distance if
present on site or by engaging the person responsible for switching to
identify all isolation points.
• Apply Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) to the energy isolation device and if multiple
energy isolation devices are involved, then Group LOTO must be
implemented with the PICW serving as the Group LOTO Leader.
4) Verify the absence of operating voltage: always test before you touch!
Only use properly rated and inspected voltage detection devices and wear
proper PPE identified in step 1:
• Test voltage detection device
• Test for voltage
• Test voltage detection device
It is highly important that the voltage detection device is tested on a known
voltage source such as a Proving Unit or by performing an internal self-test,
according to the manufacturer’s instructions, before and after testing for the
absence of operating voltage.
5) Carry out earthing and short-circuiting.
• Close and lock the earthing switch if the electrical equipment is designed
for this purpose or apply portable equipment for earthing and short circuiting.
If this is carried out by the customer, then the PICW must ensure that this
equipment is properly earthed as a part of the integration/verification and
during step 7 when the PICW walks the PTW.
6) Protect against adjacent live parts and take special precautions when close
to bare conductors.
• Determine minimum approach distances, apply screening or shrouding,
and when applicable, padlock both cable and busbar shutters.
• If working within the restricted approach boundary or vicinity zone where
inadvertent movement could cause contact with live parts, special
precautions must be employed, such as the use of the properly rated
insulated gloves and tools.
7) Complete the permit to work and “Walk the Permit”.
• Check isolation points
• Verify that all circuits are isolated and secured
• Ensure all parties are integrated with the Lockout/Tagout
• Check the earths are properly applied
• Answer specific questions from the working group
• Ensure the work can proceed without danger
• Complete and verify the “Permit to Work
Residual risks must be considered by the drive system integrator and/or plant owner when
assessing the hazards of the equipment to personnel. The following risks can pose a hazard
to drive system personnel:
1) Electric power equipment generates electro-magnetic fields which can
cause a hazard to people with metal implants and / or a pacemaker.
2) Drive system components can move unintentionally when being
commissioned, operated, or serviced due to:
• Operation of the equipment outside the scope of the specifications
• Incorrectly assembled or installed equipment
• Wrongly connected cables
• External influence on, or damage of the equipment
• Wrong parameter settings
• Software errors
• Faulty hardware
3) Hazardous touch voltages can be present on drive system components,
which can be caused by:
• Operation of the equipment outside the scope of the specifications
• External influence on, or damage of the equipment
• Induced voltages by external equipment
• Condensation on equipment components, or pollution
• Faulty hardware
4) High temperatures, noise, particles, or gases can be emitted from drive
system components caused by:
• Operation of the equipment outside the scope of the specifications
• External influence on or damage of the equipment
• Incorrect parameter settings
• Software errors
• Faulty hardware
5) Hazardous substances can be emitted from drive system components due
to incorrect disposal of components
Purchase history
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|
Total 0 Record
Related products
Customer Reviews
Satisfaction :
5 Stars
No evaluation information



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923