K-WANG


- Telephone:+86-15305925923
- contacts:Mr.Wang
- Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com
Manufacturers
ABB
Model(s)
ABB Advant Controller 31, ABB Advant OCS
Estimated Shipping Size
Dimensions: 4.0" x 3.0" x 4.0"
(10.2 cm x 7.6 cm x 10.2 cm)
Weight: 0 lbs 7.1 oz (0.2kg )
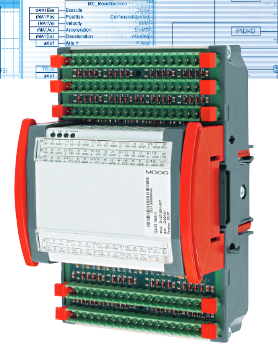
ABB 1SBP260104R1001 Extension I/O Module
Basic Information
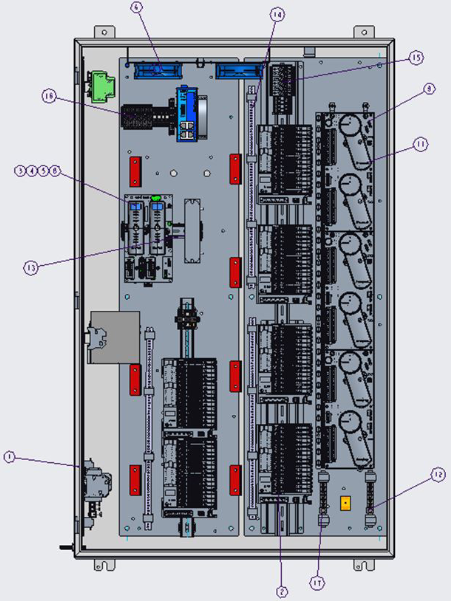
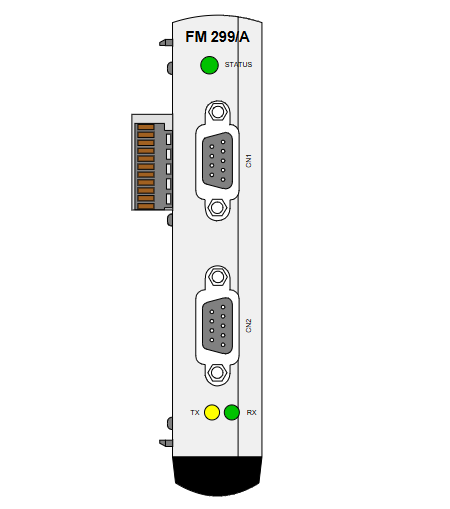
Product Overview:The ABB 1SBP260104R1001 Extension I/O Module is an Extension Input/Output (I/O) module designed to extend the number of I/O points in ABB automation systems. It plays a key role in industrial automation and control systems by enhancing the system's ability to acquire and control signals from external devices.
Physical characteristics: The module is usually supplied in a standard modular design for easy mounting on the control cabinet rails. Its shell is generally made of sturdy materials with good electromagnetic shielding, which can effectively prevent external electromagnetic interference on the module's internal circuitry. Compact size, suitable for flexible installation in the limited space of the control cabinet, relatively light weight, easy to carry and installation and operation.
Functional Features
Input and output function expansion
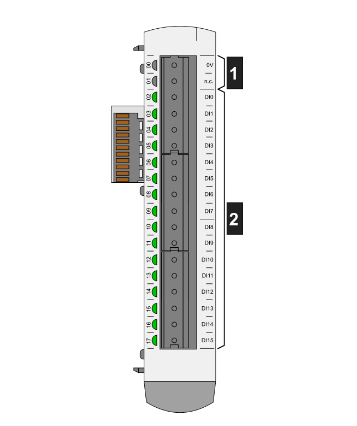
Rich combination of I/O channels: Provides a variety of ways to combine input and output channels to meet the application requirements of different users. For example, it may contain different combinations of digital input (DI), digital output (DO), analogue input (AI) and analogue output (AO) channels. This versatile design allows the user to flexibly connect various types of sensors and actuators according to the specific industrial process requirements.
Variety of signal types: For digital channels, it is possible to process e.g. switching signals (e.g. limit switches, pushbutton signals, etc.) and support different voltage levels for input and output, e.g. 24V DC, 110V AC or 220V AC. For analogue channels, it can receive and process a variety of standard analogue signals, such as 0 - 10V DC, 4 - 20mA current signals, etc., which usually come from a variety of sensors (e.g. temperature sensors, pressure sensors, etc.), and output the processed signals to the actuators (e.g. regulating valves, frequency inverters, etc.), to achieve the precise control of industrial processes.
Communication and compatibility
Communication interface support: Equipped with a variety of communication interfaces, such as Ethernet interface, serial interface (RS-232, RS-485) and so on. These interfaces support standard industrial communication protocols, such as Modbus, Profibus, etc., enabling the module to easily communicate with other devices, including the host computer monitoring system, PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), DCS (Distributed Control System), and other I/O modules. Through the communication interface, real-time transmission and sharing of data is realised, providing the basis for the collaborative work of the entire automation system.
Strong system compatibility: The module is designed to have good compatibility with other ABB automation products and can be seamlessly integrated into ABB's control system architecture. For example, it works with ABB's controllers, human-machine interfaces (HMIs) and other devices, and users have access to a unified programming and configuration environment that simplifies system development and maintenance.
Flexible configuration and programming
Rich Configurable Parameters: It supports flexible configuration of various parameters of the module through software tools. Users can set the attributes of the I/O channels according to the actual needs, such as the filtering time of the input signals, the driving capacity of the output signals, the range conversion of the analogue signals, etc. This flexibility allows the module to adapt to different industrial environments and control requirements, for example, in an application scenario that is sensitive to signal noise, the user can appropriately increase the filtering time of the input signal to improve signal stability.
Various programming methods: It supports a variety of programming languages and programming environments, such as ladder diagrams, function block diagrams, structured text and so on. This enables engineers who are familiar with different programming languages to easily program modules to achieve a variety of complex control logic. For example, in the control of an automated packaging production line, engineers can use the ladder diagram language to write programs to achieve precise control of packaging equipment, including feeding, packaging, sealing and a series of actions.

| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|



KONG JIANG


Add: Jimei North Road, Jimei District, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Tell:+86-15305925923